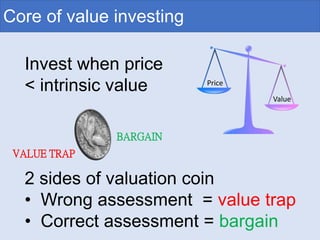
The document discusses the core concepts of value investing, including buying stocks at a discount to their intrinsic value, maintaining a margin of safety, and selling when the price exceeds intrinsic value. It emphasizes the importance of company analysis to accurately assess intrinsic value and avoid value traps. The document also provides guidance on portfolio construction, such as holding 30-50 stocks and allocating more funds to higher quality companies meeting specific metrics. Overall, the document serves as an introduction to value investing principles and strategies.