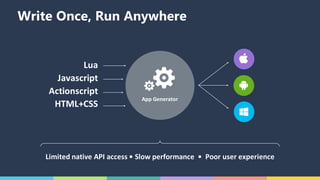
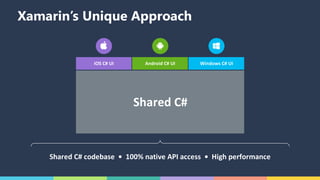
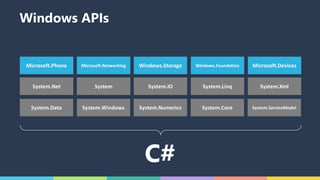
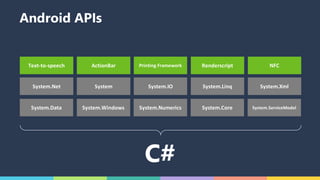
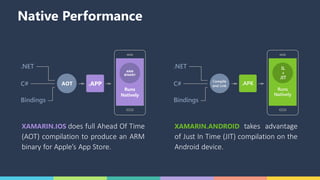
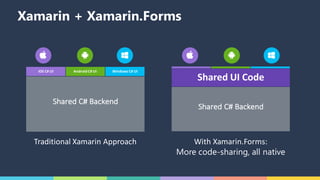
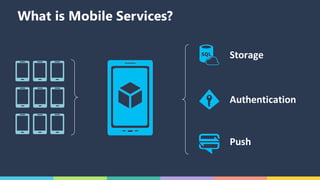
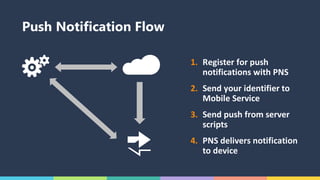
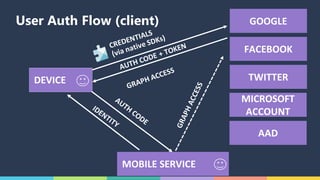
The document discusses Xamarin and Azure mobile apps, emphasizing Xamarin's unique approach of using a shared C# codebase for iOS, Android, and Windows development, allowing full native API access and high performance. It explains the differences between traditional and Xamarin.Forms approaches, noting use cases for each, including data entry apps and those requiring specialized interaction. Additionally, it highlights Azure Mobile Apps functionalities such as storage, authentication, and push notifications, designed to enhance mobile development efficiency.