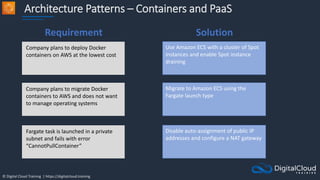
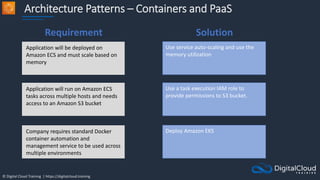
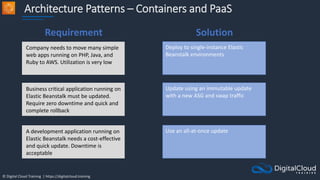
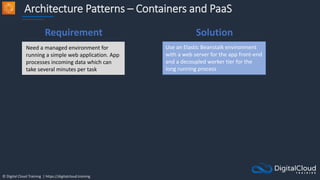
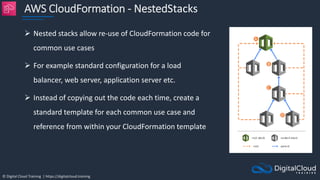
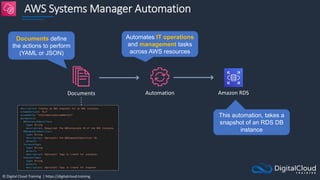
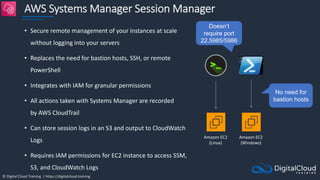
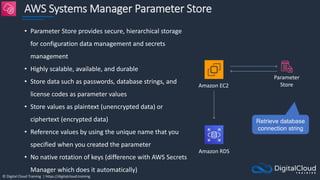
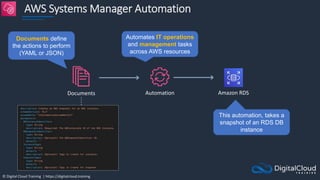
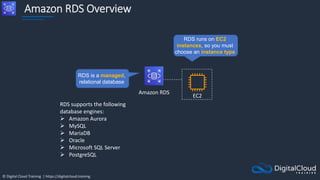
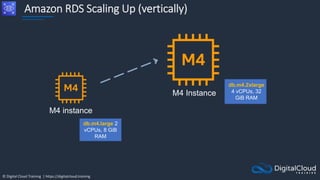
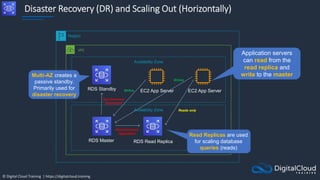
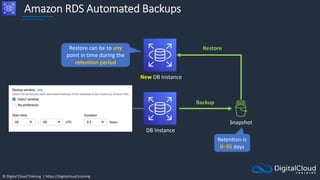
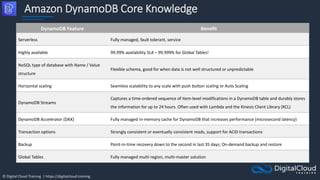
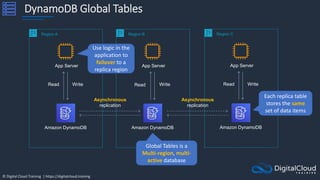
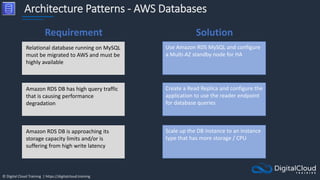
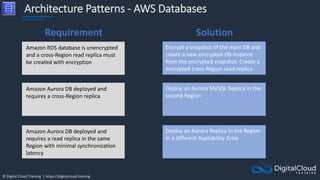
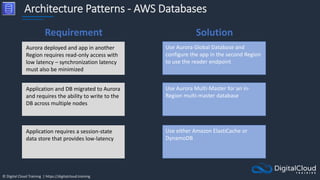
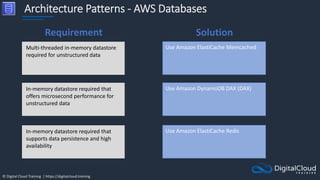
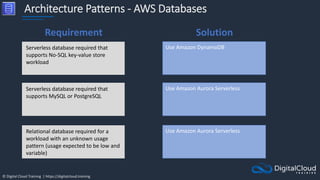
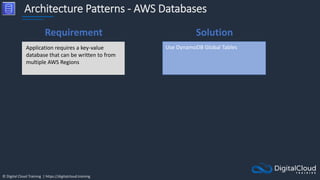
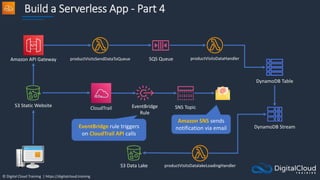
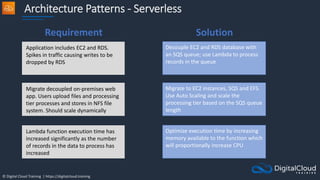
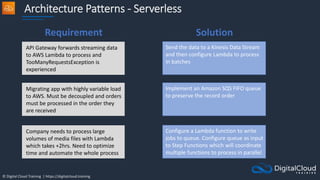
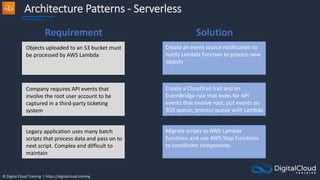
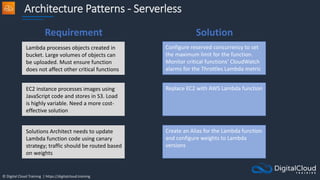
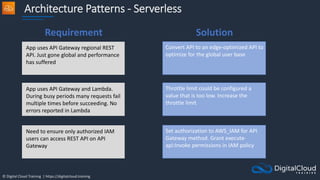
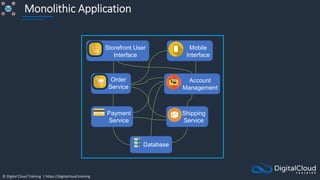
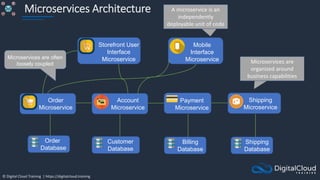
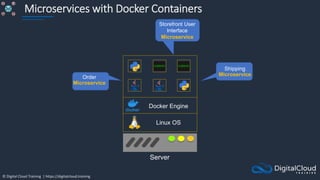
The document details AWS database services, focusing on Amazon RDS, which is a managed relational database with support for various engines like MySQL and PostgreSQL. It covers key functionalities such as scaling, disaster recovery, security features, and backup strategies, emphasizing how RDS can be used effectively depending on the requirements. Additionally, it introduces alternatives like EC2 for database management and discusses other services like Amazon ElastiCache and DynamoDB for specific use-cases.







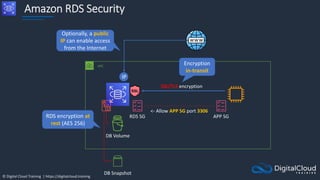


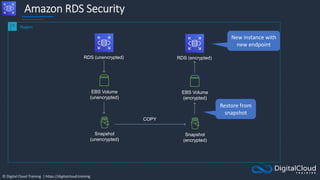


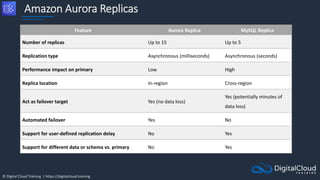

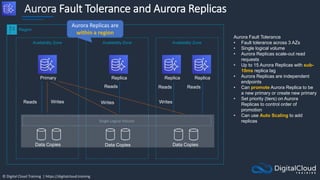













































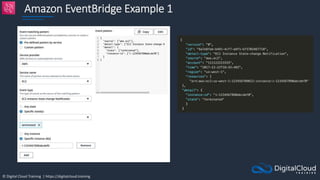
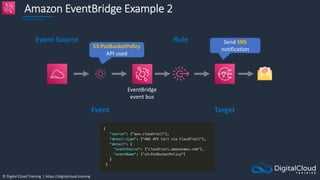

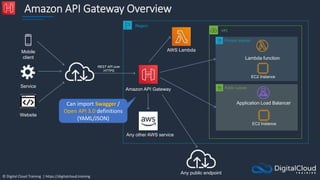
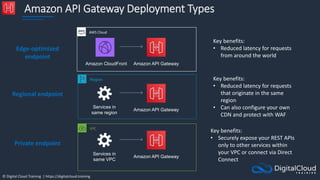
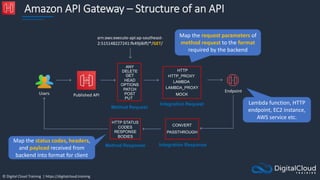

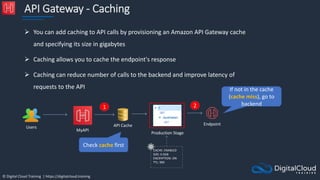

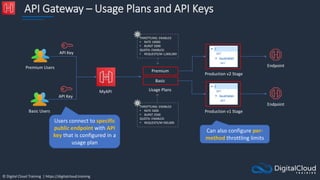

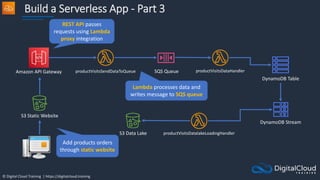






![© Digital Cloud Training | https://digitalcloud.training
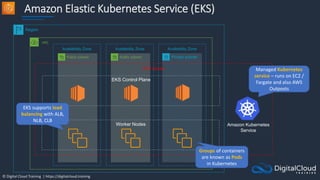
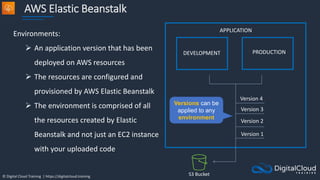
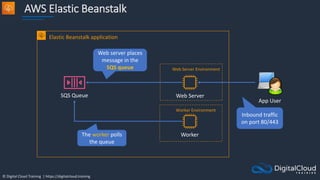
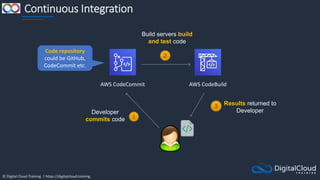
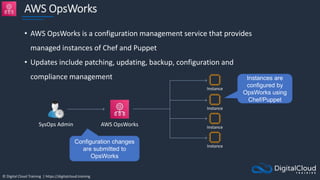
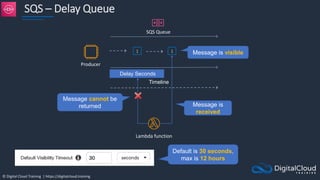
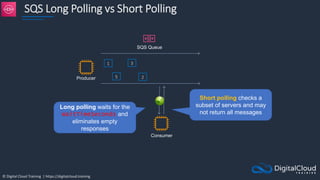
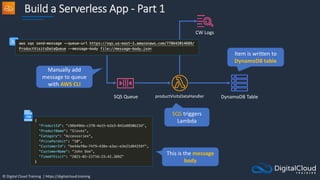
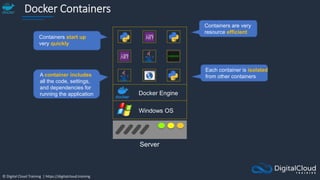
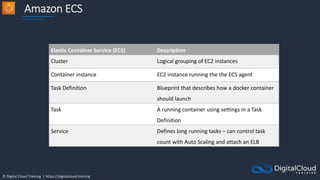
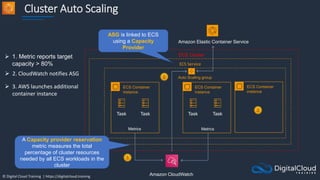
Amazon ECS
An Amazon ECS
Cluster is a logical
grouping of tasks or
services
An ECS Task is
created from a
Task Definition
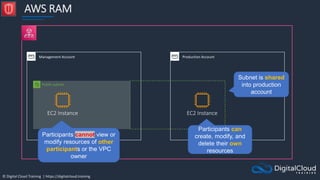
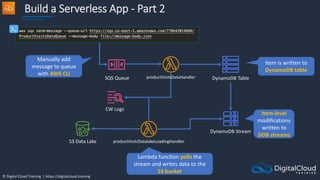
Availability Zone Availability Zone
Auto Scaling group
ECS Service
ECS Container
instance
ECS Container
instance
Task
Task Task Task
Image Image
{
"containerDefinitions": [
{
"name": "wordpress",
"links": [
"mysql"
],
"image": "wordpress",
"essential": true,
"portMappings": [
{
"containerPort": 80,
"hostPort": 80
}
],
"memory": 500,
"cpu": 10
}
Task Definition
Amazon Elastic Container Service
Amazon Elastic Container
Registry
Registry
ECS Cluster
An ECS Task is a
running Docker
container
ECS Services are
used to maintain
a desired count
of tasks
Docker images can be
stored in Amazon ECR](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csapsections10-14-210407213455/85/AWS-Certified-Solutions-Architect-Professional-Course-S10-S14-143-320.jpg)
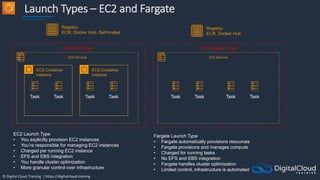
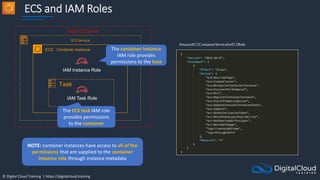
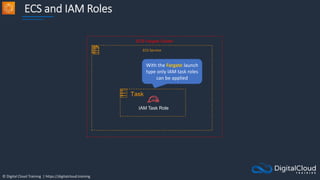




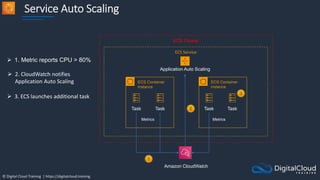



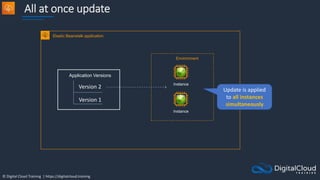
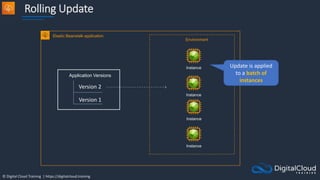
![© Digital Cloud Training | https://digitalcloud.training
[HOL] Create and Scale ECS
Tasks](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csapsections10-14-210407213455/85/AWS-Certified-Solutions-Architect-Professional-Course-S10-S14-158-320.jpg)