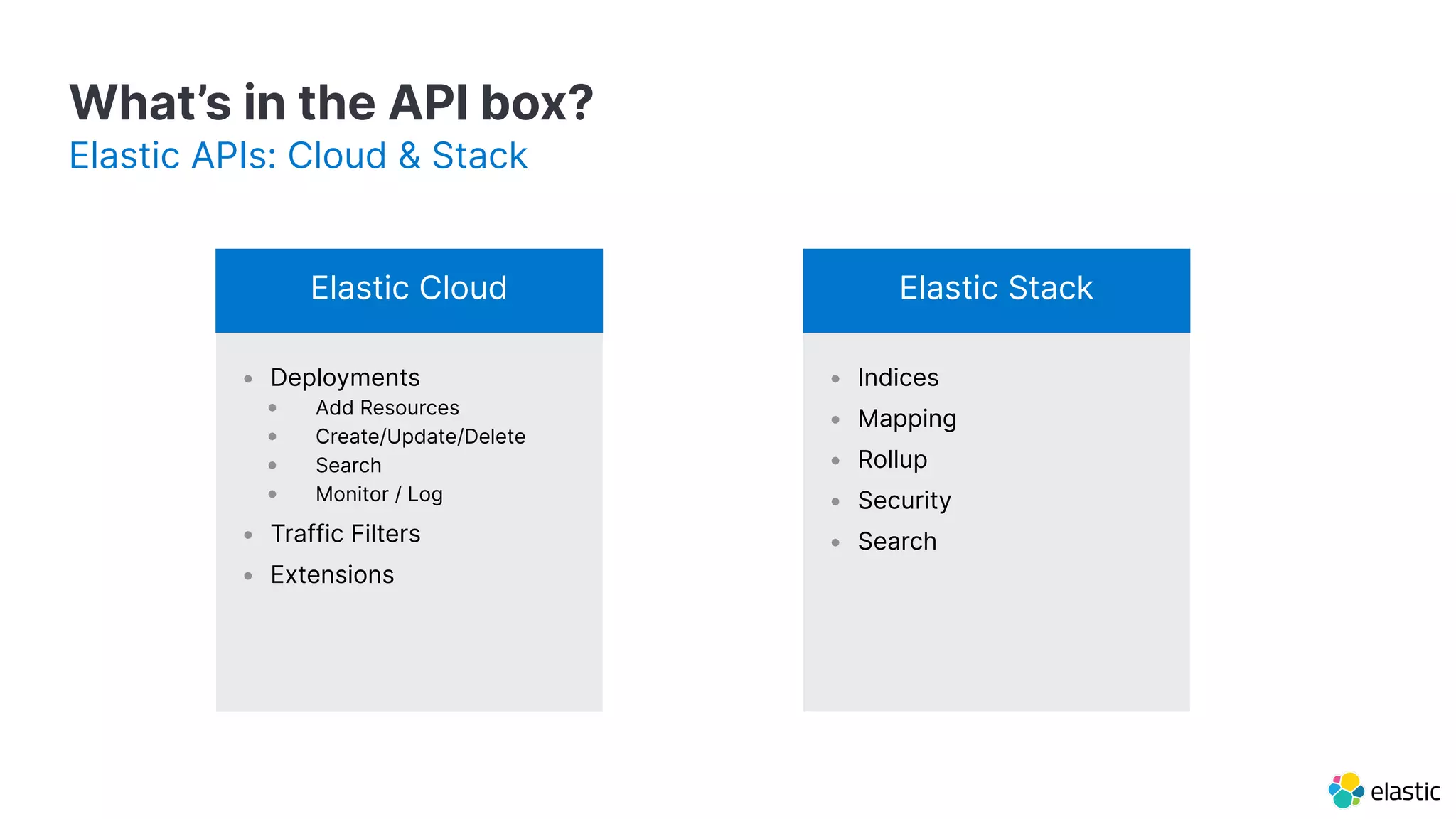
The document outlines a presentation on automating the Elastic Stack, discussing forward-looking statements and associated risks, including the potential impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic and the company's ability to innovate and maintain its customer base. It also details programmatic use cases for Elastic APIs, including deployment and management of resources using tools like Terraform and command line interfaces. The document emphasizes the importance of making purchase decisions based on currently available features and functionalities.












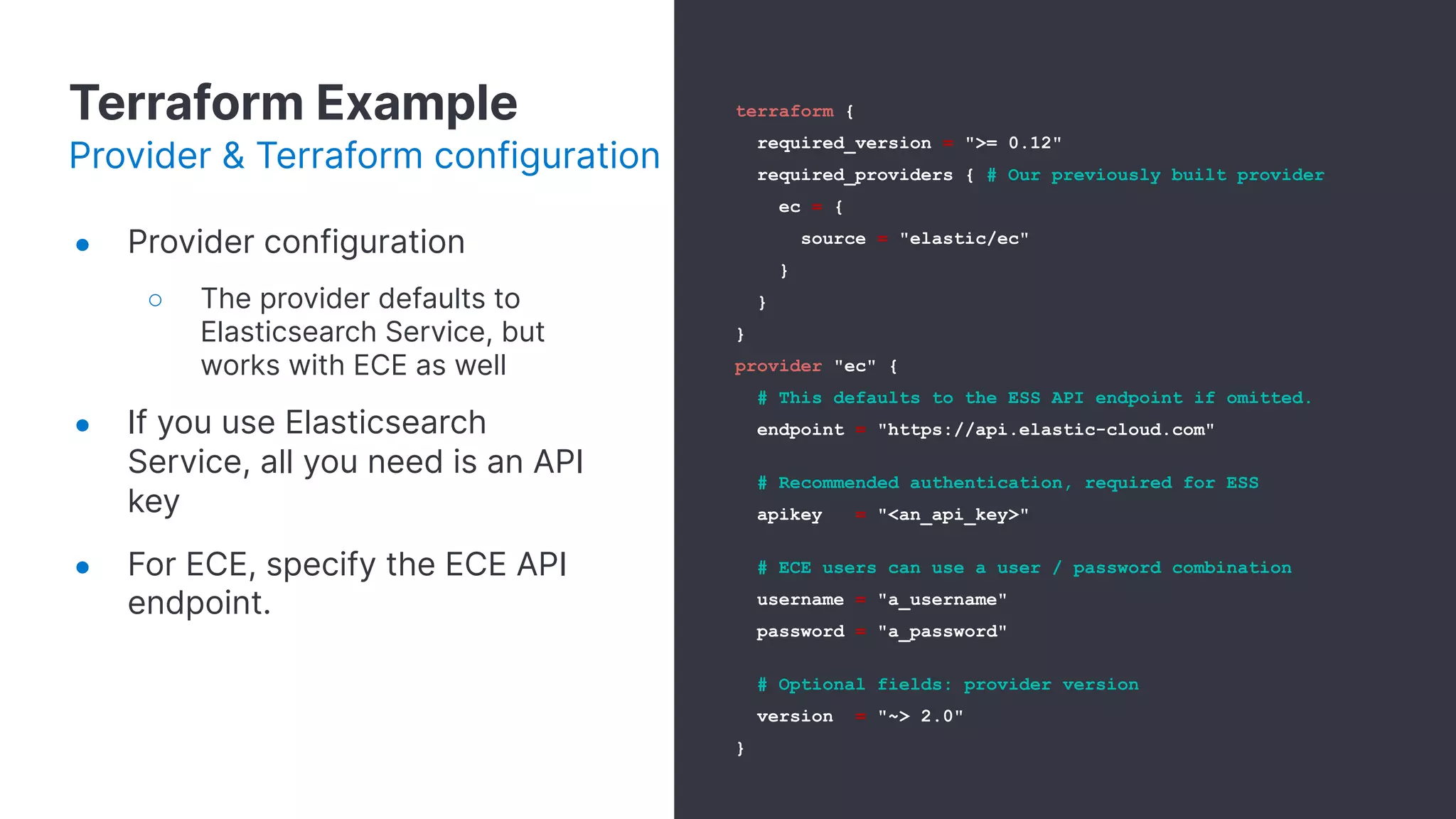
![Terraform Example
Deployment definition
resource "ec_deployment" "example_minimal" {
name = "my_example_deployment"
region = "us-east-1"
version = "7.9.1"
deployment_template_id = "aws-io-optimized-v2"
traffic_filter = [ec_traffic_filter.allow_all.id]
elasticsearch {
topology {
instance_configuration_id = "aws.data.highio.i3"
memory_per_node = "8g"
}
config {
user_settings_yaml = file("./es_settings.yml")
}
}
kibana {
topology {
instance_configuration_id = "aws.kibana.r5d"
memory_per_node = "1g"
}
}
}
● Elasticsearch topology section
determines nodes topology:
○ Node types
■ Data
■ Master
■ Ingest
■ ML
○ Memory per node
○ Instance Configuration
● Kibana, Enterprise Search,
APM supported
● Traffic filters](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/031finaldeckautomatingelasticstack-201030033759/75/Automating-the-Elastic-Stack-20-2048.jpg)

![Terraform Example
Init script
● “Null resource” executes a
local script (not related to the
ec provider)
● Template_file uses the values
generated by our created
ec_deployment resource, and
injects them into a simple bash
script
○ elastic-user
○ elastic-password
○ es-url
resource "null_resource" "bootstrap-elasticsearch" {
provisioner "local-exec" {
command =
data.template_file.elasticsearch-configuration.rendered
}
}
data template_file elasticsearch-configuration {
template = file(es_config.sh)
depends_on = [ec_deployment.example_minimal]
vars = {
elastic-user =
ec_deployment.example_minimal.elasticsearch_username
elastic-password =
ec_deployment.example_minimal.elasticsearch_password
es-url =
ec_deployment.example_minimal.elasticsearch[0].https_endpoint
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/031finaldeckautomatingelasticstack-201030033759/75/Automating-the-Elastic-Stack-22-2048.jpg)

