This document provides an overview of Australia's people and history. It discusses:
1) Indigenous Australians as the original inhabitants who have lived in Australia for over 60,000 years. Early European settlement began in 1788 with British convict ships arriving.
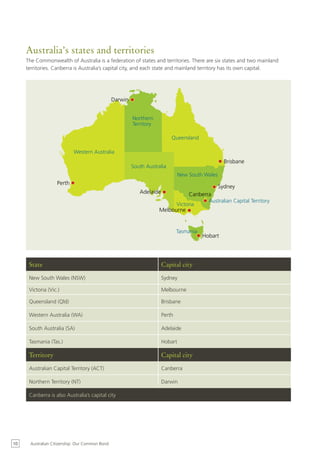
2) How Australia developed from separate British colonies to a federation of states called the Commonwealth of Australia in 1901. Migration from Britain and other parts of the world increased the population.
3) Australia today has a population of around 22 million people, over a quarter of whom were born overseas. While English is the national language, over 200 languages are spoken reflecting Australia's diversity.
harbour is one of the most beautiful natural harbours
in the world