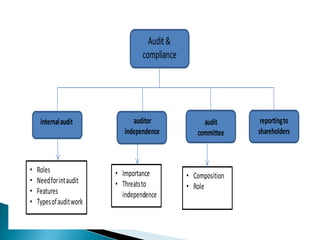
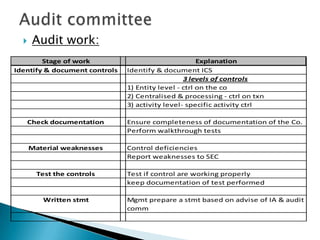
The document discusses the roles and responsibilities of internal auditors and audit committees. It notes that internal auditors review controls, compliance, operations, and risks. They ensure controls are working properly and in accordance with laws and regulations. The audit committee oversees the internal audit function and monitors financial reporting, controls, and compliance. It reviews internal and external audit reports and the company's internal control statement. The committee helps provide assurance to shareholders that risks are adequately managed and controls are functioning effectively.