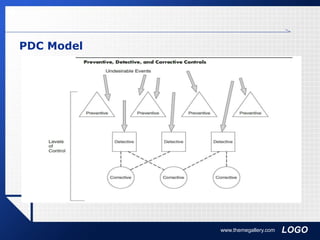
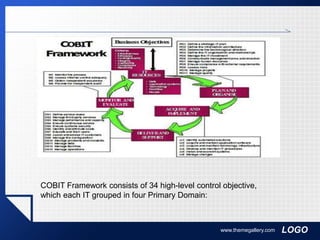
The document discusses key concepts in auditing information systems, including defining internal and external audits, describing the five phases of the audit cycle, and outlining components of an effective internal control system such as preventive, detective, and corrective controls.