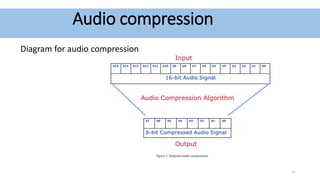
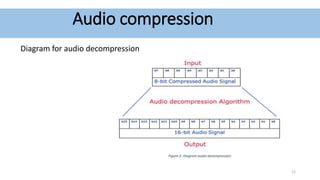
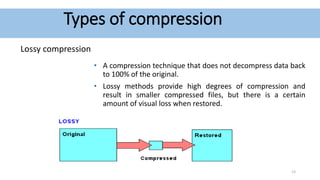
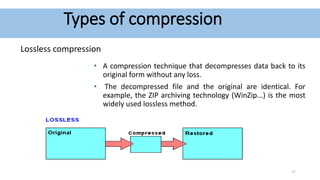
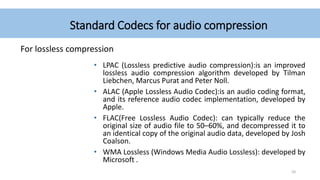
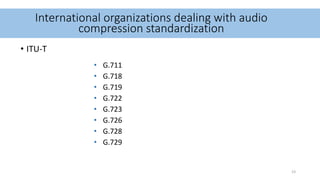
Audio compression reduces the size of audio files through lossy or lossless techniques. Lossy compression uses psychoacoustic algorithms to filter out sounds imperceptible to humans, reducing file size but introducing data loss. Lossless compression compresses files without any loss, allowing perfect restoration. Common lossy codecs include MP3, while lossless options are FLAC, ALAC, and WMA Lossless. International standards bodies like MPEG and ITU-T develop and standardize audio compression formats.