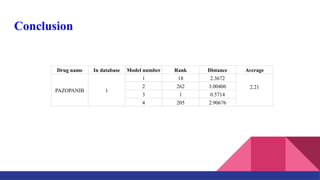
This document discusses the use of AI and machine learning for predicting drug interactions and vaccine candidates for COVID-19, with a focus on the drug pazopanib. It outlines various AI methodologies, including artificial neural networks and gradient boosting decision trees, used for drug repurposing and vaccine design. Additionally, it provides a case study for pazopanib, detailing its characteristics and AI model performance results.


![AI/ML based studies on COVID-19 vaccine design
AI/ML tools Details Website URL References
Artificial neural
network
Identification of SARS-CoV-2 T-cell and B-cell epitopes based on
viral protein antigen presentation and antibody binding properties
NA [Fast and chen, 2019]
XGBoost Prediction of vaccine candidates from non-structural proteins NA [Ong et al., 2020]
Feed-forward
neural network
Prediction of HLA-binding peptides from SARS-CoV-2 virus by
binding stability
NA [Prachar et al., 2020]
Deep neural
network
Prediction and design of multi-epitope vaccine that can manage
with the mutation of the virus
https://github.com/
zikunyang/DCVST
[Yang et al., 2021]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/airanking3-241203132751-3e85f7d4/85/Artificial-Intelligence-Ranking-in-drug-repurposing-pptx-4-320.jpg)
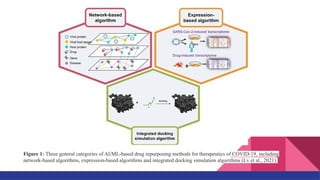
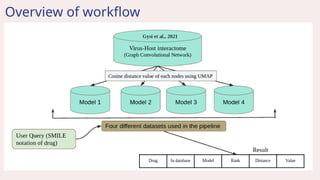
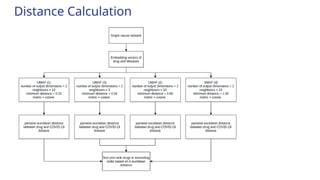
![Introduction
● Used virus-host interactome integration [GCN Gysi et al., 2021]
● Predicts the average cosine distance of the drug.
● Minimum the distance value, higher the closeness with SARS-CoV-2 disease.
● The average value is calculated by using the formula:
Sum of distance value from all four model
number of models (4)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/airanking3-241203132751-3e85f7d4/85/Artificial-Intelligence-Ranking-in-drug-repurposing-pptx-5-320.jpg)
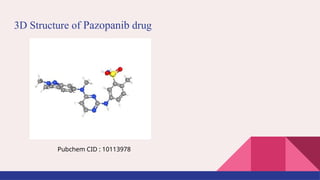
![Pazopanib Drug [Aeppli et al, 2020]
● Drugbank ID : DB06589
● Antineoplastic agent.
● Used in treatment of advanced renal cell cancer.
● Inhibitor of multiple protein tyrosine kinases.
● Developed by GlaxoSmithKline.
● FDA approved on October 19, 2009.
● SMILES were taken from drugbank database.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/airanking3-241203132751-3e85f7d4/85/Artificial-Intelligence-Ranking-in-drug-repurposing-pptx-8-320.jpg)