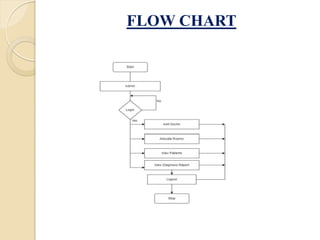
The document outlines a Smart Health Monitoring System using Python and Tkinter, focusing on a software-based solution for health monitoring without physical sensors. It highlights objectives, features, hardware and software requirements, limitations, and potential applications, while also addressing challenges and benefits associated with the system. Future development includes plans for AI integration and enhancing capabilities to promote proactive health management.