The document provides a comprehensive overview of arrays in C programming, detailing their types, declaration syntax, initialization, and usage. It covers one-dimensional, two-dimensional, and three-dimensional arrays, including example code to illustrate how to create and manipulate them. Key practices, such as initializing arrays and accessing their elements, are also highlighted.


![One dimensional array in C
• Array declaration syntax:
data_type arr_name [arr_size];
• For example,
float mark[5];
Here, we declared an array, mark, of floating-point
type and size 5. Meaning, it can hold 5 floating-
point values.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5-array-240924150914-df607da4/85/Array-definition-and-uses-in-computer-pptx-3-320.jpg)
![Initialization of an array
• data_type arr_name [arr_size]=(value1,
value2, value3,….);
• int age[5]={0, 1, 2, 3, 4};
• age[0]; /*0 is accessed*/
age[1]; /*1 is accessed*/
age[2]; /*2 is accessed*/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5-array-240924150914-df607da4/85/Array-definition-and-uses-in-computer-pptx-4-320.jpg)
![Example 1
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
int main()
{
int i;
int arr[5] = {10,20,30,40,50};
clrscr();
for (i=0; i<5; i++)
{
// Accessing each variable
printf("value of arr[%d] is %d n", i, arr[i]);
}
getch();
}
Output:
value of arr[0] is 10
value of arr[1] is 20
value of arr[2] is 30
value of arr[3] is 40
value of arr[4] is 50](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5-array-240924150914-df607da4/85/Array-definition-and-uses-in-computer-pptx-5-320.jpg)
![Example 2
// Program to find the average of n (n < 10) numbers using arrays
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{ int marks[10], i, n, sum = 0, average;
printf("Enter n: ");
scanf("%d", &n);
for(i=0; i<n; ++i)
{
printf("Enter number%d: ",i+1);
scanf("%d", &marks[i]);
sum += marks[i];
}
average = sum/n;
printf("Average = %d", average);
return 0;
}
Output:
Enter n: 5 Enter
number1: 45 Enter
number2: 35 Enter
number3: 38 Enter
number4: 31 Enter
number5: 49
Average = 39](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5-array-240924150914-df607da4/85/Array-definition-and-uses-in-computer-pptx-6-320.jpg)
![Two dimensional array in C
• Two dimensional array is nothing but array of
array.
• syntax :
data_type array_name[num_of_rows][num_of_column];
• Example:
• int x[4][4];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5-array-240924150914-df607da4/85/Array-definition-and-uses-in-computer-pptx-7-320.jpg)
![Initialization of a two dimensional array
• int c[2][3] = {{1, 3, 0}, {-1, 5, 9}};
• int c[][3] = {{1, 3, 0}, {-1, 5, 9}};
• int c[2][3] = {1, 3, 0, -1, 5, 9};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5-array-240924150914-df607da4/85/Array-definition-and-uses-in-computer-pptx-8-320.jpg)
![Example
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int i,j;
// declaring and Initializing array
int arr[2][2] = {10,20,30,40};
/* Above array can be initialized as below also
arr[0][0] = 10; // Initializing array
arr[0][1] = 20;
arr[1][0] = 30;
arr[1][1] = 40; */
for (i=0;i<2;i++)
{
for (j=0;j<2;j++)
{
// Accessing variables
printf("value of arr[%d] [%d] : %dn",i,j,arr[i][j]);
}
}
}
Output:
value of arr[0] [0] is 10
value of arr[0] [1] is 20
value of arr[1] [0] is 30
value of arr[1] [1] is 40](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5-array-240924150914-df607da4/85/Array-definition-and-uses-in-computer-pptx-9-320.jpg)
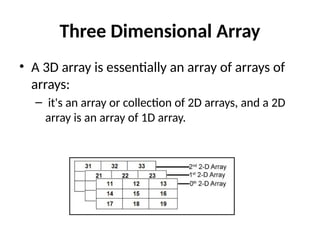
![Example for 3 Dimensional Array
• #include <stdio.h>
• int main()
• {
• int i, j, k, test[2][3][2];
• printf("Enter 12 values: n");
• for(i = 0; i < 2; ++i)
• {
• for (j = 0; j < 3; ++j)
• {
• for(k = 0; k < 2; ++k )
• { scanf("%d", &test[i][j][k]);
• }
• }
• }
• printf("nDisplaying values:n");
• for(i = 0; i < 2; ++i)
• {
• for (j = 0; j < 3; ++j)
• {
• for(k = 0; k < 2; ++k )
• { printf(“%dn", i, j, k, test[i][j][k]);
• }
• }
• }
• return 0;
• }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5-array-240924150914-df607da4/85/Array-definition-and-uses-in-computer-pptx-11-320.jpg)