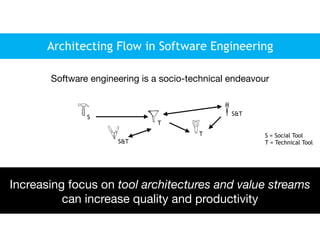
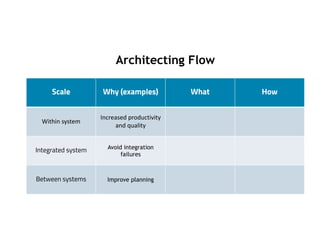
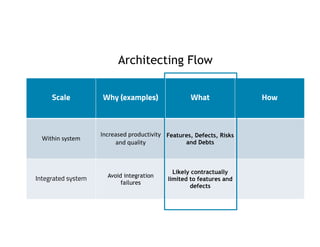
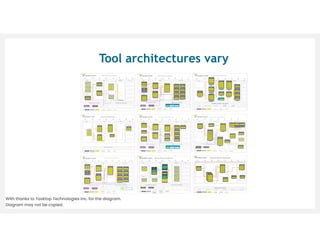
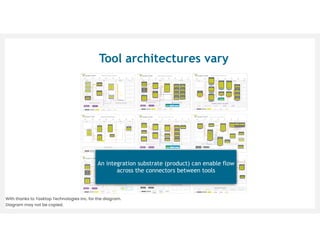
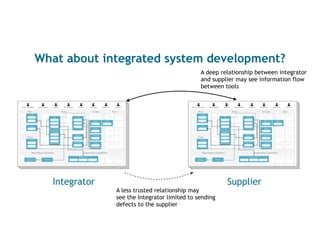
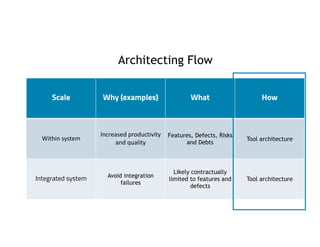
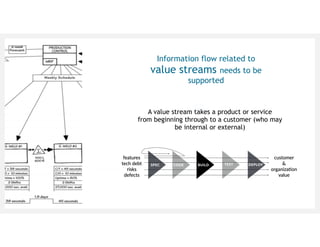
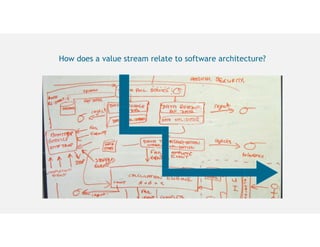
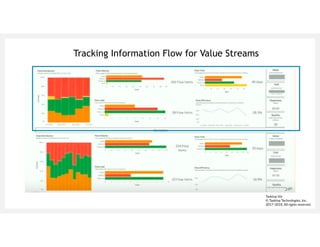
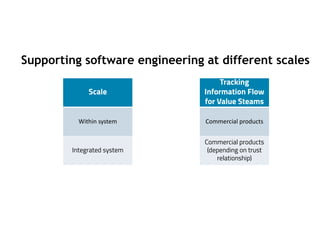
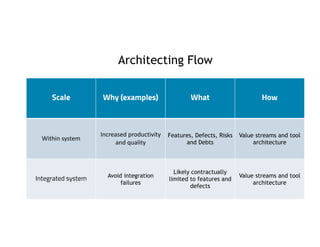
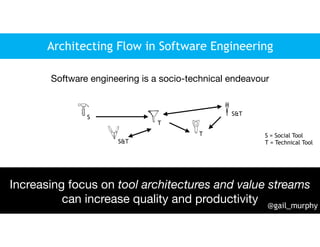
This document discusses architecting flow in software engineering. It argues that software engineering involves multi-person, multi-version development across different scales, from individual components to integrated systems. It emphasizes that information flow between technical and social tools can improve productivity and quality, especially with higher levels of socio-technical congruence. The document presents examples of information flow within and between systems, and how tool architectures that support information flow along value streams can help track important items like features, defects, risks, and debts across teams and tools.



![Software engineering involves
multi-person multi-version development
— Brian Randell
[Parnas 2011]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/architecting-flow-in-se-221017182618-adc2d8ce/85/Architecting-Flow-in-SE-pdf-4-320.jpg)



![Completely network collaborative
services via centric initiatives.
Completely network collaborative
services via centric initiatives.
Completely network collaborative
services via centric initiatives.
Socio-technical
congruence A
B
C
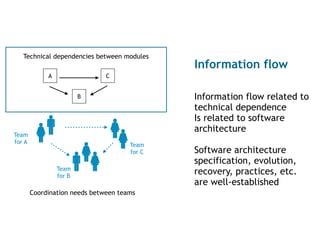
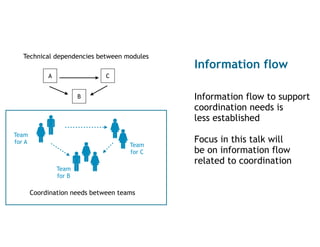
Technical dependencies between modules
Coordination needs between teams
Team
for A
Team
for C
Team
for B
Congruence leads to
improved productivity
Higher levels of congruence
associated with lower levels
of fault proneness
[Cataldo & Herbsleb, 2013]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/architecting-flow-in-se-221017182618-adc2d8ce/85/Architecting-Flow-in-SE-pdf-11-320.jpg)
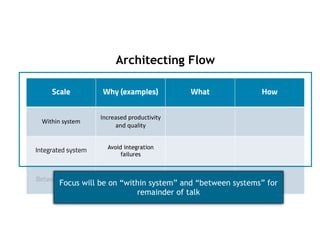
![Example 1: Within System
Cataldo & Herbsleb studied two developments in depth
- Project A - Distributed system for a data storage product
(114 developers, 5m lines of code, C & C++)
- Project B - Embedded system for automotive sector
(380 developers, 8 sites, 7m lines of code, C)
Less mature system
More mature system
finding that:
Higher-levels of socio-technical congruence are associated with better software quality. True for
both projects, but with more benefit for Project B (more mature).
Higher-levels of socio-technical congruence associated with improvements in productivity. True for
both projects, but with more benefit for Project A (less mature).
[Cataldo & Herbsleb, 2013]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/architecting-flow-in-se-221017182618-adc2d8ce/85/Architecting-Flow-in-SE-pdf-12-320.jpg)

![Example 3: Between Systems
What happens in ecosystems that are weakly inter-connected, like Java?
Guava
mcMMO
Vault
Netty
Assertj
Junit
Appsgate
JSONassert
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
4 32 256 2048
Number of user repositories
R
s
:
Ratio
of
user
repositories
having
a
social
link
Red Dots are Java projects
on GitHub.
The farther right, the more
other technically dependent
Java systems.
[Palyart, Murphy & Masrani, 2017]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/architecting-flow-in-se-221017182618-adc2d8ce/85/Architecting-Flow-in-SE-pdf-14-320.jpg)
![Example 3: Between Systems
What happens in ecosystems that are weakly inter-connected, like Java?
Guava
mcMMO
Vault
Netty
Assertj
Junit
Appsgate
JSONassert
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
4 32 256 2048
Number of user repositories
R
s
:
Ratio
of
user
repositories
having
a
social
link
This is a testing library
(JUnit) with lots of
systems using it.
[Palyart, Murphy & Masrani, 2017]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/architecting-flow-in-se-221017182618-adc2d8ce/85/Architecting-Flow-in-SE-pdf-15-320.jpg)
![Example 3: Between Systems
What happens in ecosystems that are weakly inter-connected, like Java?
Guava
mcMMO
Vault
Netty
Assertj
Junit
Appsgate
JSONassert
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
4 32 256 2048
Number of user repositories
R
s
:
Ratio
of
user
repositories
having
a
social
link
The vertical axis provides an
indication of how many of
the using systems have a
social dependence.
Reasonable number of using
systems and high-level of social
dependencies from those
systems.
Lots of users, less social
dependencies from those
systems.
[Palyart, Murphy & Masrani, 2017]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/architecting-flow-in-se-221017182618-adc2d8ce/85/Architecting-Flow-in-SE-pdf-16-320.jpg)
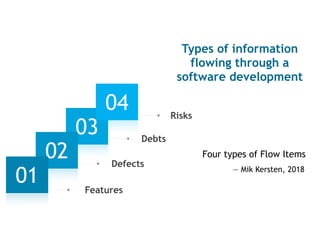



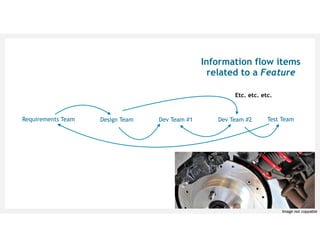
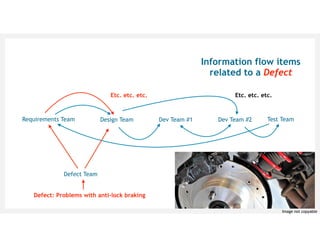
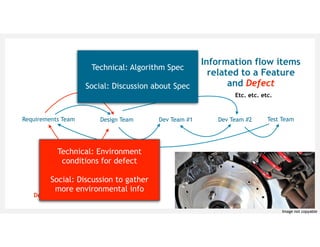





![[Cataldo & Herbsleb, 2013] Cataldo, M. and Herbsleb, J. Coordination breakdowns and their
impact on development productivity and software failures. IEEE TSE, vol 39, no 3, 2013.
[Kersten, 2018] Kersten, M. Project to product: How to survive and thrive in the age of digital
disruption with the flow framework. IT Revolution Press, 2018.
[Palyart, Murphy & Masrani, 2017] Palyart, M., Murphy, G.C. and Masrani, V. A study of social interactions
in open source component use. IEEE TSE, vol 44, no 12, 2017.
[Parnas 2011] Parnas, D. Software engineering: Multi-person development of multi-version programs.
In Dependable and Historic Computing - Essays dedicated to Brian Randell on the Occasion of His 75th
Birthday. LNCS Vol. 6875, 2011.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/architecting-flow-in-se-221017182618-adc2d8ce/85/Architecting-Flow-in-SE-pdf-55-320.jpg)