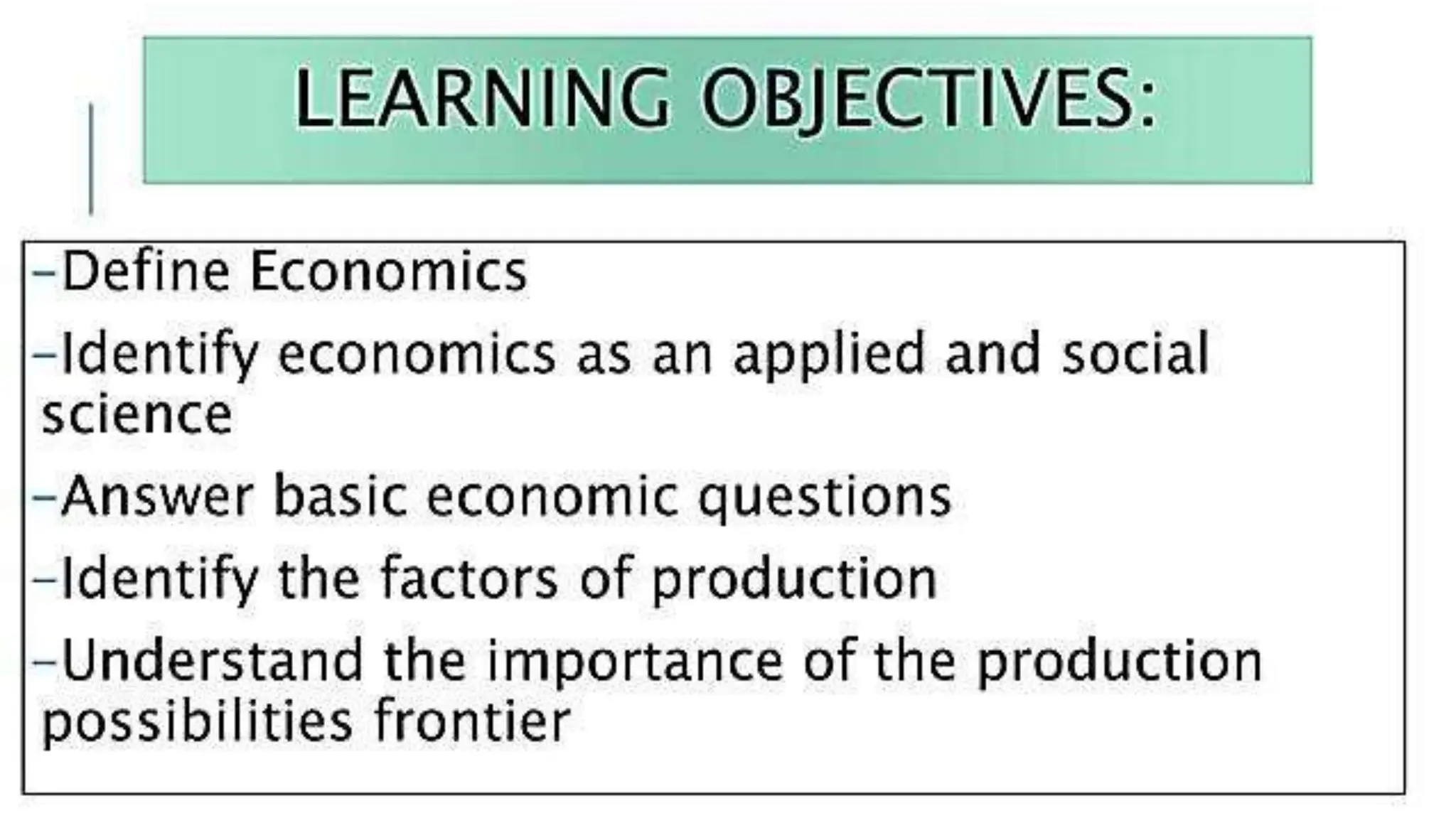
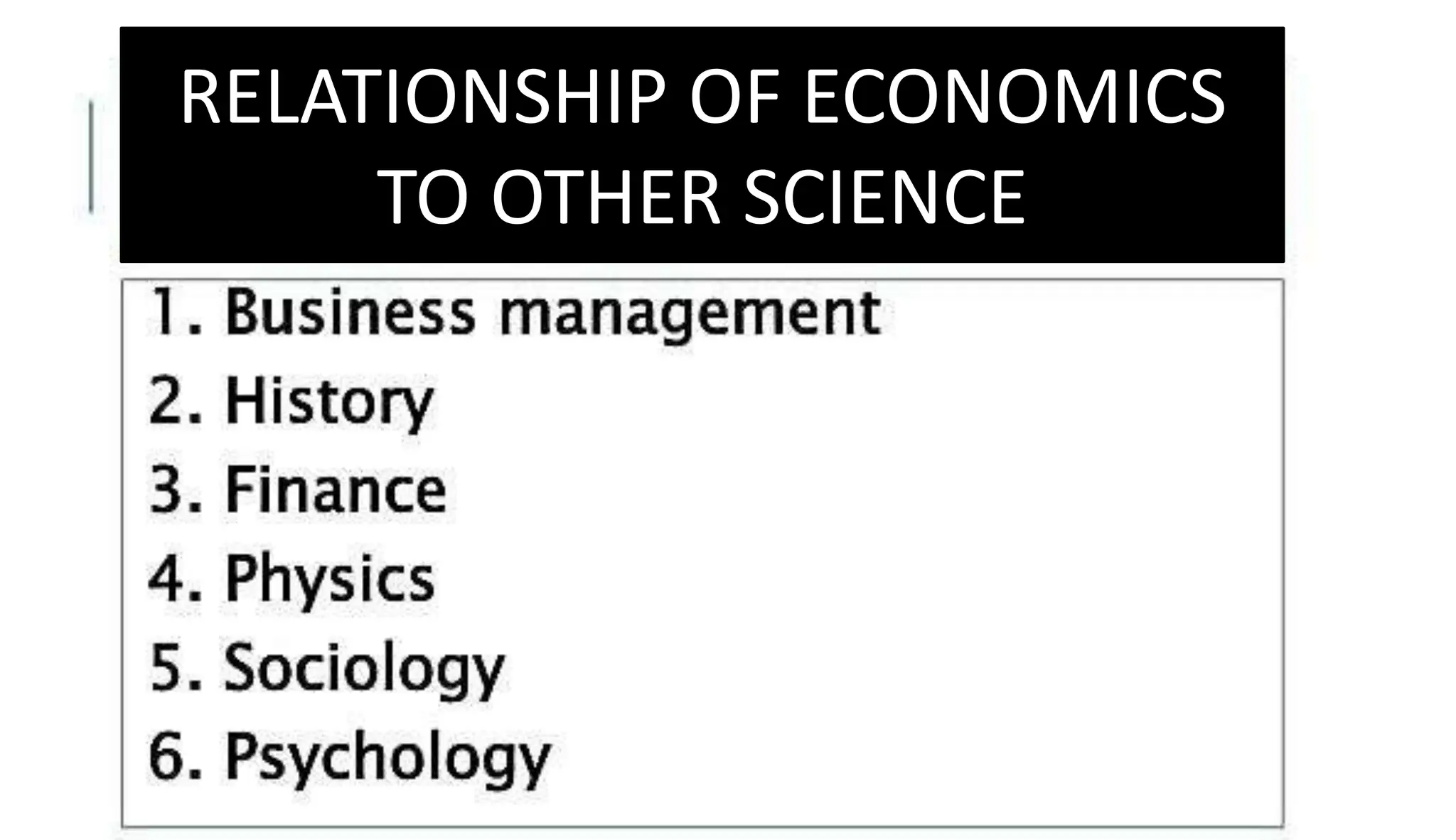
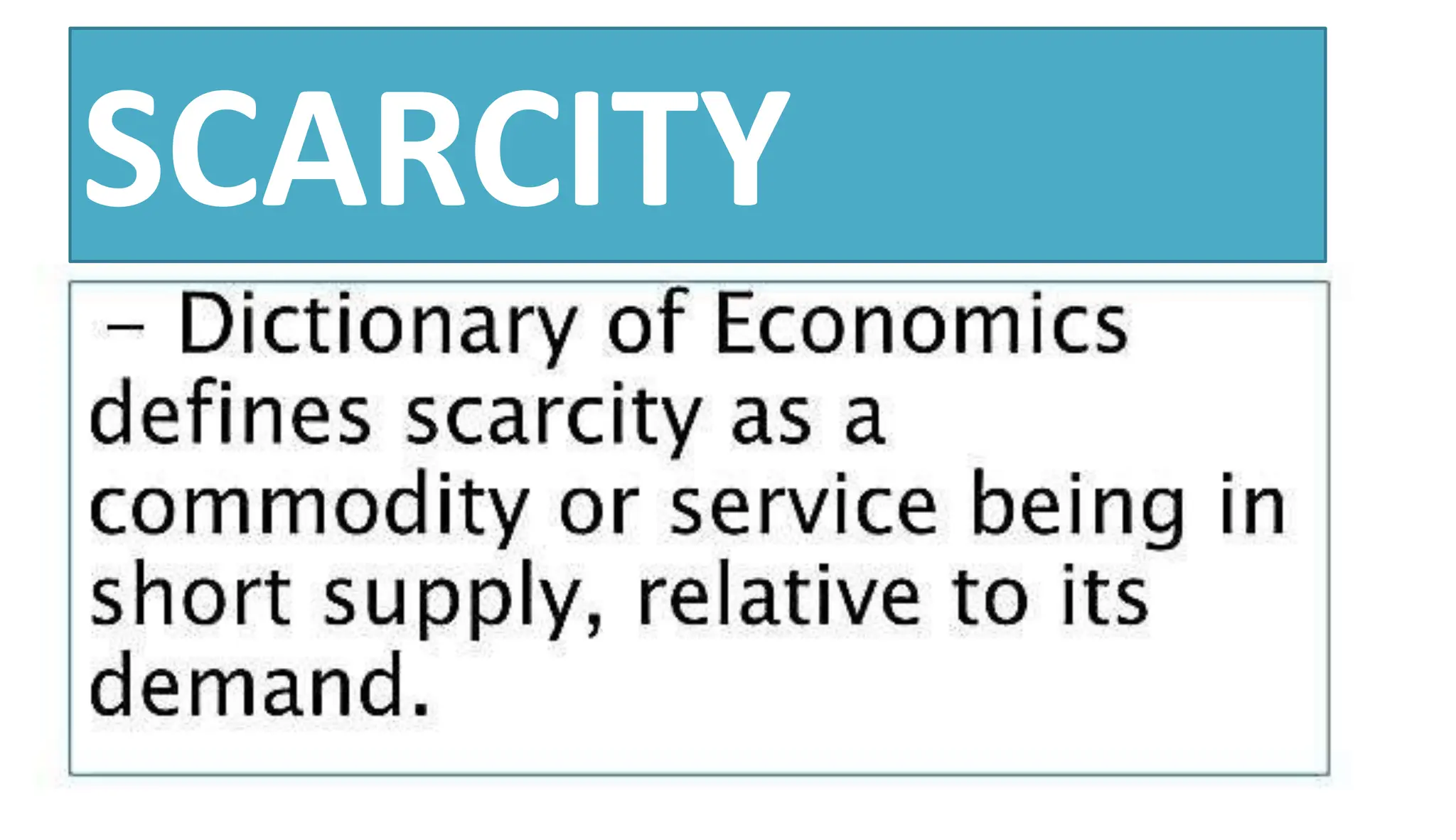
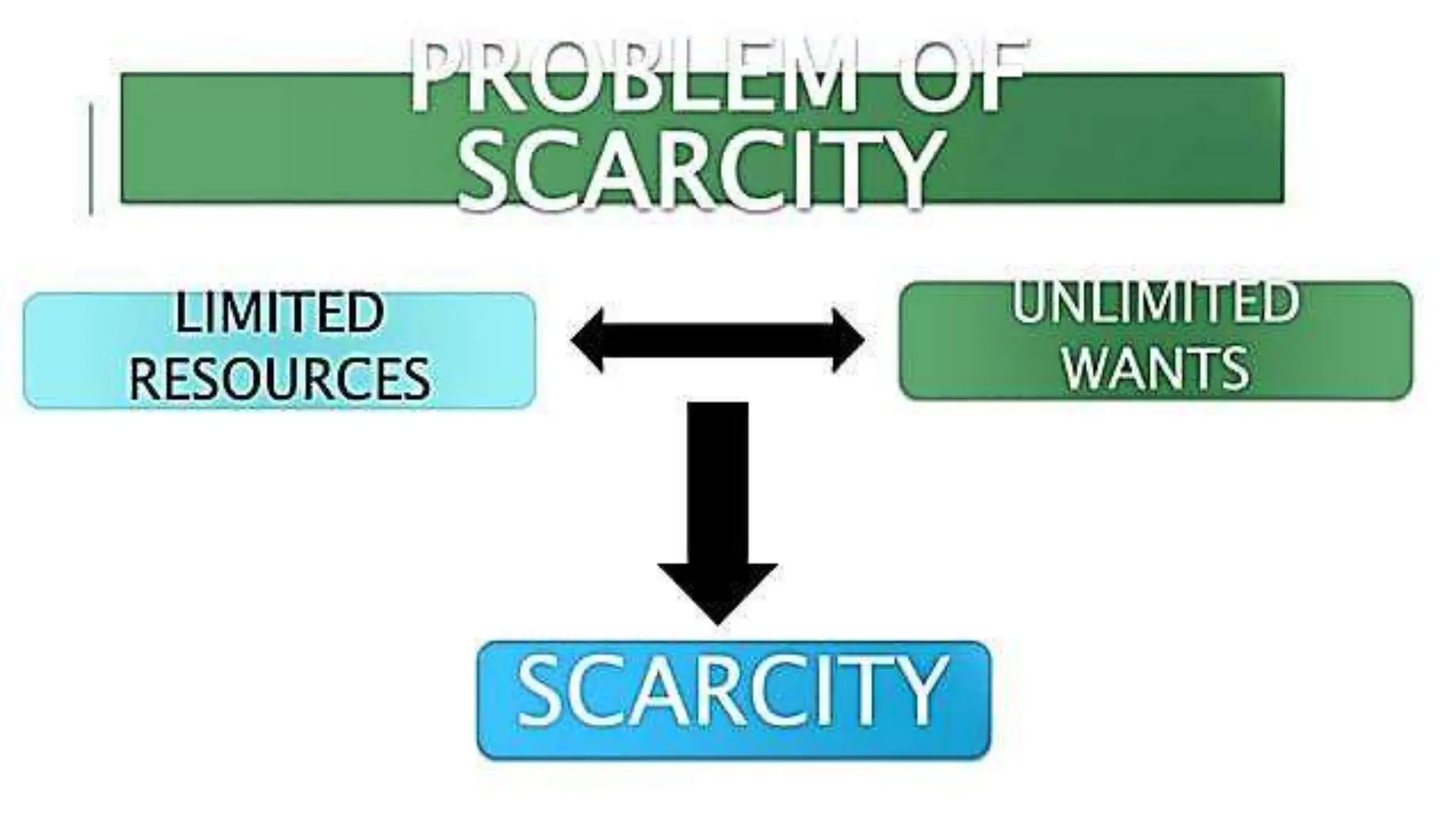
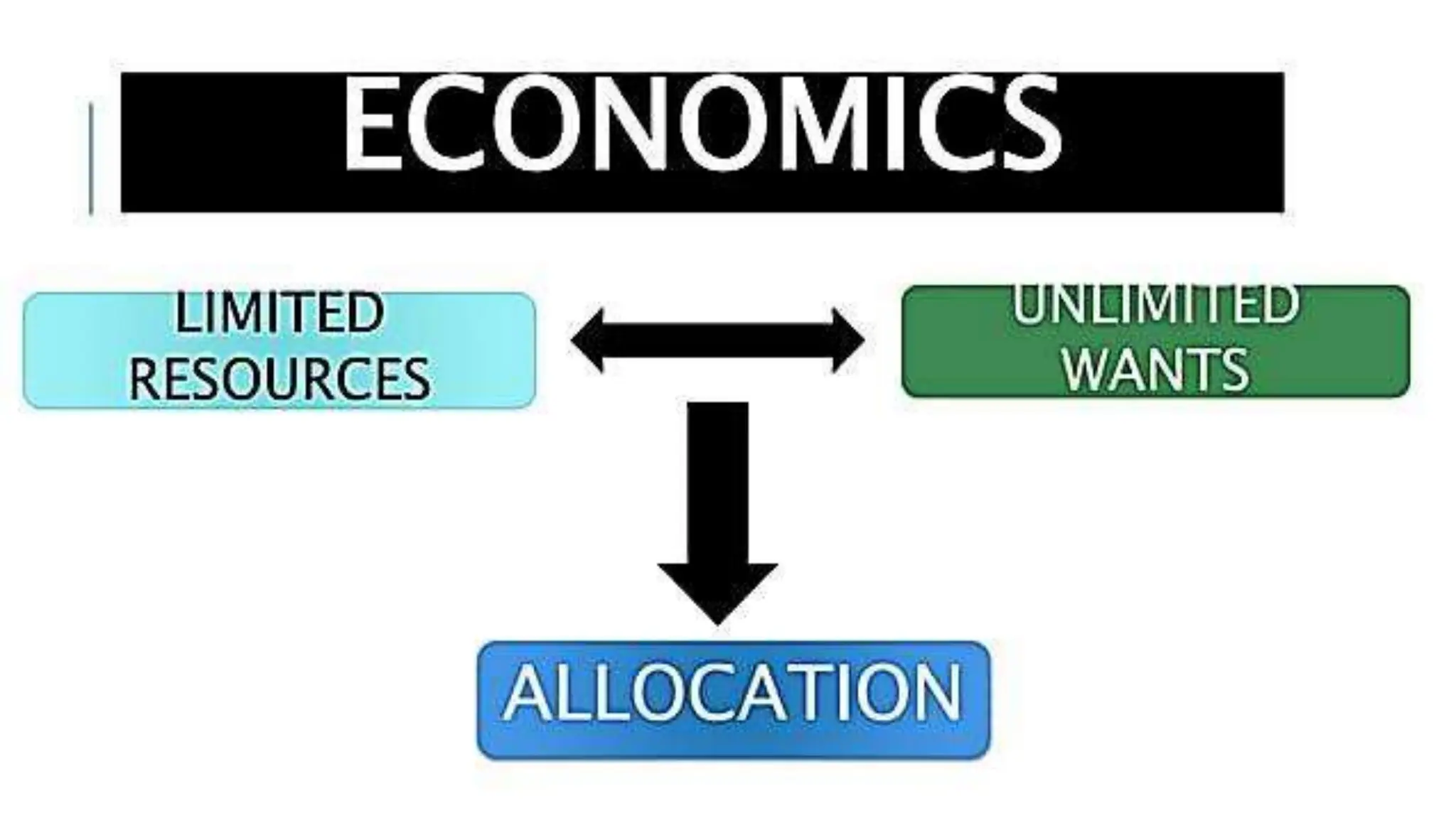
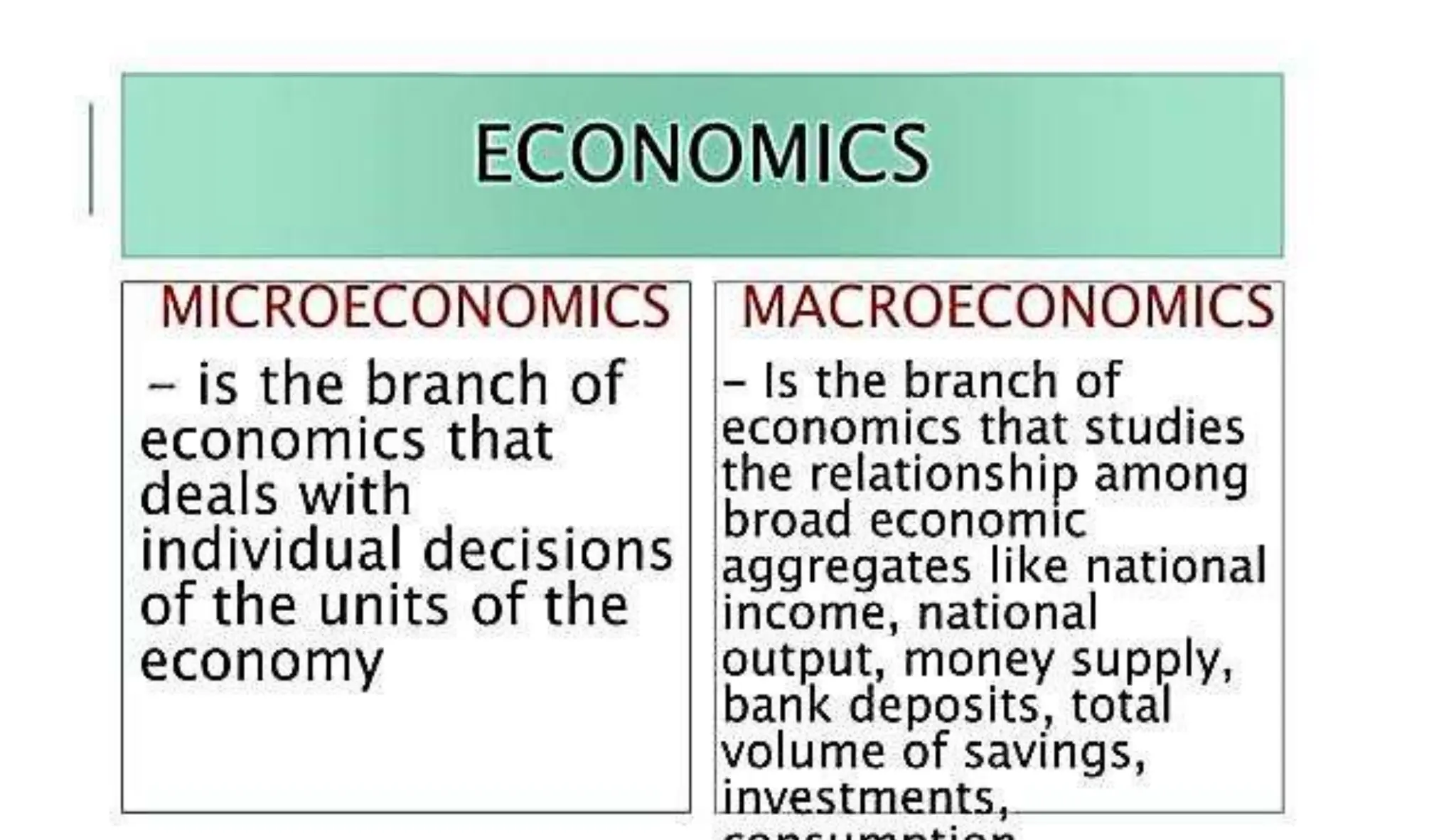
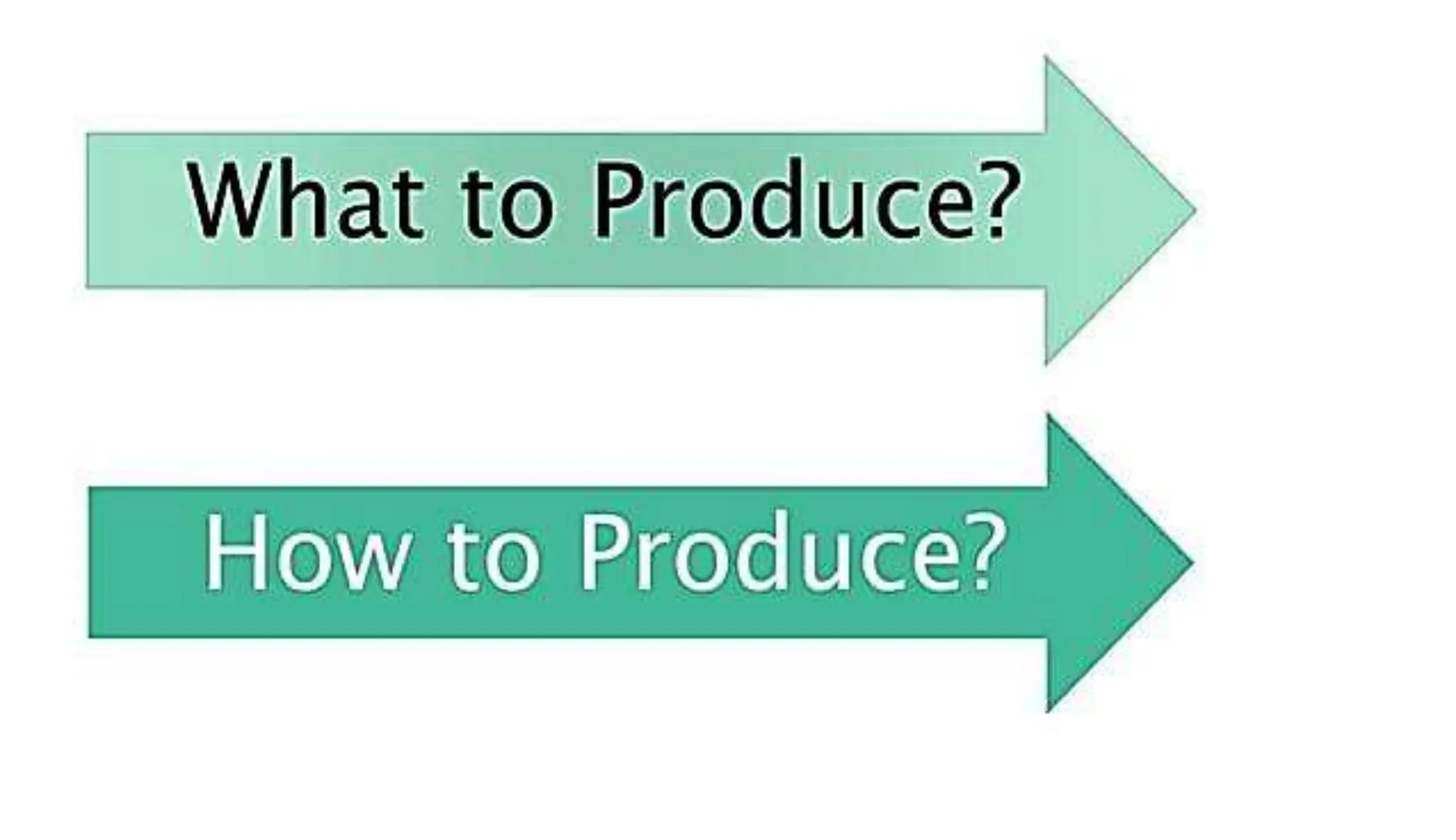
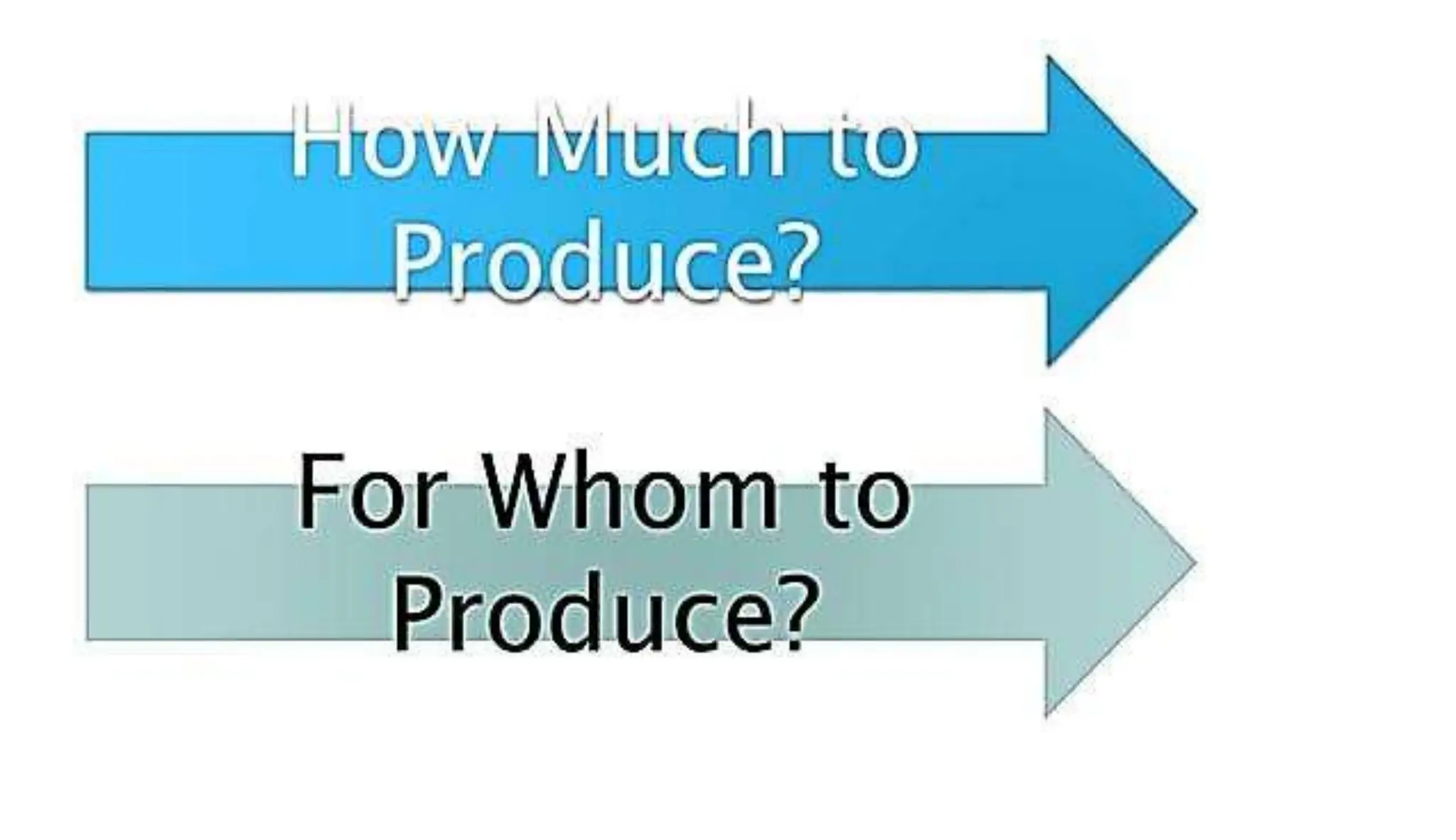
Economics studies how societies allocate scarce resources. It examines microeconomics topics like supply and demand and macroeconomics topics like GDP. There are three main factors of production - land, labor, and capital. Economic systems can be traditional, command, or market-based. A market economy allows for decentralized decision making based on supply and demand. Economics helps explain the importance of resource allocation and budgeting for both individuals and governments.