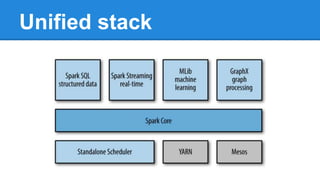
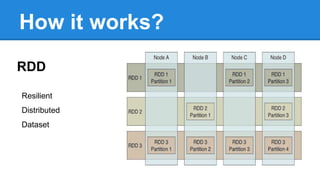
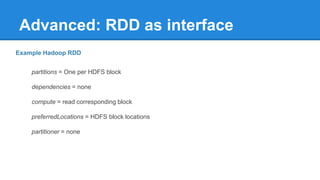
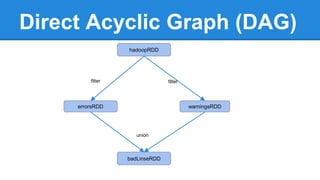
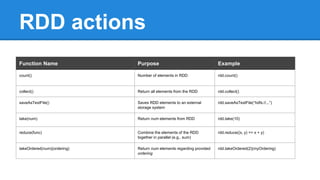
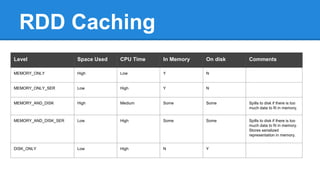
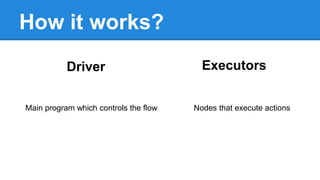
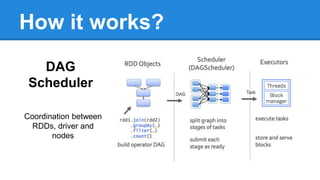
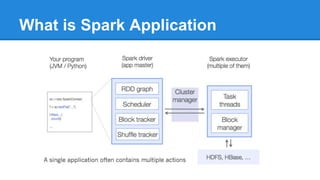
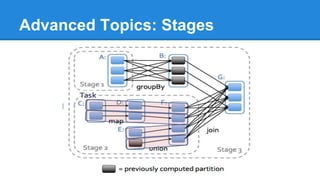
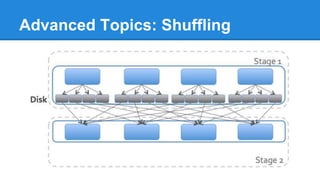
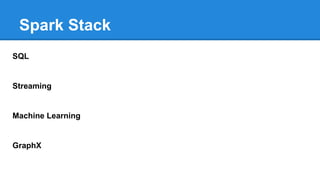
Apache Spark is a cluster computing platform designed to be fast and general-purpose. It provides a unified analytics engine for large-scale data processing across SQL, streaming, machine learning, and graph processing. Spark programs can be written in Java, Scala, Python and R. It works by building resilient distributed datasets (RDDs) that can be operated on in parallel. RDDs support transformations like map, filter and join and actions like count, collect and save. Spark also provides caching of RDDs in memory for improved performance.