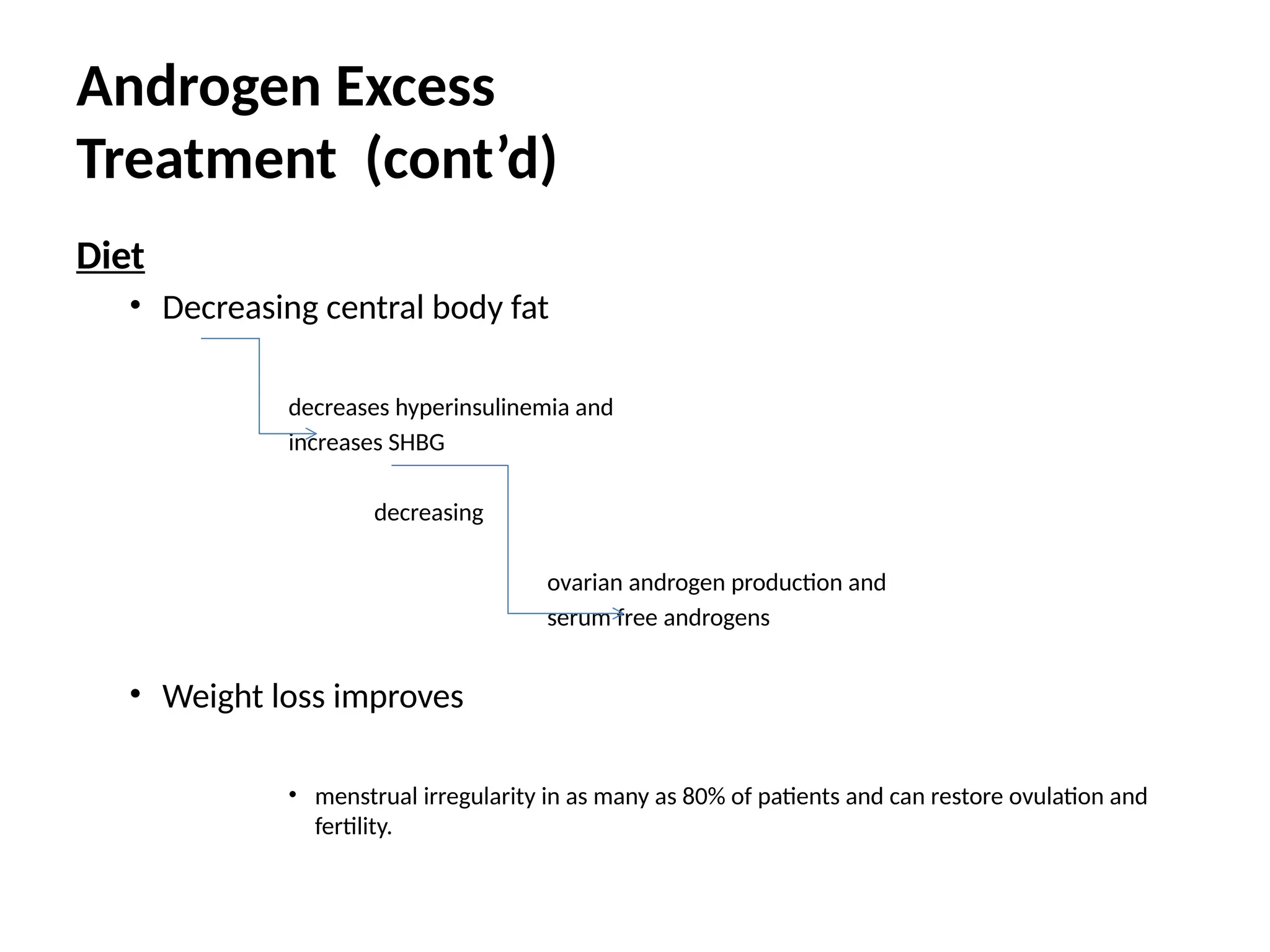
The document outlines treatment options for androgen excess, focusing on medical interventions such as hormonal therapy, antiandrogens, and insulin-sensitizing drugs. It details first-line treatments for hirsutism and acne, emphasizing the importance of combined therapies, while also discussing surgical options and the role of lifestyle changes like diet and weight loss. Long-term maintenance of therapy is essential, with varying efficacy among treatments and potential risks associated with specific medications.