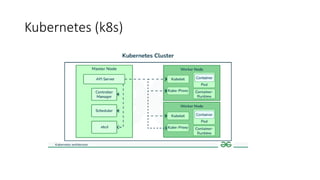
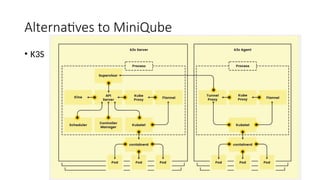
Kubernetes (k8s) is a container orchestration tool introduced by Google in 2014, designed for deploying and scaling applications, especially microservices. It can run multiple container runtimes and offers various alternatives for learning and production, such as Minikube, K3s, and Microk8s, each tailored for different use cases and resource requirements. Pods, the smallest deployable units in Kubernetes, can be created through deployments and can leverage features such as replication and management through a control plane.