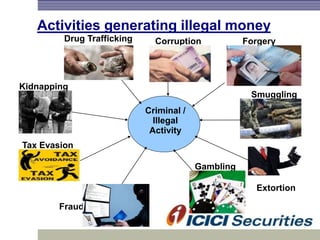
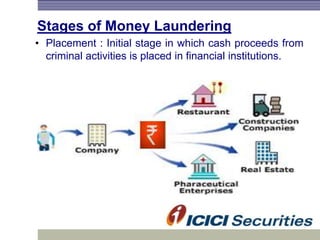
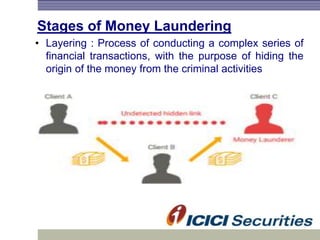
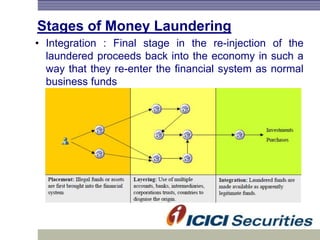
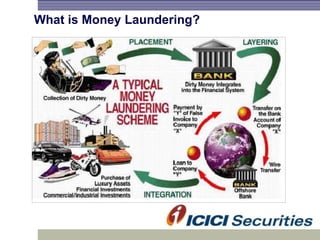
Money laundering involves disguising illegally obtained money to make it appear legitimate. It occurs in three stages: placement, layering, and integration. In India, the Prevention of Money Laundering Act of 2002 established the Financial Intelligence Unit and requires financial institutions to implement anti-money laundering procedures like customer due diligence, suspicious transaction monitoring and reporting, and employee training. Regulated entities like I-Sec must comply with these regulatory requirements to prevent money laundering and financing of terrorist activities.