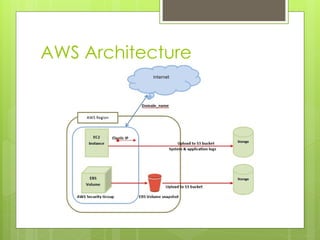
Amazon Web Services provides scalable cloud computing resources including Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) virtual servers, Simple Storage Service (S3) object storage, and Elastic Block Store (EBS) volumes. EC2 allows launching virtual servers as needed and attaching EBS volumes for block-level storage. S3 provides scalable storage for files up to 5 GB. EBS volumes can be attached to EC2 instances for primary storage and snapshots are used to back up EBS volumes to S3 for incremental backups.