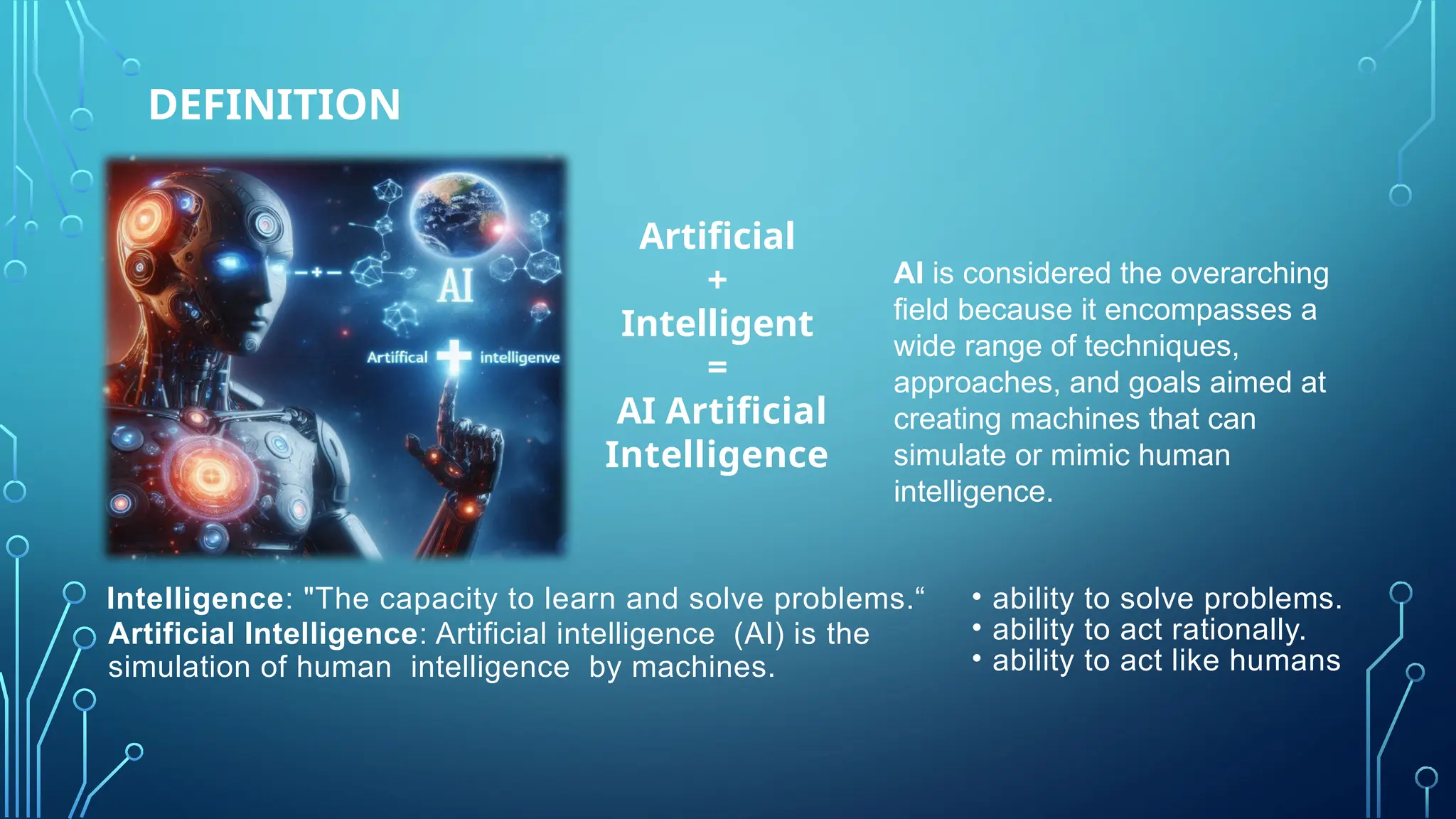
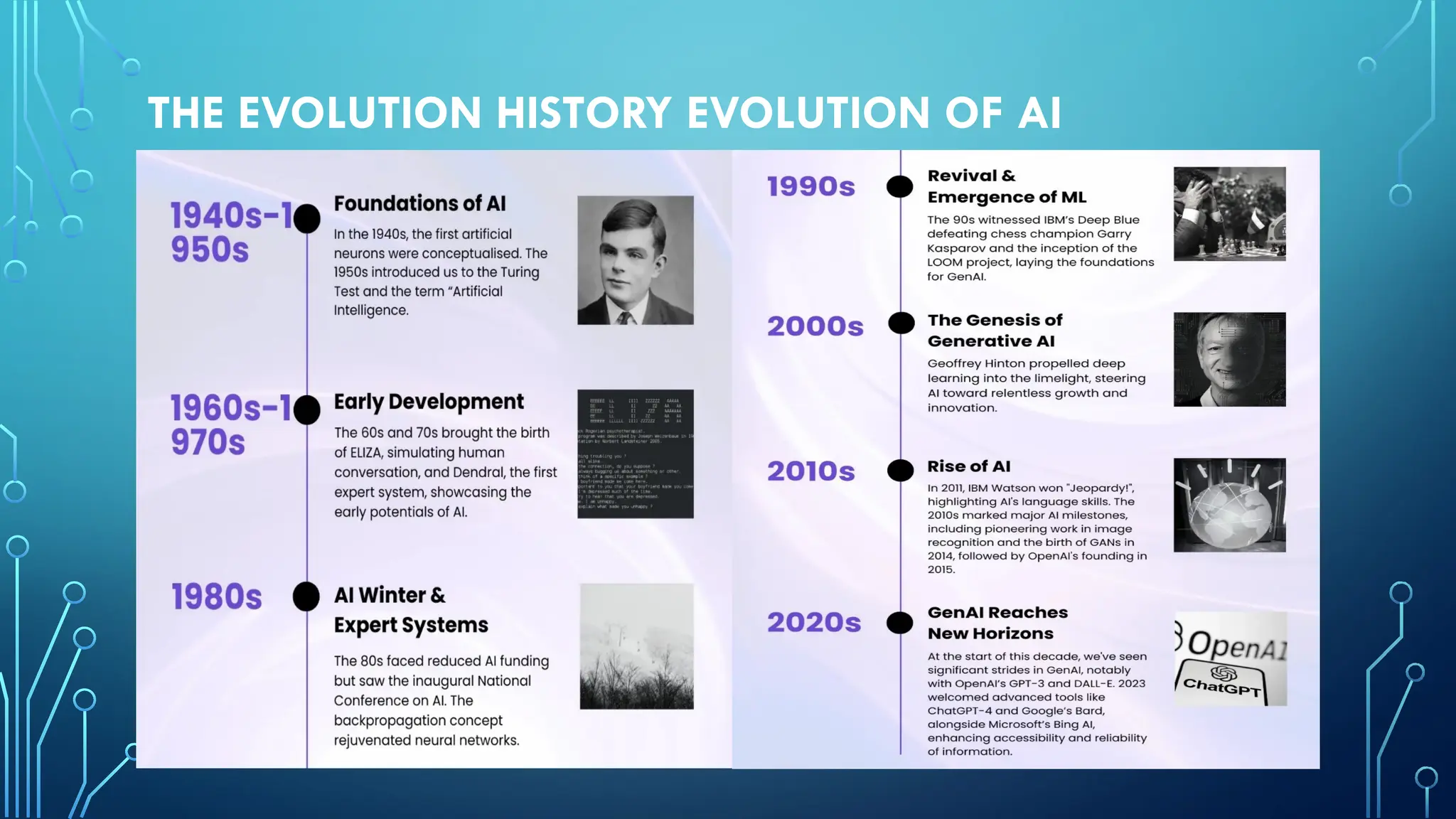
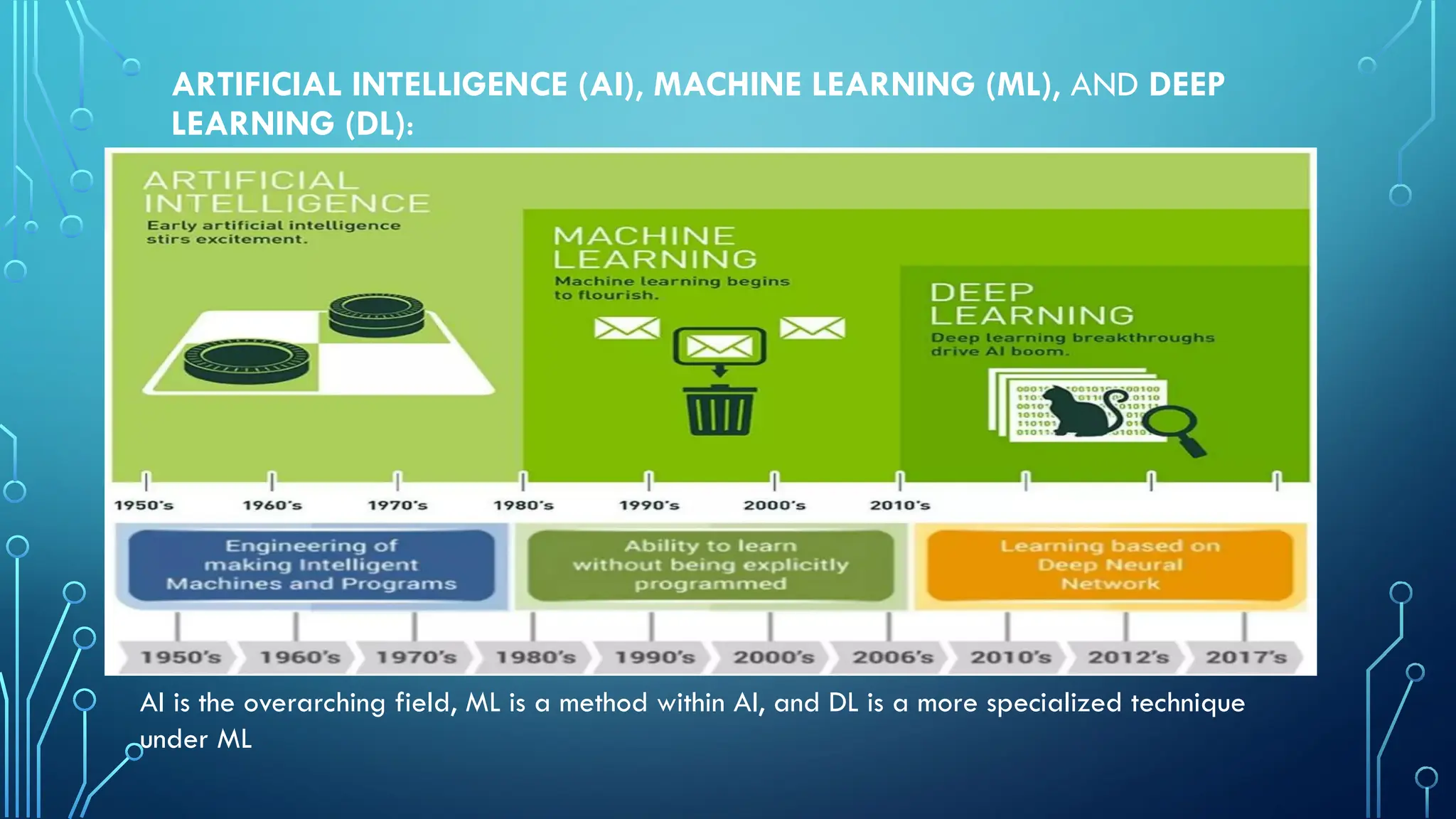
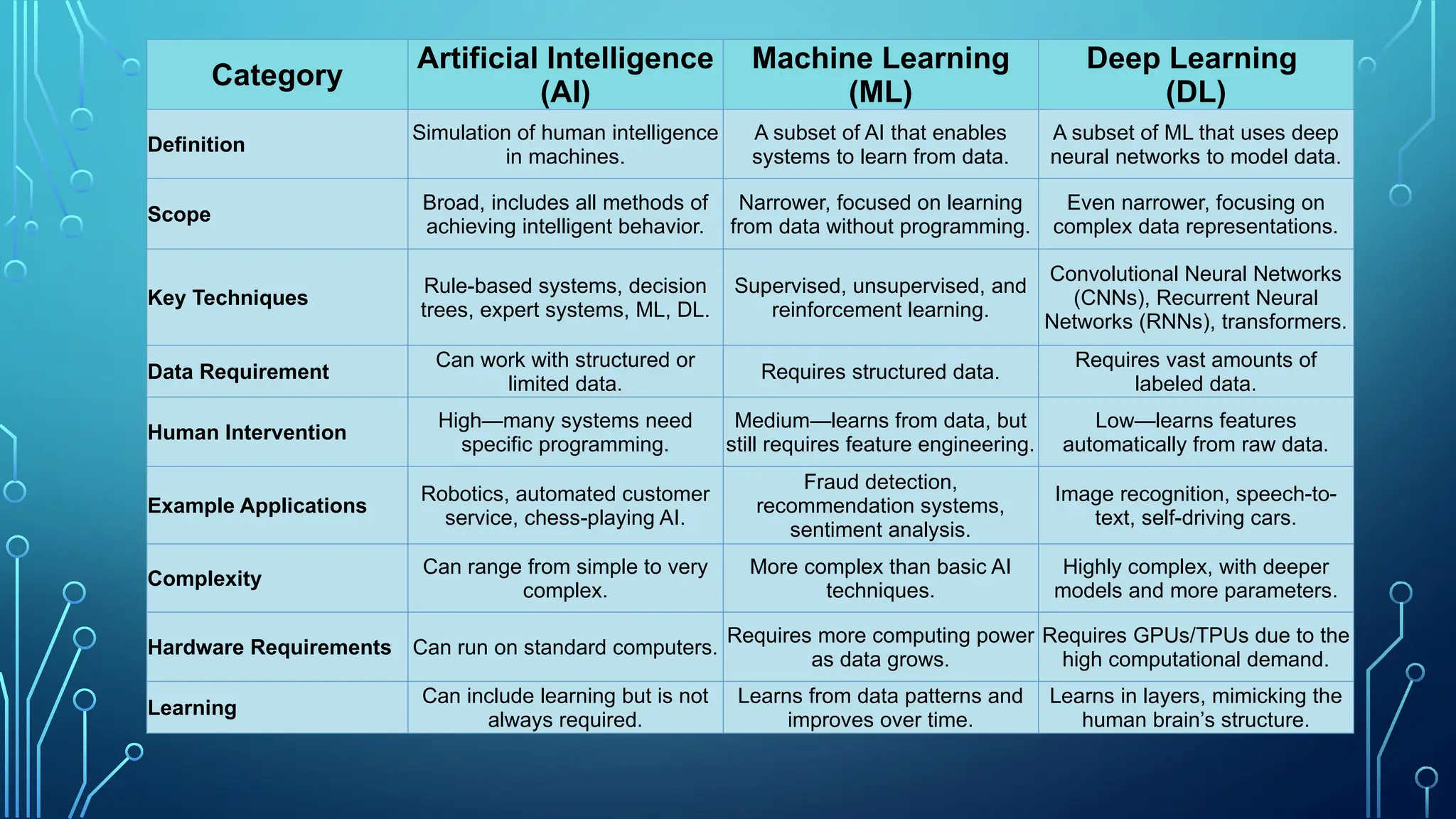
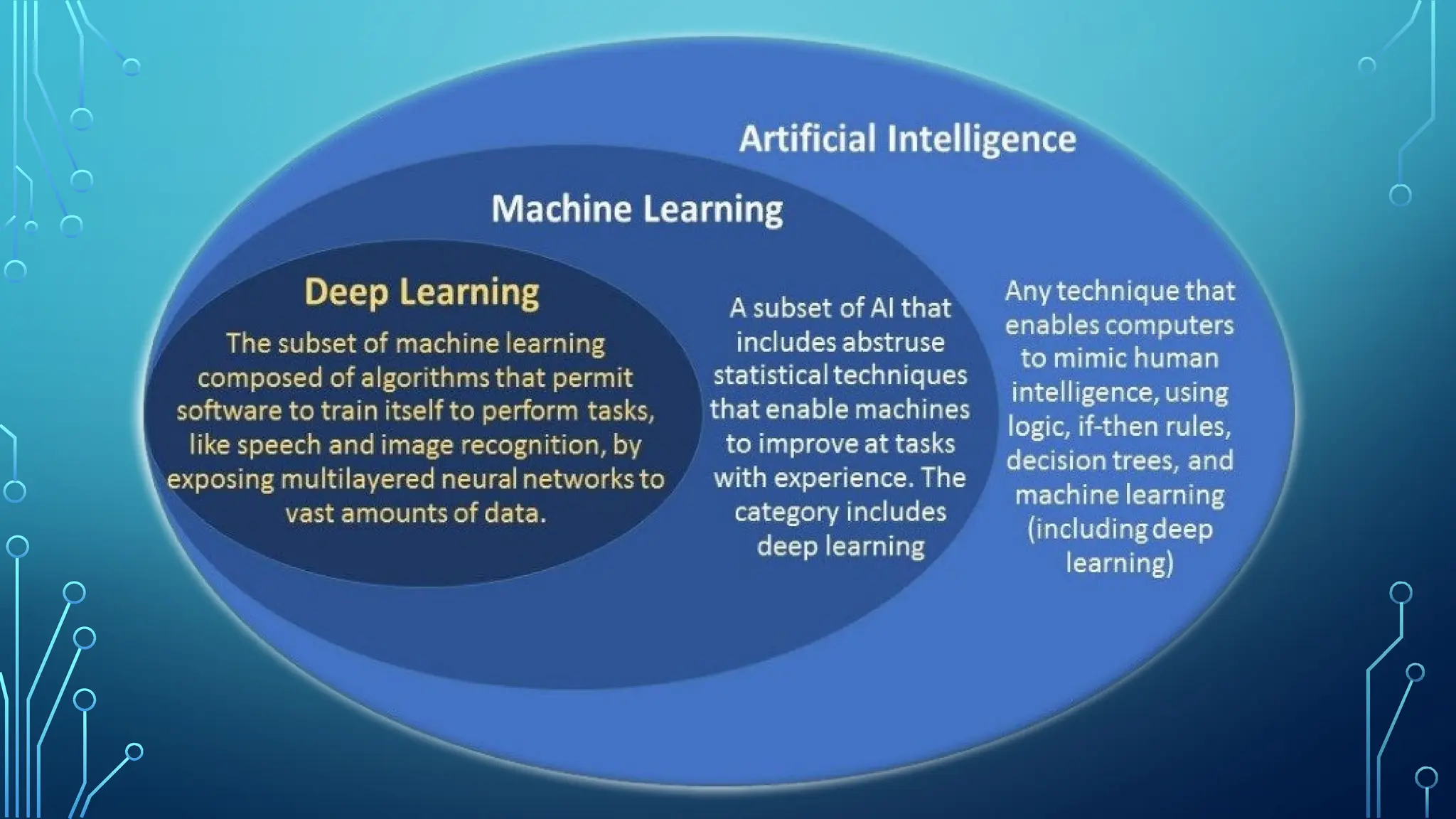
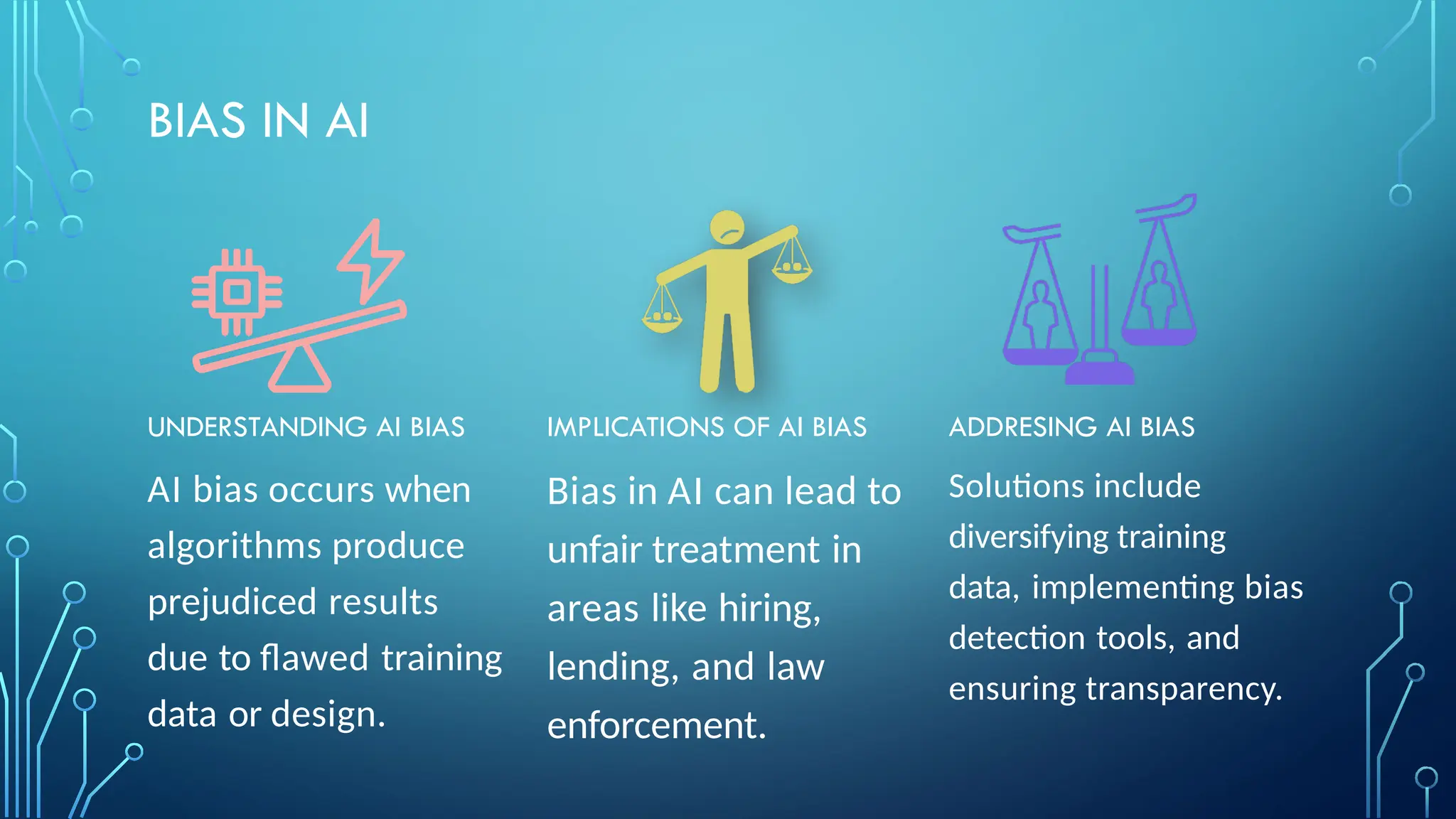
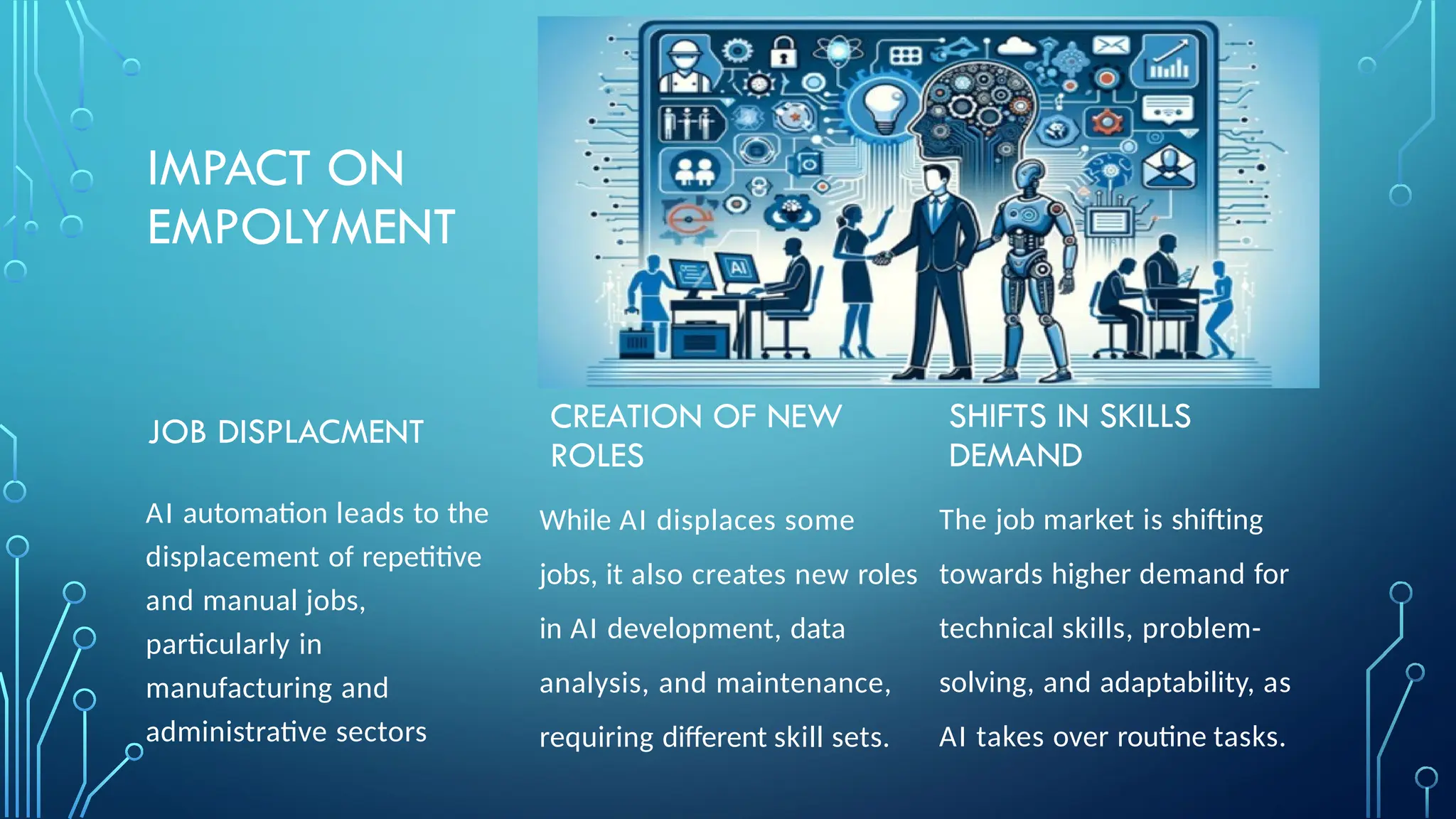
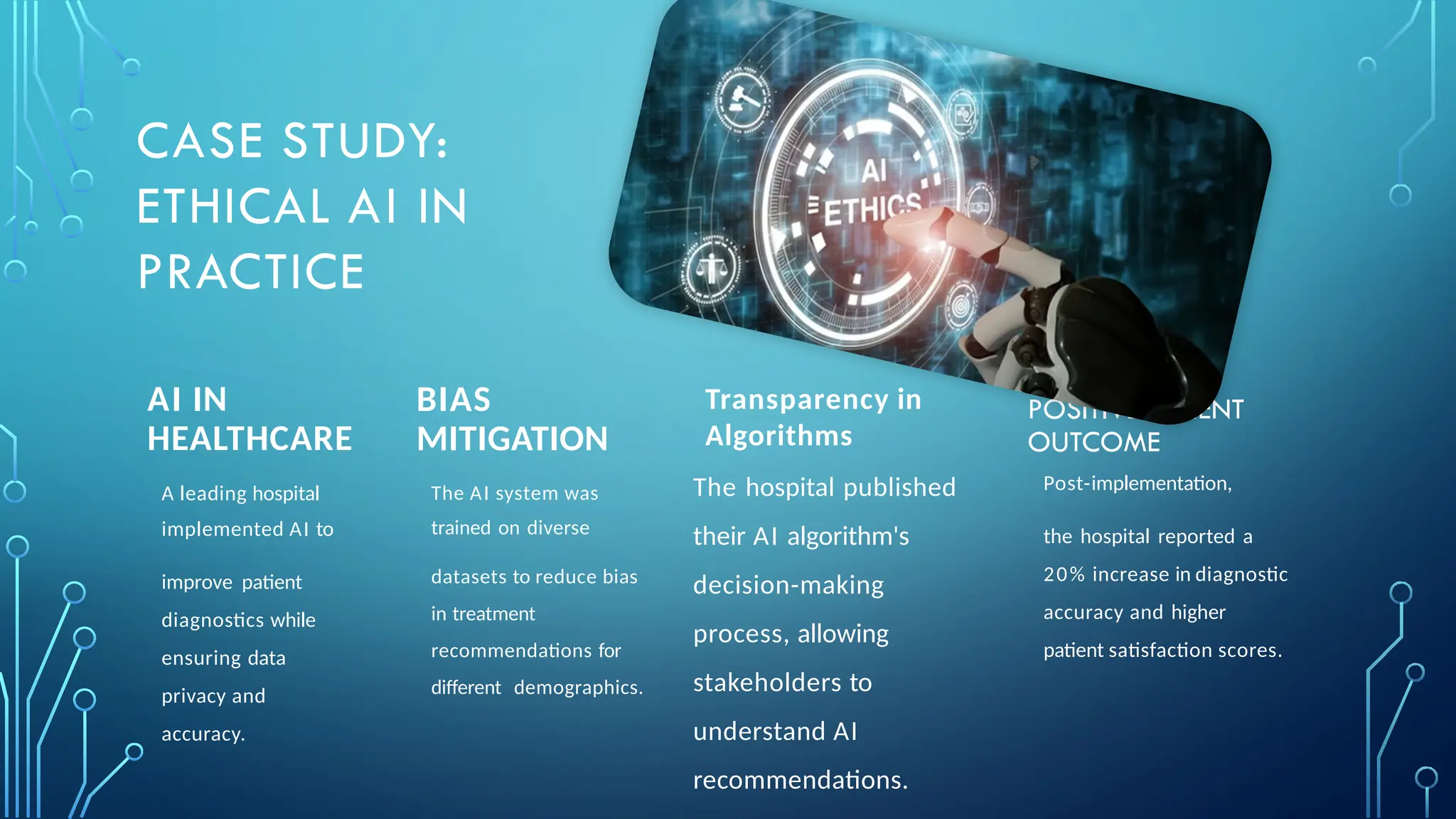
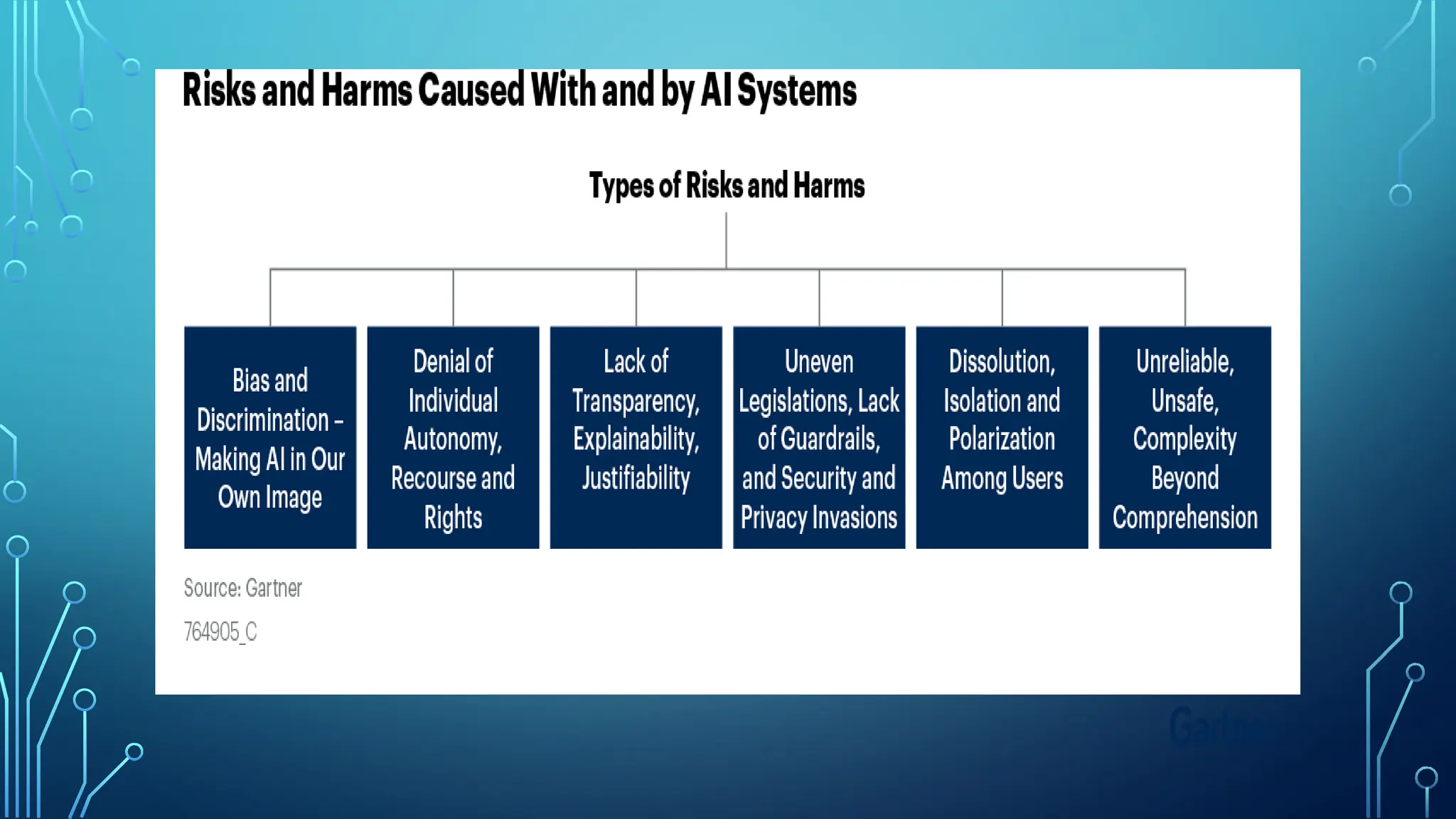
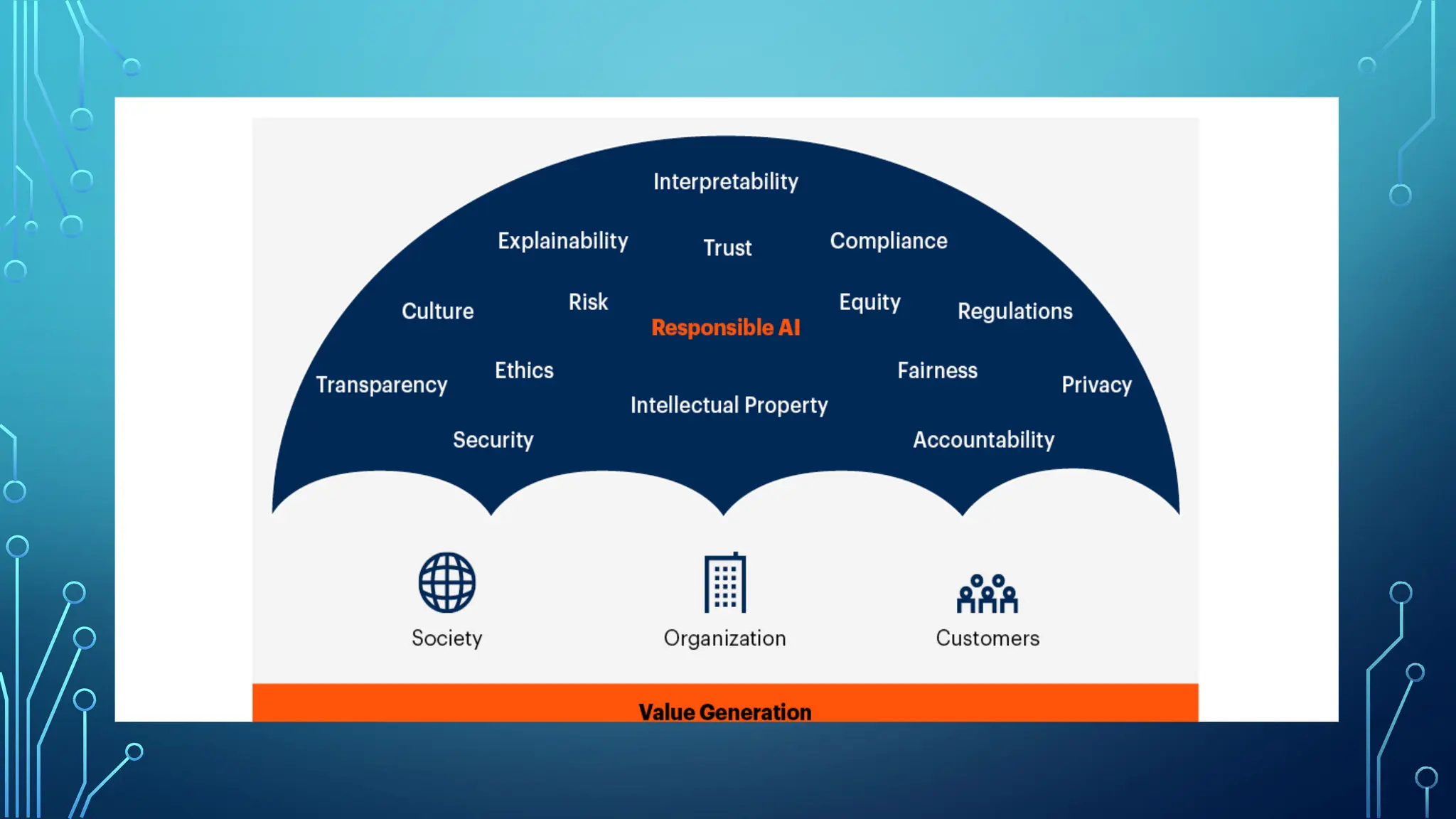
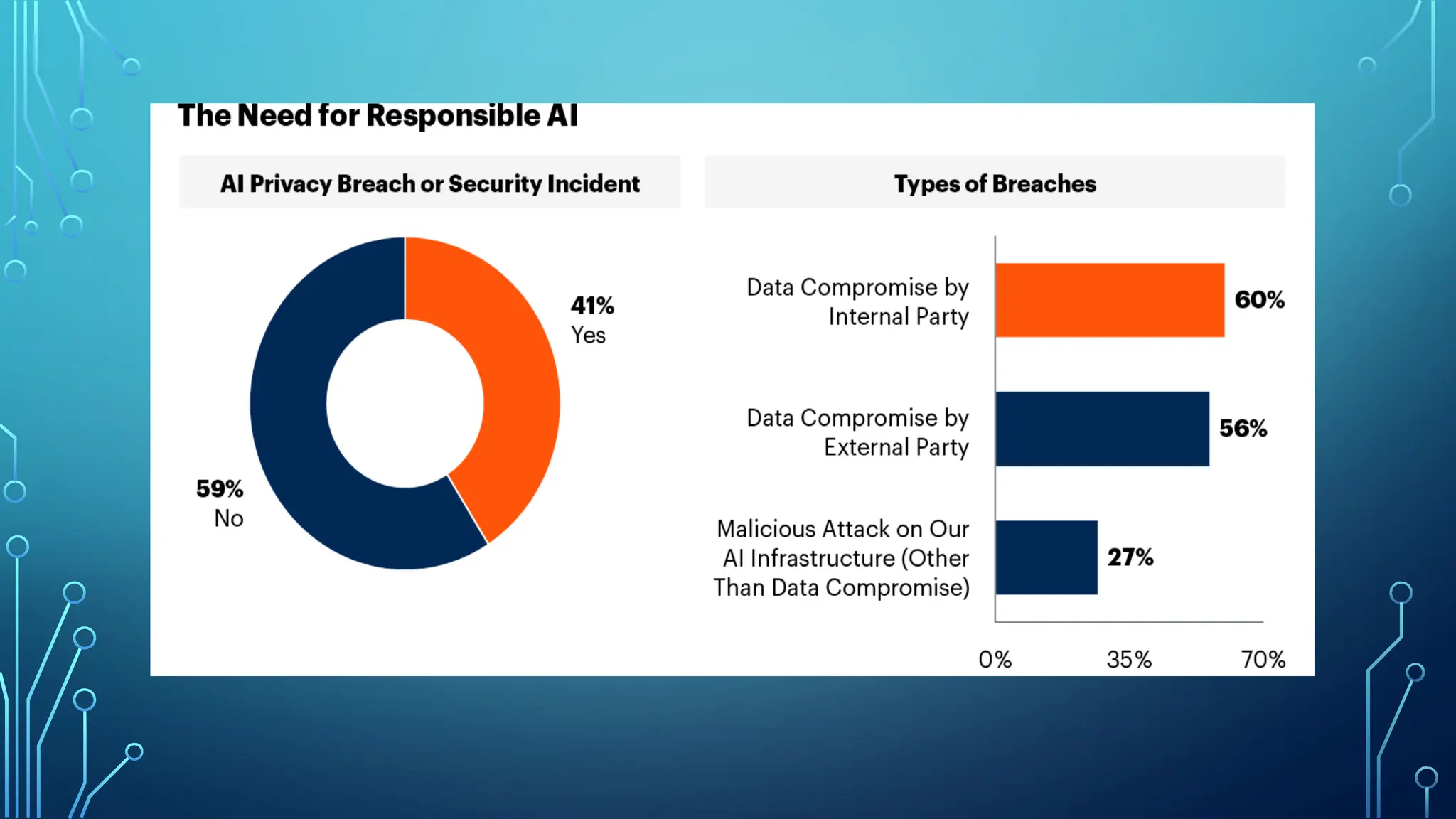
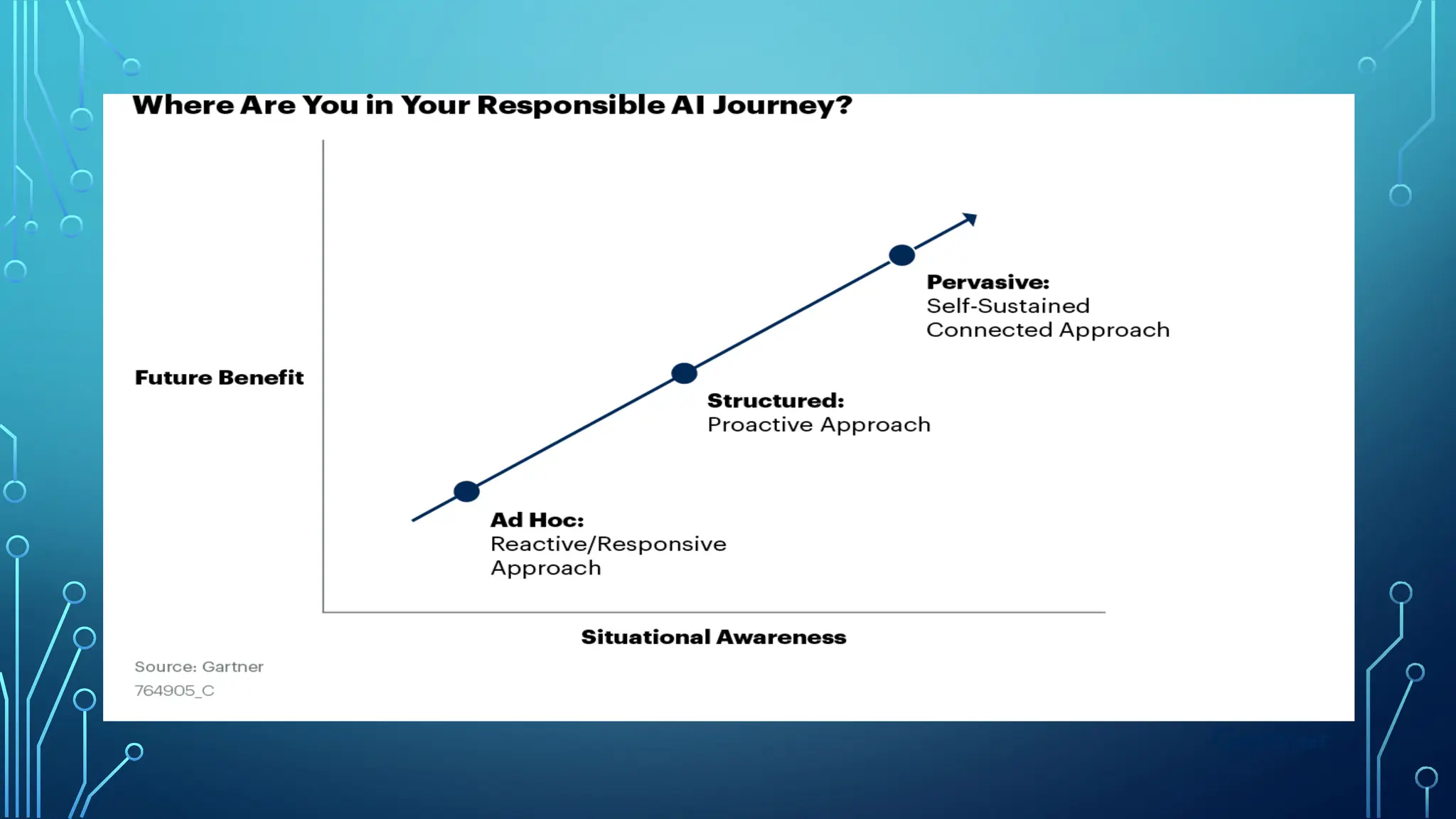
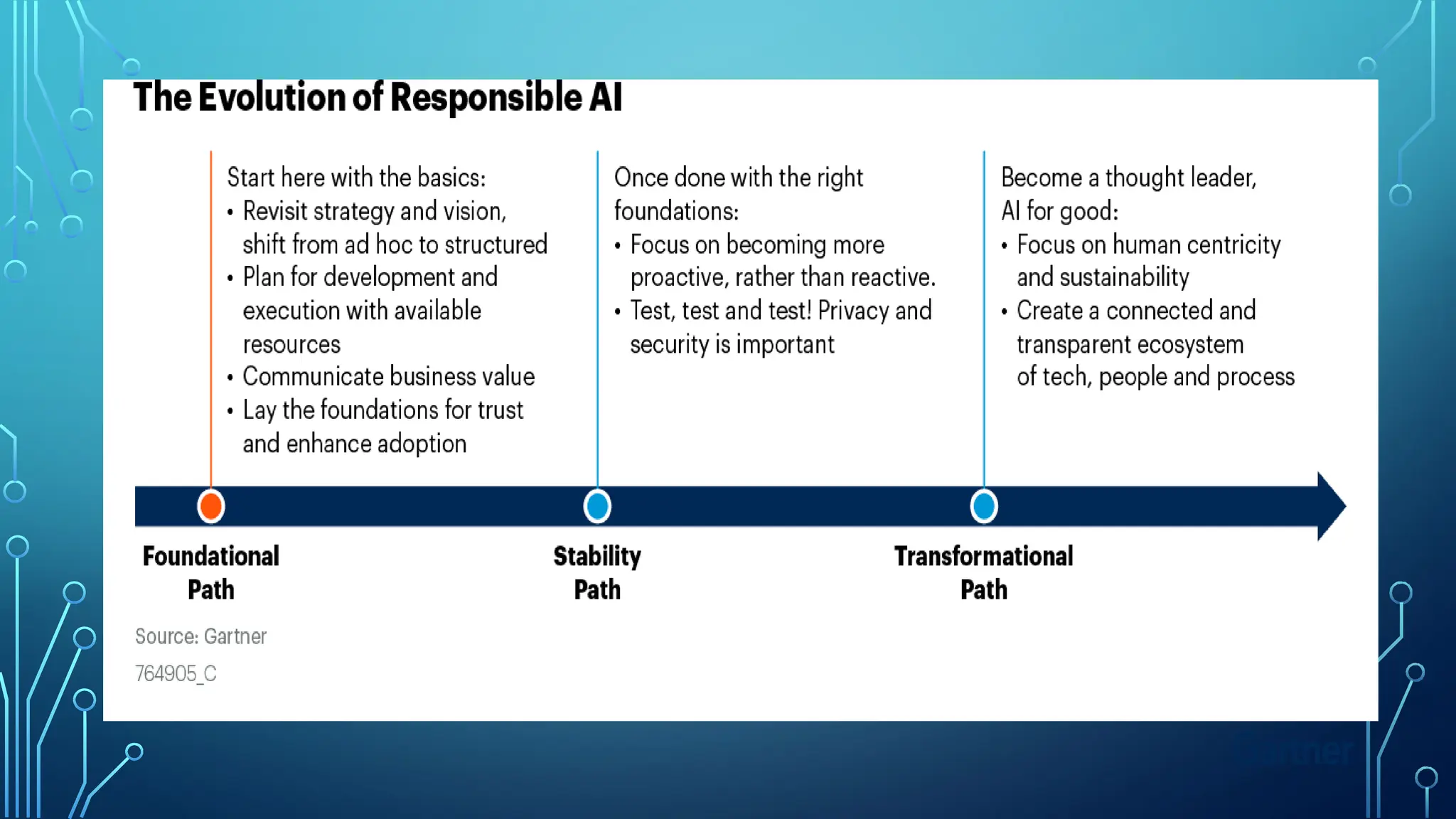
The document provides a comprehensive overview of artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and deep learning (DL), detailing their definitions, evolution, and applications in various sectors. It highlights the strategic roles AI plays in technology management, including infrastructure optimization, decision-making, and human capital management, while also addressing the ethical considerations surrounding AI use. Additionally, the transformational potential of DL in automating complex tasks and enhancing personalization is emphasized, along with the impact of AI on job displacement and the evolving demands for new skill sets.































![THE FUTURE OF EMPLOYEE SERVICE
AUTOMATE THE SERVICE LIFE CYCLE
• RCAs
• Knowledge gaps
• Upskilling
• Contextual
handoffs
• Trending issues
• Configurable
thresholds
Request
[Catalog | Knowledge]
Learn
[KCS | CSI]
[Orchestration]
Resolve
Diagnose
[IPC | Config]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aiartificialintelligent-machinelearning-deeplearning-241217130134-04e4aa73/75/AI-Artificial-Intelligent-Machine-Learning-Deep-Learning-pptx-58-2048.jpg)
![BILLIONS [MORE] SERVED… THANKS TO AI
AUTOMATION REDUCES DOWNTIME… FOR TWO
MILLION EMPLOYEES IN 40,000 RESTAURANTS
“We started using AI to route tickets
and within weeks it automated our
manual process. It saved us $3M in
the first year. We have big plans for
AI!”
Joel Eagle
McDonald’s Sr. Director
Technology & Architecture](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aiartificialintelligent-machinelearning-deeplearning-241217130134-04e4aa73/75/AI-Artificial-Intelligent-Machine-Learning-Deep-Learning-pptx-59-2048.jpg)