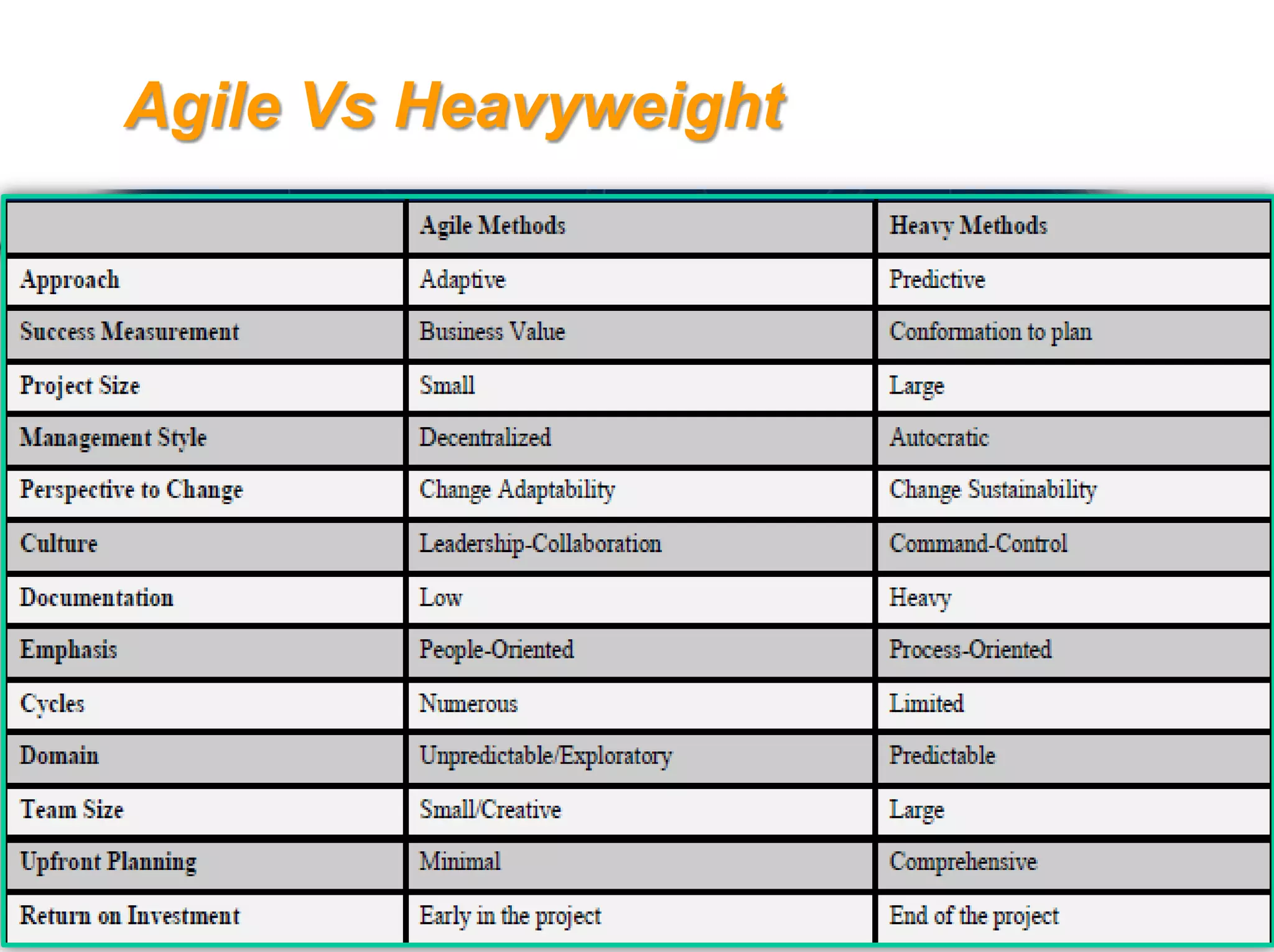
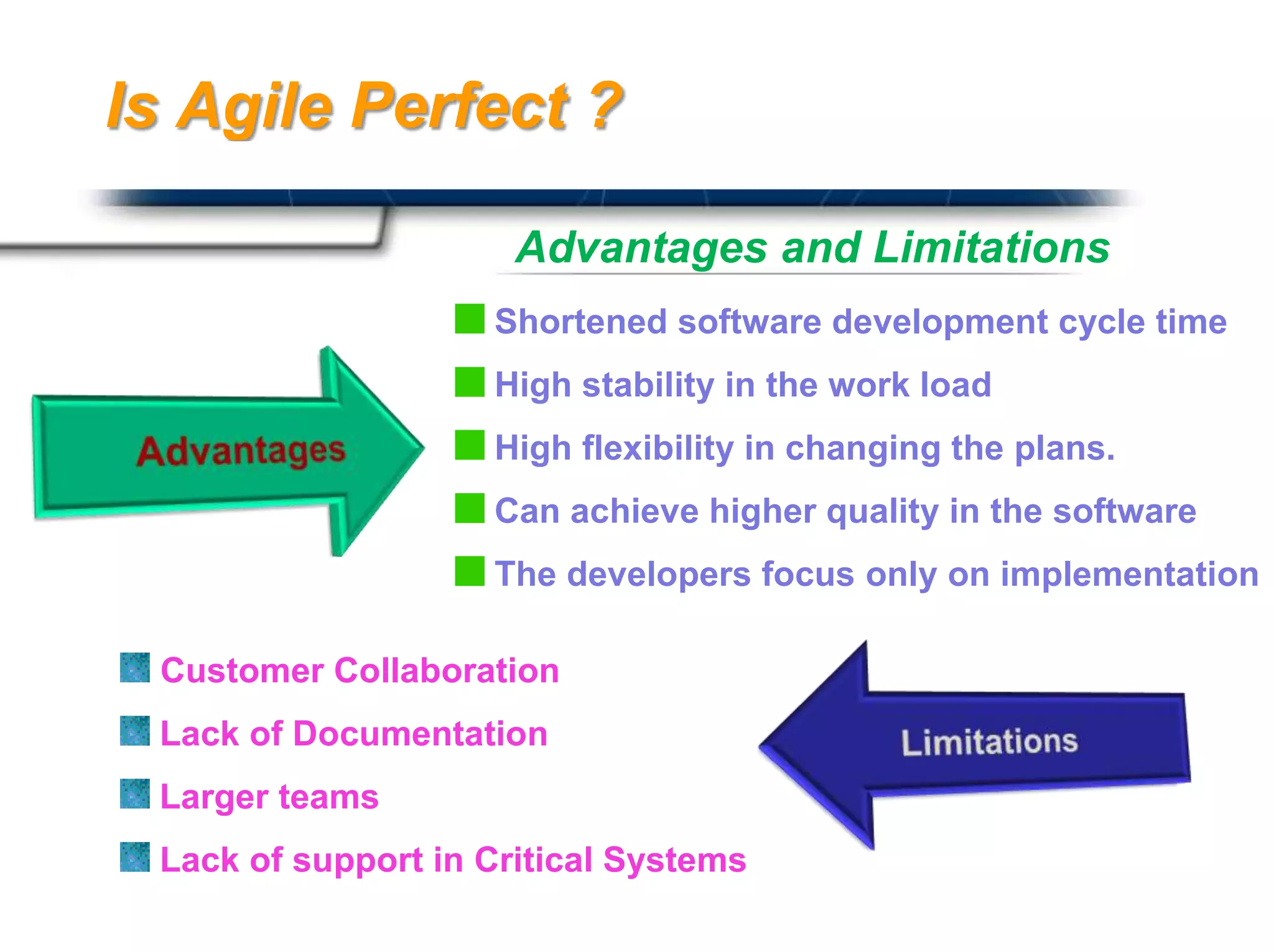
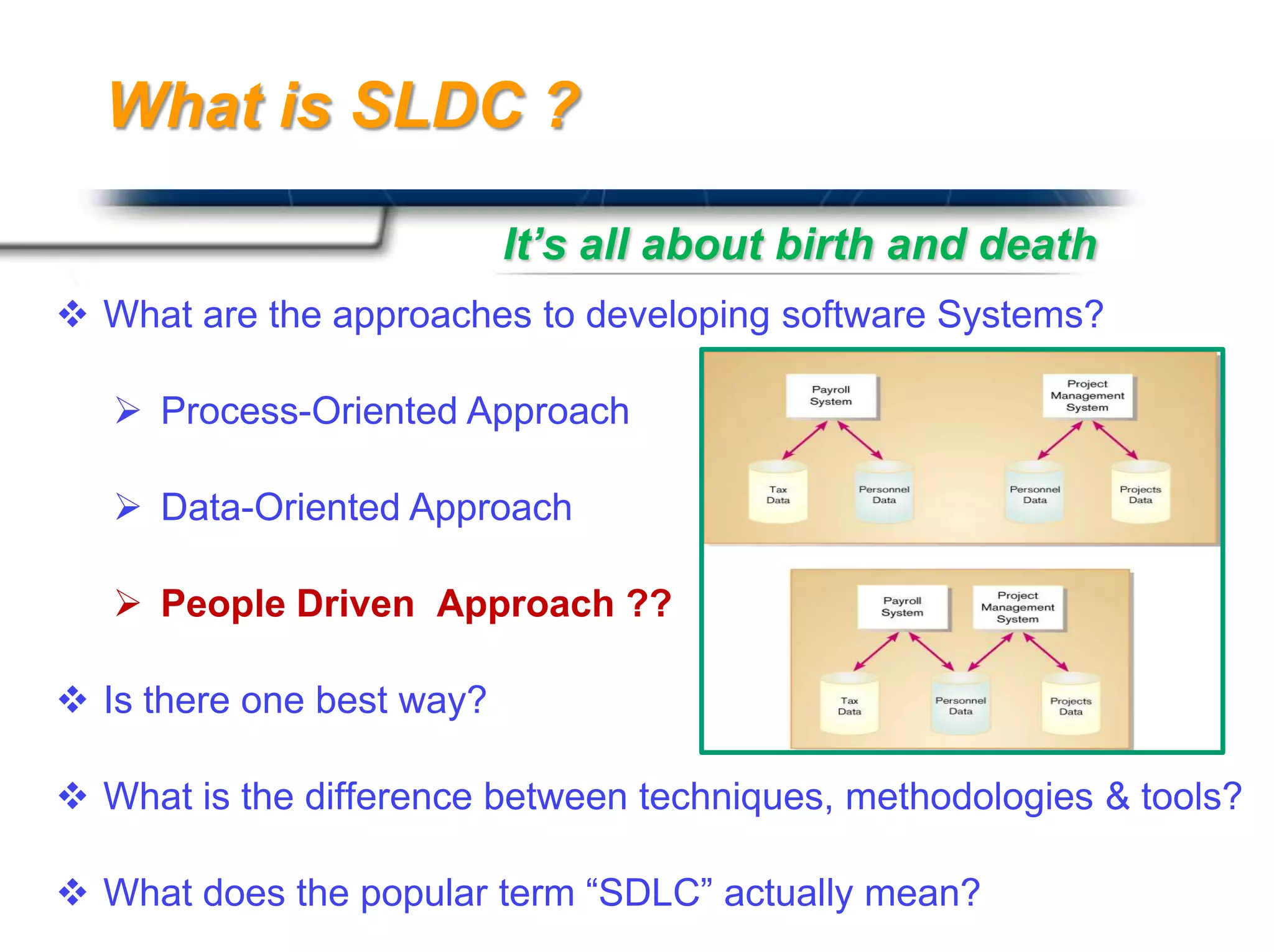
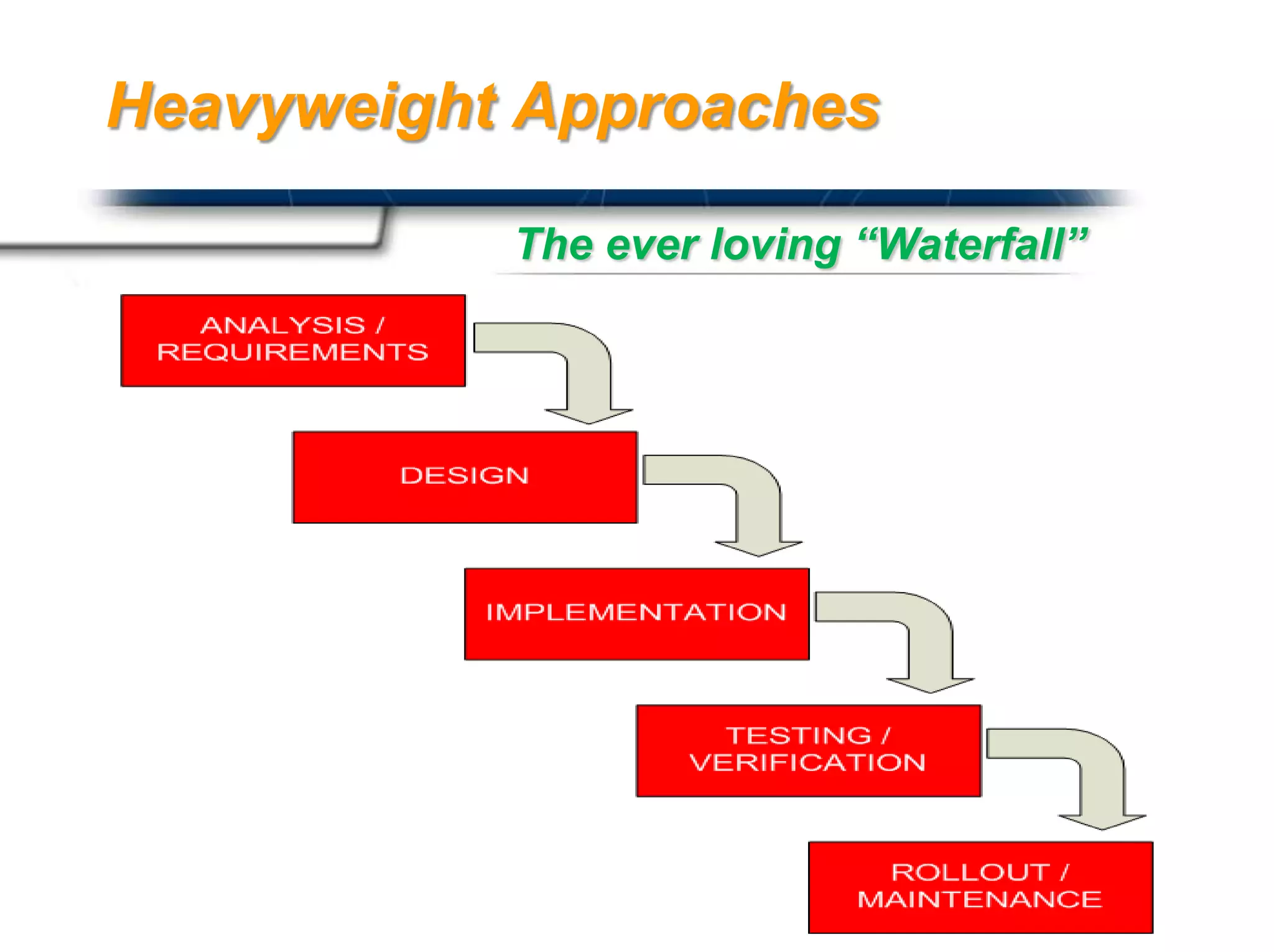
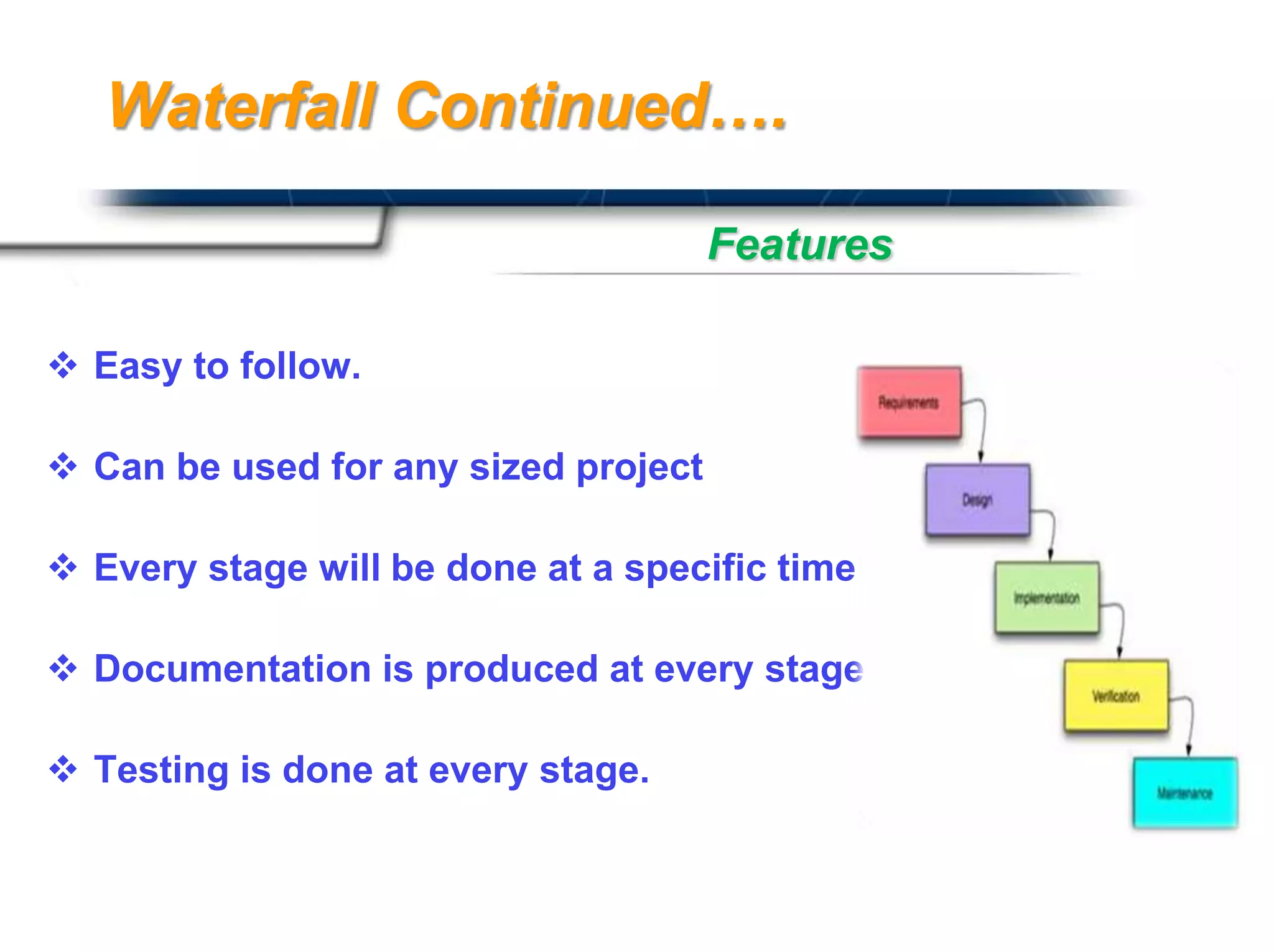
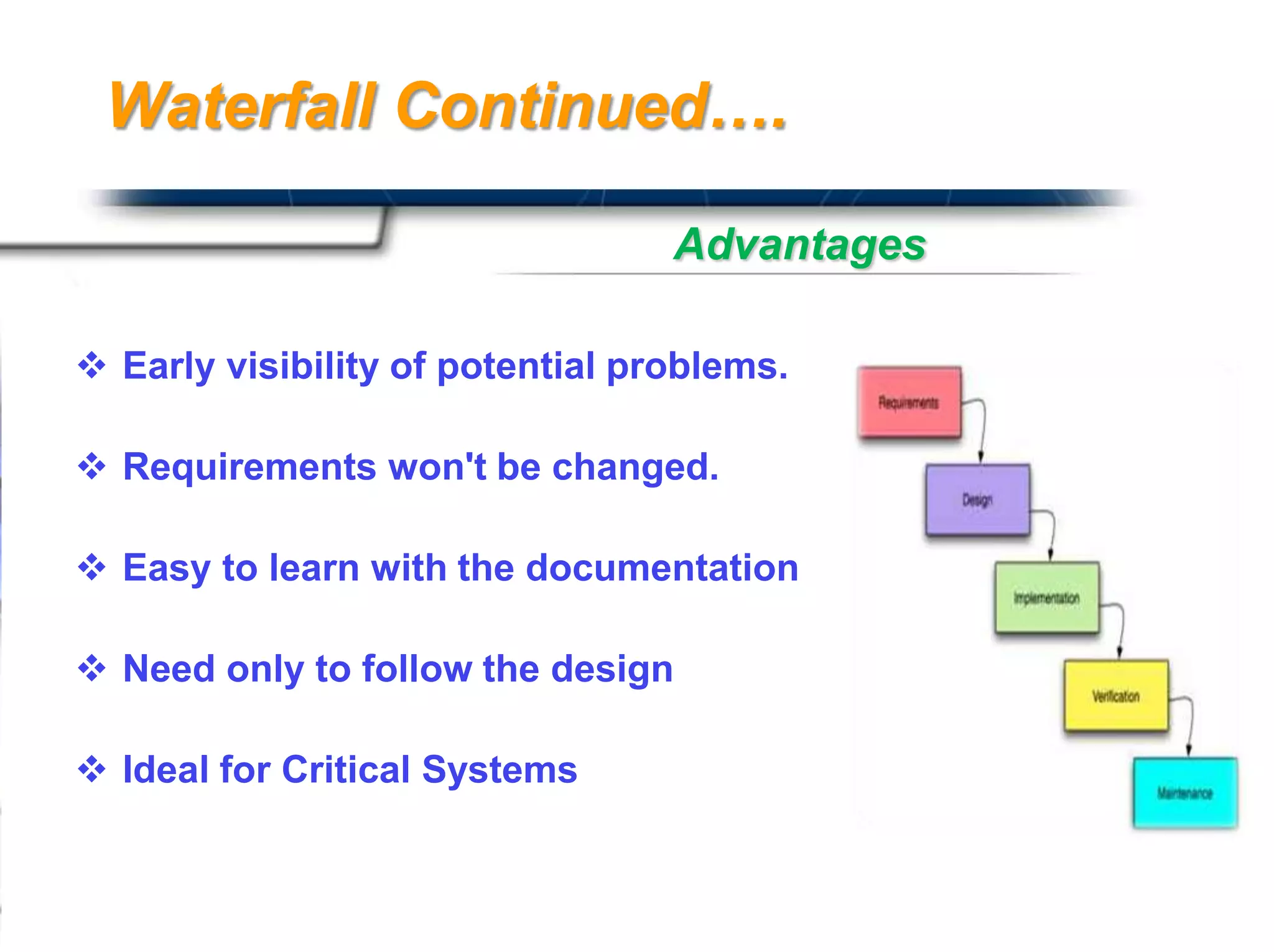
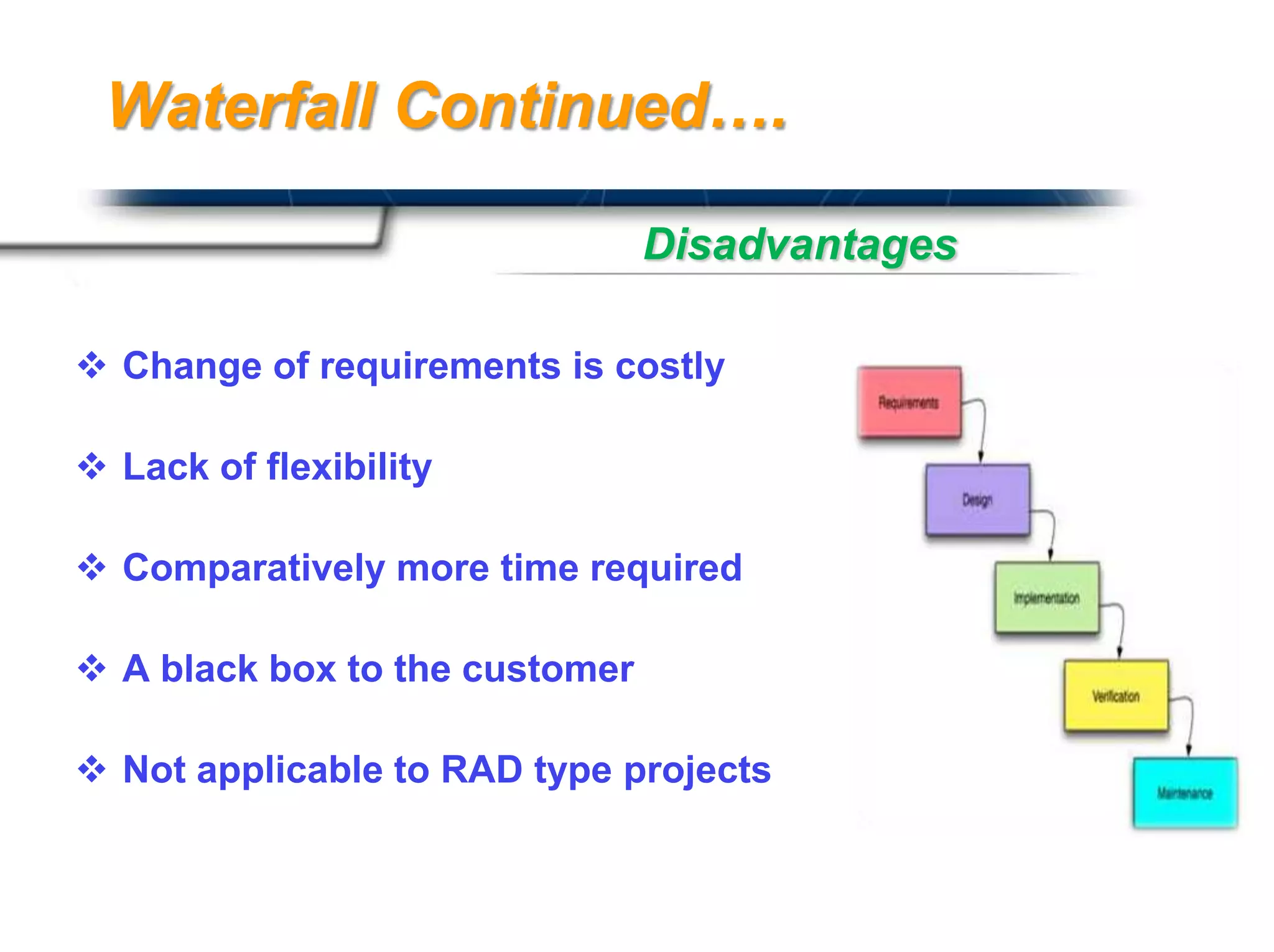
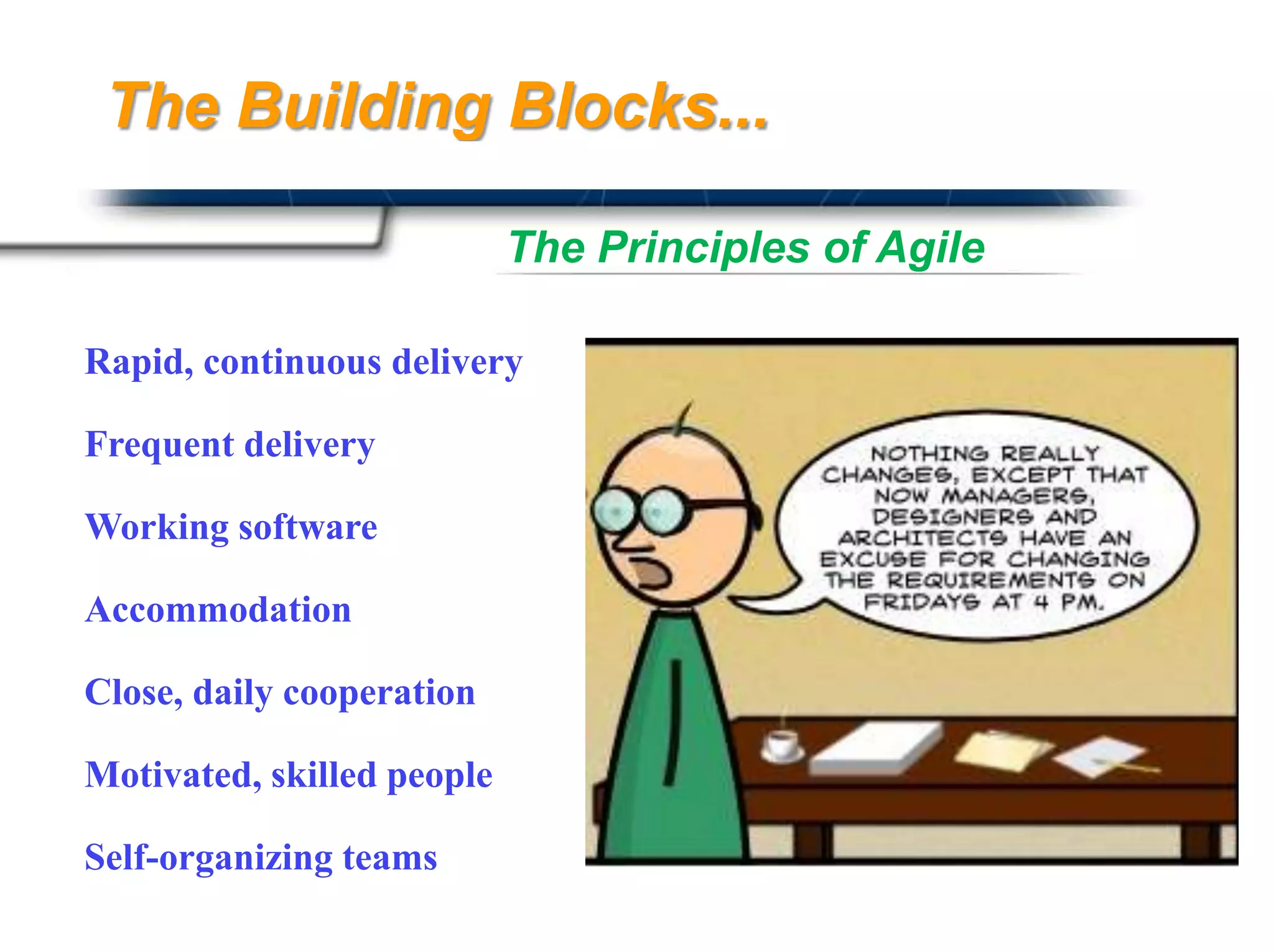
The document discusses agile software development methodologies. It begins with an overview of traditional software development lifecycles and heavyweight approaches like waterfall modeling. It then introduces why agile approaches were developed, focusing on principles like rapid delivery, accommodation to change, and close cooperation between developers and customers. The rest of the document details specific agile practices and methodologies like scrum, extreme programming, and crystal methods. It compares agile and traditional approaches and discusses both the advantages and limitations of agile development.







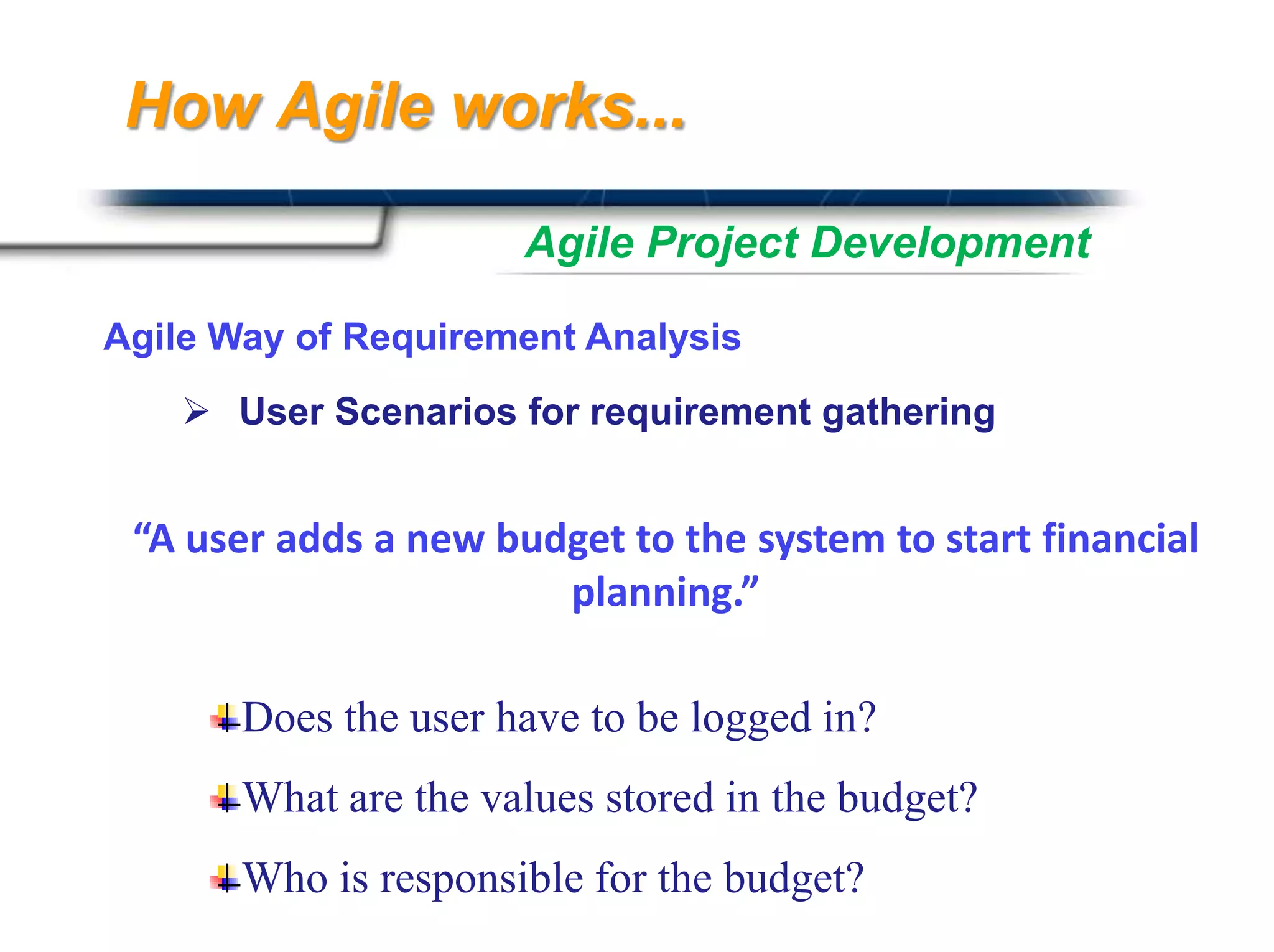
![User Scenarios Continued…
Characteristics of a User Scenario
As a [type or role of user]
I want to [perform some task]
So that I can [reach some goal]
User Scenarios Should be…
Independent
Negotiable
Valuable
Estimable
Brief
Presented By
Testable Harry Mills / PRESENTATIONPRO](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/agile-130204040650-phpapp02/75/Agile-Software-Development-Methodology-16-2048.jpg)