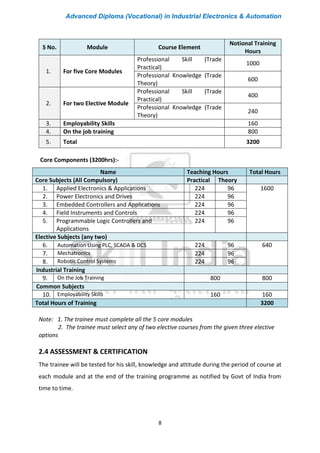
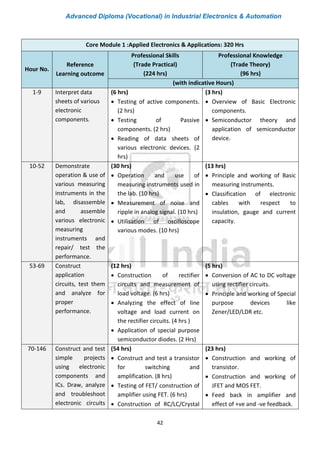
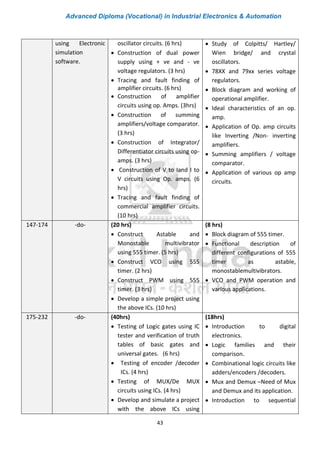
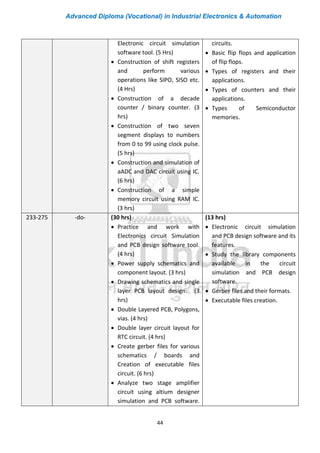
The document outlines the curriculum for an Advanced Diploma (Vocational) in Industrial Electronics & Automation. The two-year program consists of five core modules in the first year covering topics like applied electronics, power electronics, embedded controllers, field instruments and controls, and programmable logic controllers. In the second year, students can choose two elective modules from options like automation using PLC, SCADA & DCS, mechatronics, and robotic control systems. Students will also undergo 800 hours of on-the-job training in industry. The curriculum aims to develop practical skills for job roles in automation at various levels from technician to supervisor.