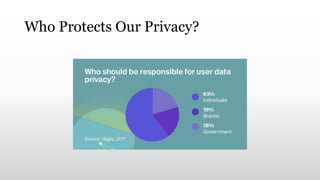
This document discusses online and digital privacy. It defines online privacy as the level of protection of personal and financial data when connected to the internet. It notes that personal information collected from devices and online activities can be shared with third parties. The document outlines three types of digital privacy: information privacy regarding how digital information is collected and used; communication privacy regarding secure communications; and individual privacy regarding control over exposed information. It provides tips for individuals and discusses the role of governments in passing laws to protect privacy and hold companies accountable for data collection and use.