This study investigates the comparative effectiveness of traditional and digital marketing strategies within the rapidly evolving e-commerce landscape. Employing a mixed-method approach, it analyzes consumer perceptions, engagement, and purchase behavior through surveys, interviews, and secondary data from diverse industries in India. Key findings reveal that digital marketing significantly influences consumer decision-making, with higher reach, cost-efficiency, and engagement levels, while traditional methods remain vital for brand trust and visibility. The results suggest that integrating both approaches into hybrid, omnichannel strategies enhances overall marketing impact. These insights underscore the importance for businesses to adopt a balanced, consumer-centric approach that leverages the strengths of both channels to optimize brand presence and foster long-term loyalty in a competitive digital environment. The study highlights the critical need for adaptive marketing models to sustain growth and relevance in the e-commerce era.
![a International Journal of Engineering, Business and Management (IJEBM)
ISSN: 2456-7817
[Vol-9, Issue-3, Jul-Sep, 2025]
Issue DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.22161/ijebm.9.3
Article Issue DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.22161/ijebm.9.3.1
Int. j. eng. bus. manag.
www.aipublications.com Page | 1
A Comparative Analysis of Traditional and Digital
Marketing Strategies in Era of E-Commerce
Umamaheswararao Gobbilla1
, Dadi Sai Kiran2
1
Associate Professor, Department Of MBA, CMR Institute of Technology, Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
orcid.org/0000-0002-4467-4600
2
Student of MBA, CMR Institute of Technology, Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
Received: 15 Jun 2025; Received in revised form: 09 Jul 2025; Accepted: 13 Jul 2025; Available online: 17 Jul 2025
©2025 The Author(s). Published by AI Publications. This is an open-access article under the CC BY license
(https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/)
Abstract— This study investigates the comparative effectiveness of traditional and digital marketing
strategies within the rapidly evolving e-commerce landscape. Employing a mixed-method approach, it
analyzes consumer perceptions, engagement, and purchase behavior through surveys, interviews, and
secondary data from diverse industries in India. Key findings reveal that digital marketing significantly
influences consumer decision-making, with higher reach, cost-efficiency, and engagement levels, while
traditional methods remain vital for brand trust and visibility. The results suggest that integrating both
approaches into hybrid, omnichannel strategies enhances overall marketing impact. These insights
underscore the importance for businesses to adopt a balanced, consumer-centric approach that leverages
the strengths of both channels to optimize brand presence and foster long-term loyalty in a competitive digital
environment. The study highlights the critical need for adaptive marketing models to sustain growth and
relevance in the e-commerce era.
Keywords— Traditional Marketing, Digital Marketing, E-Commerce, Marketing Strategies, Consumer
Behaviour, Online Advertising, Brand Engagement, Marketing Effectiveness, Customer Retention,
Marketing Channels.
I. INTRODUCTION
The landscape of marketing has undergone a dramatic
transformation in recent years, largely driven by the rapid
growth of e-commerce. As the digital world continues to
evolve, businesses are faced with the challenge of selecting
the most effective marketing strategies to engage with
consumers. Traditional marketing and digital marketing
represent two distinct approaches to this challenge.
Traditional marketing, rooted in the analog world, relies on
methods such as print media, television ads, and direct mail,
while digital marketing focuses on online platforms such as
social media, search engines, email, and websites.
The rise of e-commerce has shifted the balance towards
digital strategies, as the internet and mobile technology
have made it easier for businesses to connect with global
audiences in real time. However, despite the proliferation of
digital marketing tools, traditional marketing techniques
remain relevant in certain contexts. Understanding the
comparative strengths and weaknesses of both approaches
is critical for businesses looking to navigate the increasingly
complex marketing landscape.
This analysis delves into the key features, advantages, and
challenges of traditional and digital marketing strategies in
the context of the e-commerce era. The objective is to
provide a comprehensive understanding of how these
strategies work in tandem, how they can be integrated, and
how businesses can use them to stay competitive in an
evolving market environment.
The Evolution of Marketing in the E-commerce Era:
E-commerce, which began as a niche market in the 1990s,
has now become a dominant force in the global economy.
According to data from Statista, global retail e-commerce
sales amounted to approximately $4.9 trillion in 2021 and
are projected to continue growing in the coming years. This
rapid growth has led to a shift in how businesses market
their products and services. The digital age has introduced](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1ijebm-may202584-acomparative-250717070703-e44ae529/75/A-Comparative-Analysis-of-Traditional-and-Digital-Marketing-Strategies-in-Era-of-E-Commerce-1-2048.jpg)








![Gobbilla and Kiran A Comparative Analysis of Traditional and Digital Marketing Strategies in Era of E-Commerce
Int. j. eng. bus. manag.
www.aipublications.com Page | 18
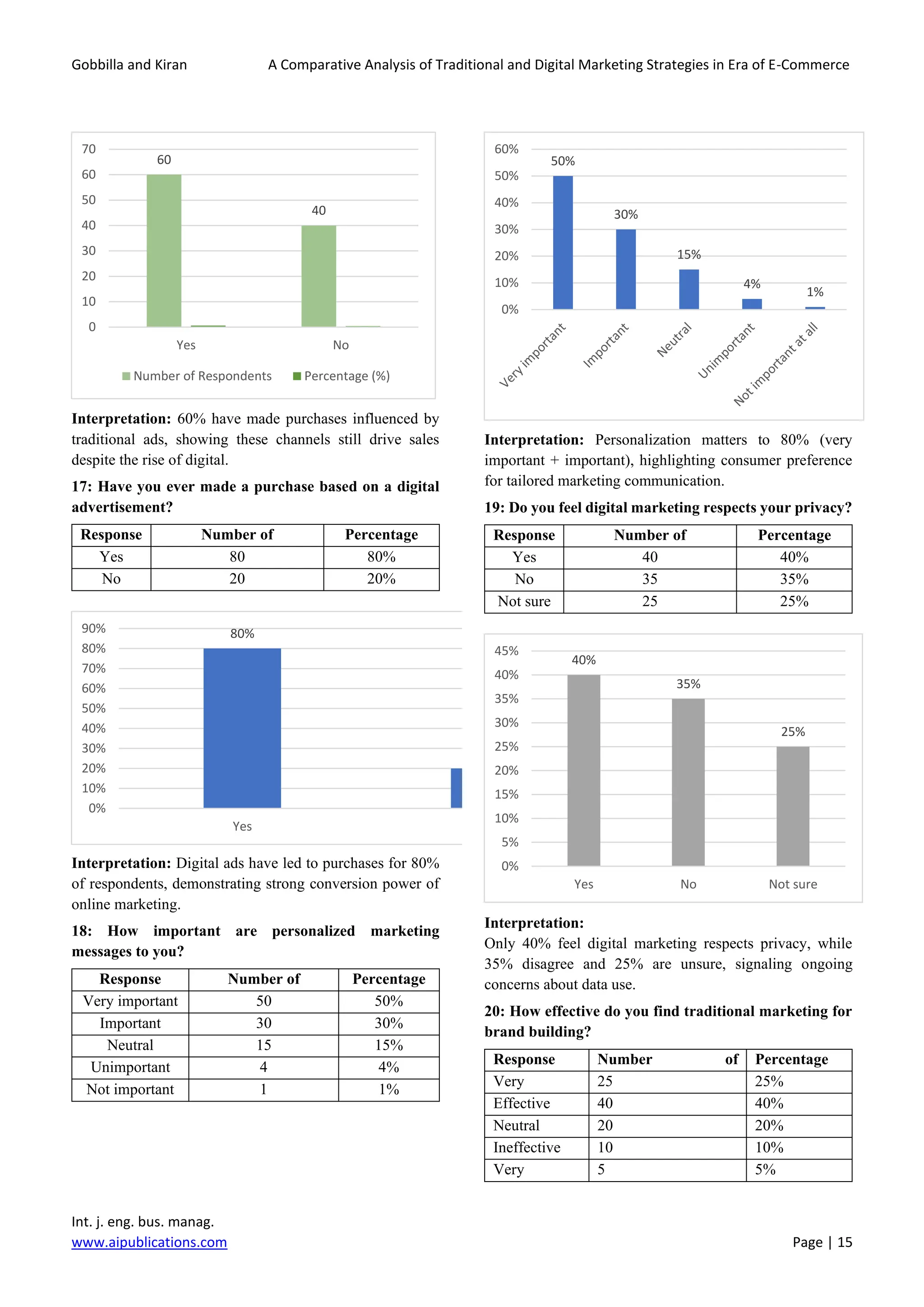
With 35% of respondents expressing concerns about
privacy, businesses should make an effort to be more
transparent about their data collection practices. Clearly
communicating how personal data is being used and
offering customers control over their privacy settings can
alleviate concerns. Providing customers with the option to
opt-in or opt-out of personalized marketing could also build
trust and encourage participation in digital campaigns.
As 80% of respondents believe digital marketing is more
cost-effective for consumers, businesses can further
emphasize the affordability of their products or services
through digital platforms. Offering discounts, time-
sensitive deals, and flash sales promoted through email and
social media can be a powerful tool in driving conversions.
Also, leveraging cost-effective digital advertising platforms
such as Google Ads, Facebook Ads, and Instagram Ads can
ensure businesses reach their target audience at a lower cost.
Considering the increasing reliance on mobile devices for
browsing, shopping, and social media interaction,
businesses should ensure that their digital marketing
campaigns and e-commerce platforms are optimized for
mobile. This includes mobile-friendly websites, fast-
loading pages, and easy-to-navigate interfaces.
Additionally, mobile-specific ads and push notifications can
further engage users and drive conversions.
Despite the dominance of digital marketing, 65% of
respondents find traditional marketing methods effective
for brand building. To strengthen the impact of traditional
marketing, companies could consider combining these
channels with digital campaigns. For example, running a
traditional TV or print campaign alongside digital ads can
create a cohesive brand experience across multiple
platforms. Additionally, offering incentives like QR codes
in traditional ads to direct customers to online stores or
social media pages can help bridge the gap between the two
methods.
IX. CONCLUSION
The comparative analysis of traditional and digital
marketing strategies in the context of e-commerce reveals
significant insights into consumer behavior, preferences,
and the effectiveness of various marketing channels. In
today’s digital era, it is clear that digital marketing holds a
dominant position in influencing consumer decisions,
driving engagement, and offering cost-effective solutions
for businesses. A substantial majority of respondents favor
digital platforms for receiving promotional content,
engaging with brands, and making purchases. The high trust
placed in digital marketing, coupled with its ease of use and
convenience for product comparison, demonstrates its
power in shaping modern consumer behaviors.
However, traditional marketing still plays a crucial role,
particularly in brand visibility and trust-building, with a
significant portion of respondents acknowledging the
effectiveness of traditional channels in these areas. The
continued relevance of traditional media, such as TV, radio,
and print, indicates that businesses should not completely
abandon these methods, but rather integrate them with
digital strategies for a more comprehensive approach.
Furthermore, consumers' growing concerns about privacy
in digital marketing highlight the need for businesses to
adopt transparent data practices and ensure respect for user
privacy. Personalization and tailored messaging also stand
out as essential components of a successful marketing
strategy, as consumers are increasingly looking for relevant
and customized experiences.
Ultimately, the most successful marketing strategies in the
era of e-commerce will be those that seamlessly combine
the strengths of both traditional and digital methods. A
hybrid, omnichannel approach will enable brands to reach a
wider audience, enhance customer trust, and foster long-
term relationships with consumers. Businesses that can
effectively navigate this dual approach—leveraging
digital’s flexibility and reach while maintaining traditional
marketing’s credibility and broad appeal—will be best
positioned to thrive in the competitive landscape of modern
e-commerce.
REFERENCES
[1] Kotler, P., & Armstrong, G. (2017). Principles of
Marketing (17th ed.). Pearson.
[2] Chaffey, D., & Ellis-Chadwick, F. (2019). Digital
Marketing: Strategy, Implementation, and Practice
(7th ed.). Pearson.
[3] Ryan, D. (2016). Understanding Digital Marketing:
Marketing Strategies for Engaging the Digital
Generation (3rd ed.). Kogan Page.
[4] Lamb, C. W., Hair, J. F., & McDaniel, C. (2018).
MKTG: Principles of Marketing (12th ed.). Cengage
Learning.
[5] Smith, P. R., & Zook, Z. (2011). "Marketing
Communications: Integrating Offline and Online with
Social Media." Journal of Marketing Communications,
17(2), 133-148.
[6] Chaffey, D. (2015). "Digital Marketing: Strategy,
Implementation, and Practice." Journal of Strategic
Marketing, 23(6), 509-526.
[7] Gartner, W. B. (2015). "The Changing Face of
Marketing." International Journal of Marketing
Studies, 7(3), 89-103.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1ijebm-may202584-acomparative-250717070703-e44ae529/75/A-Comparative-Analysis-of-Traditional-and-Digital-Marketing-Strategies-in-Era-of-E-Commerce-18-2048.jpg)
![Gobbilla and Kiran A Comparative Analysis of Traditional and Digital Marketing Strategies in Era of E-Commerce
Int. j. eng. bus. manag.
www.aipublications.com Page | 19
[8] Leeflang, P. S. H., Verhoef, P. C., Dahlström, P., &
Freundt, T. (2014). "Challenges and Solutions for
Marketing in a Digital Era." European Journal of
Marketing, 48(7/8), 1354-1376.
[9] Hutter, K., Hautz, J., & Füller, J. (2013).
"Advertising in Social Media: A Comparative Study of
Facebook, Twitter, and YouTube." Journal of
Advertising, 42(2), 180-198.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1ijebm-may202584-acomparative-250717070703-e44ae529/75/A-Comparative-Analysis-of-Traditional-and-Digital-Marketing-Strategies-in-Era-of-E-Commerce-19-2048.jpg)