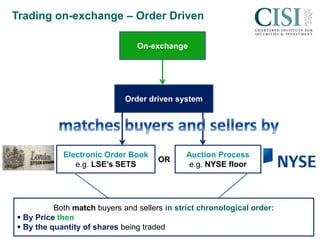
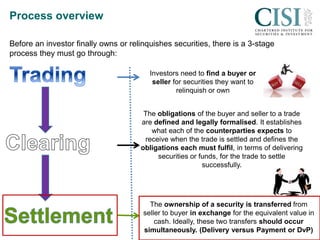
Before a trade is completed, there is a three stage process: 1) finding a buyer or seller, 2) legally formalizing the trade obligations, 3) transferring ownership from seller to buyer in exchange for cash. Ideally these last two stages occur simultaneously. Trades can take place on or off an exchange, with on-exchange utilizing either quote-driven or order-driven systems like the London Stock Exchange's SETS platform. Ownership of shares is evidenced through registered shares on a company's share register or historically through bearer shares physically held by the owner. Settlement of registered shares now typically occurs electronically through CREST, while bearer shares may take longer to settle with paperwork.