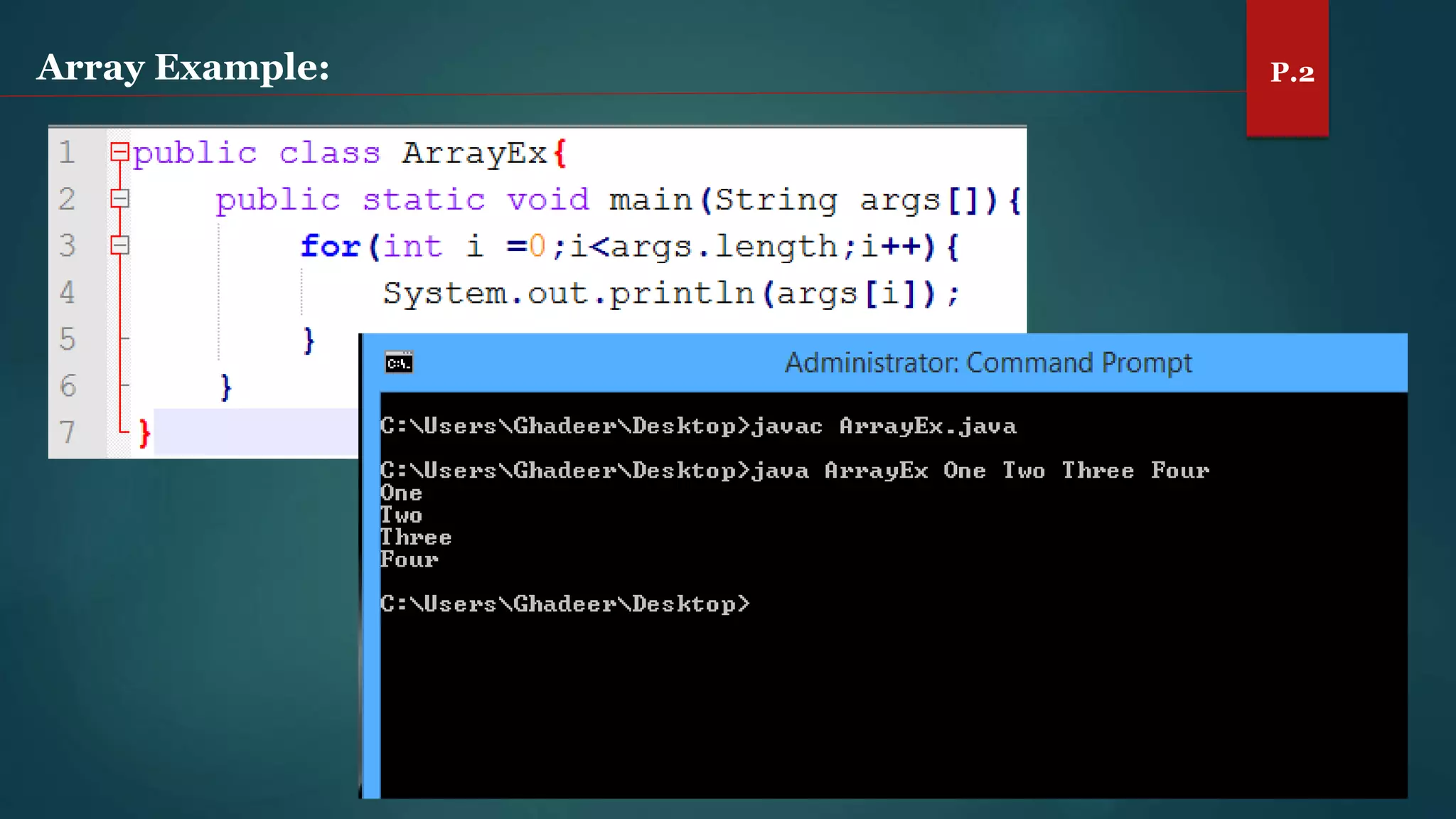
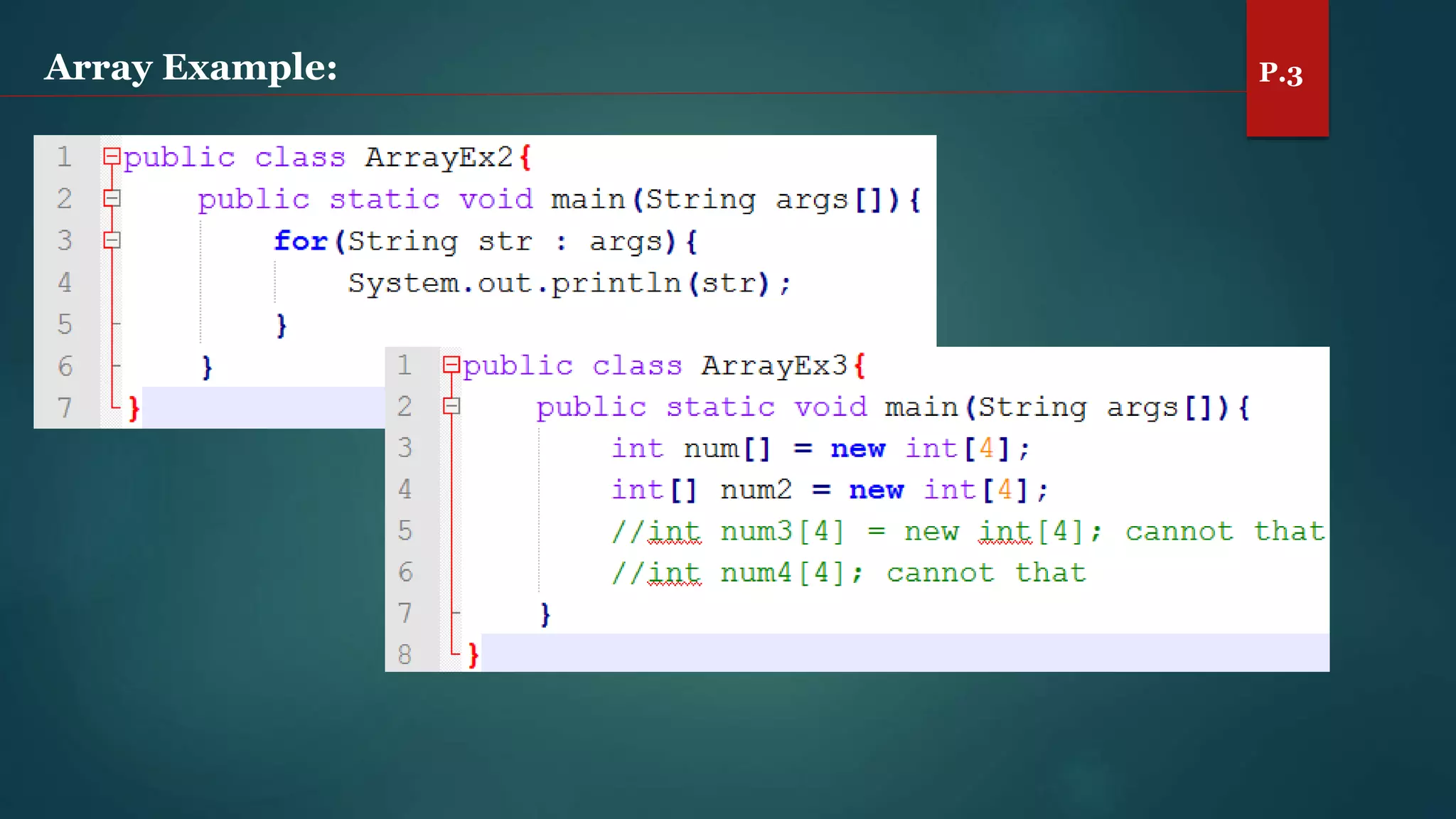
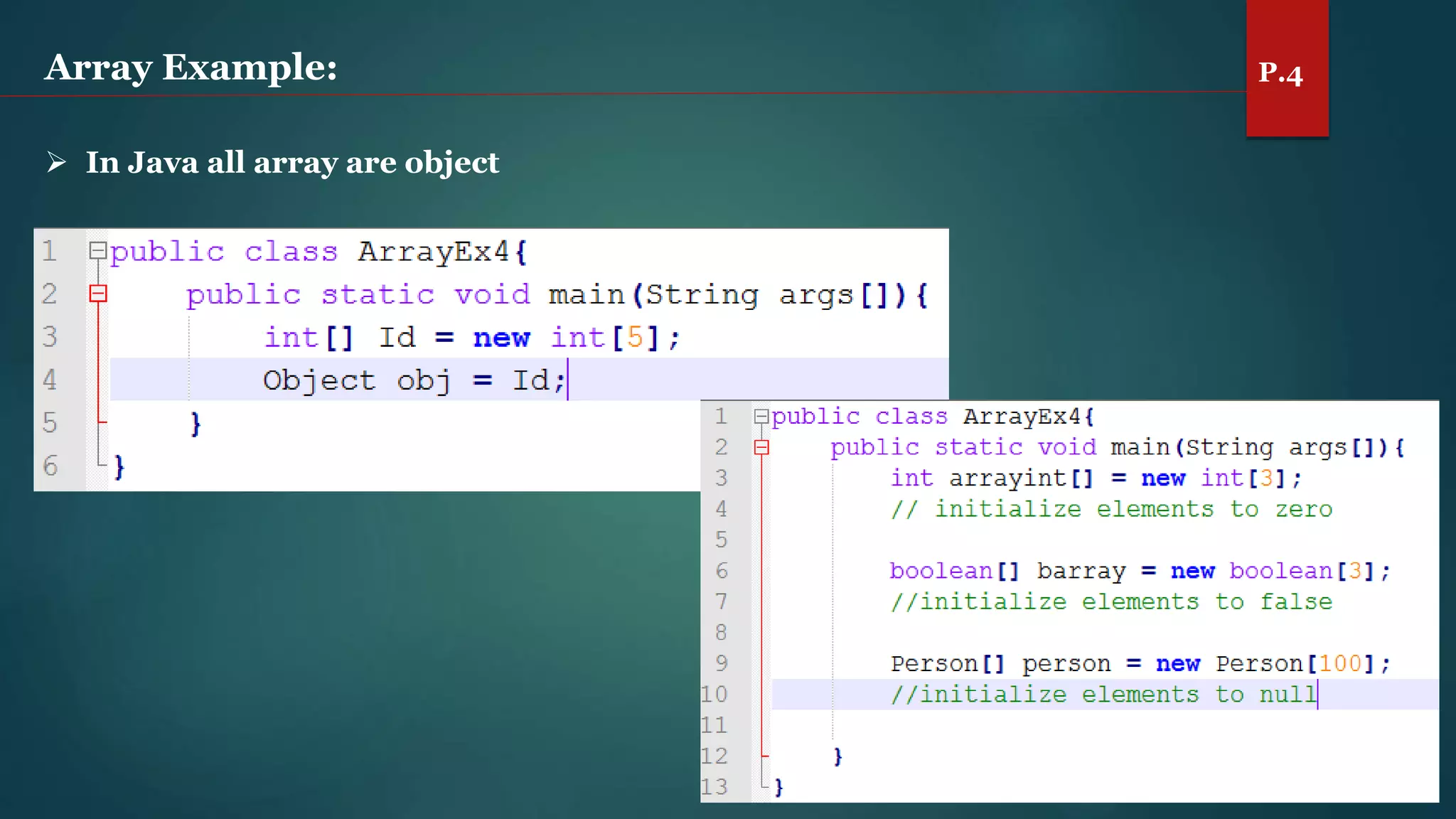
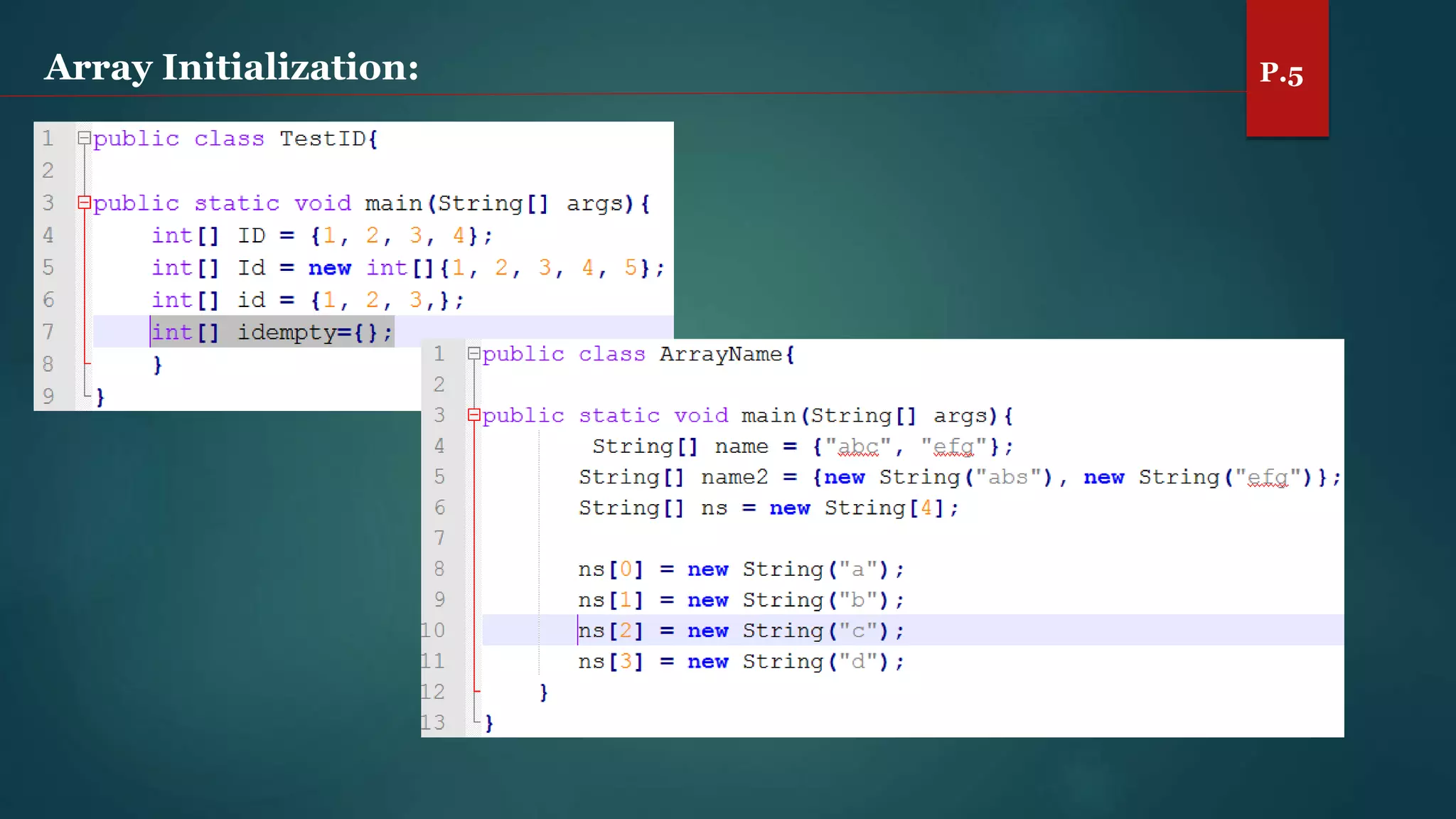
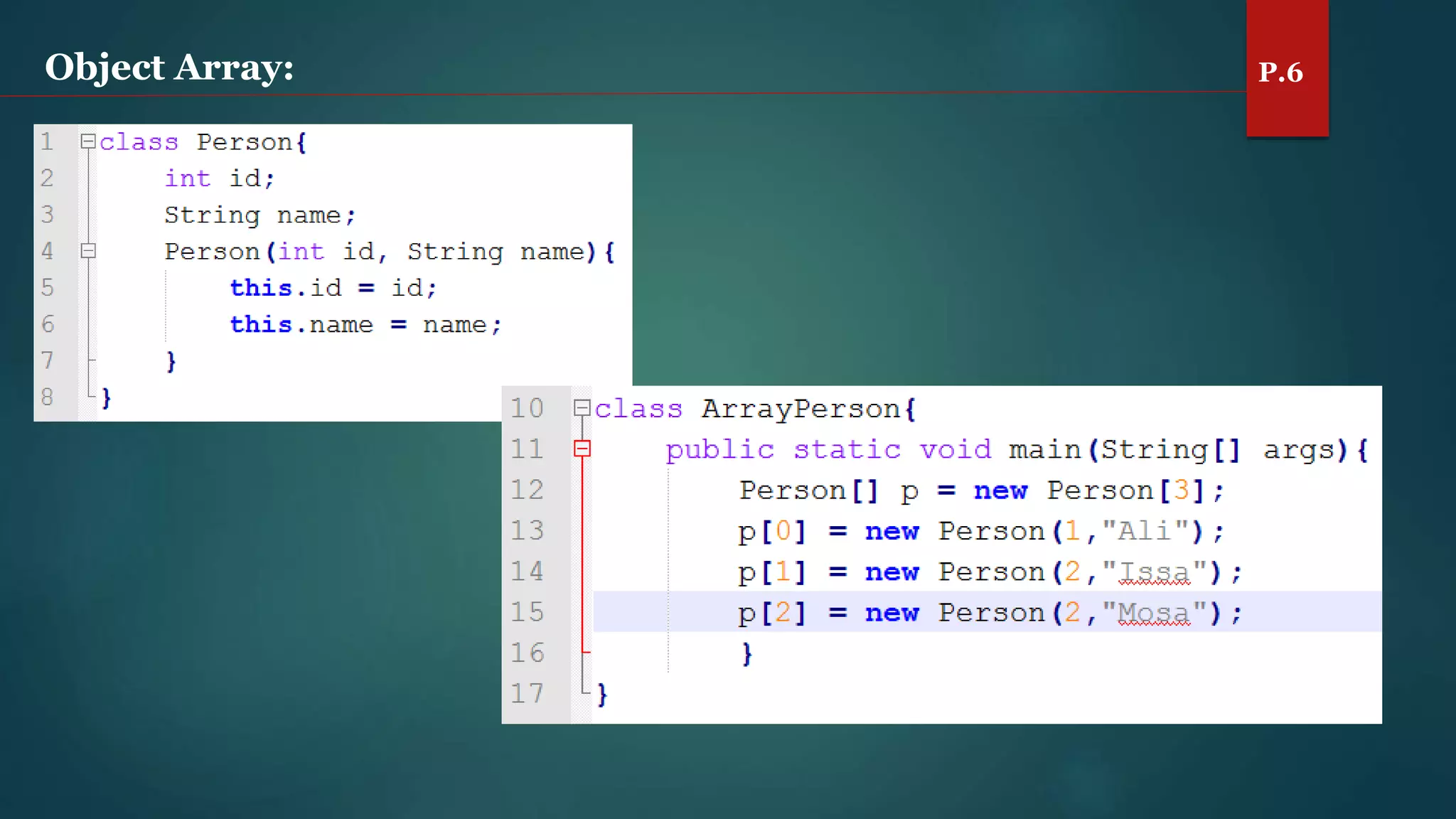
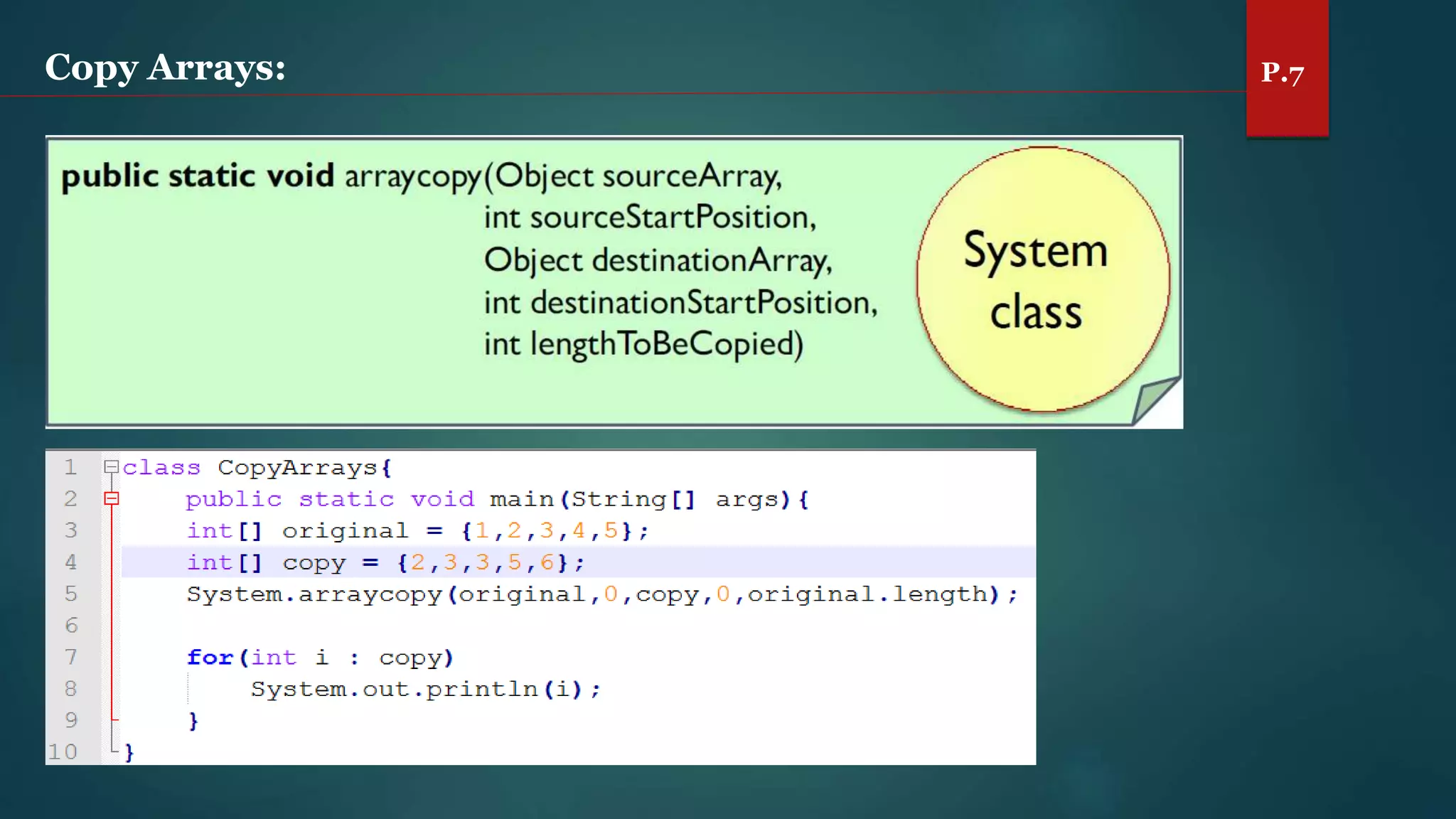
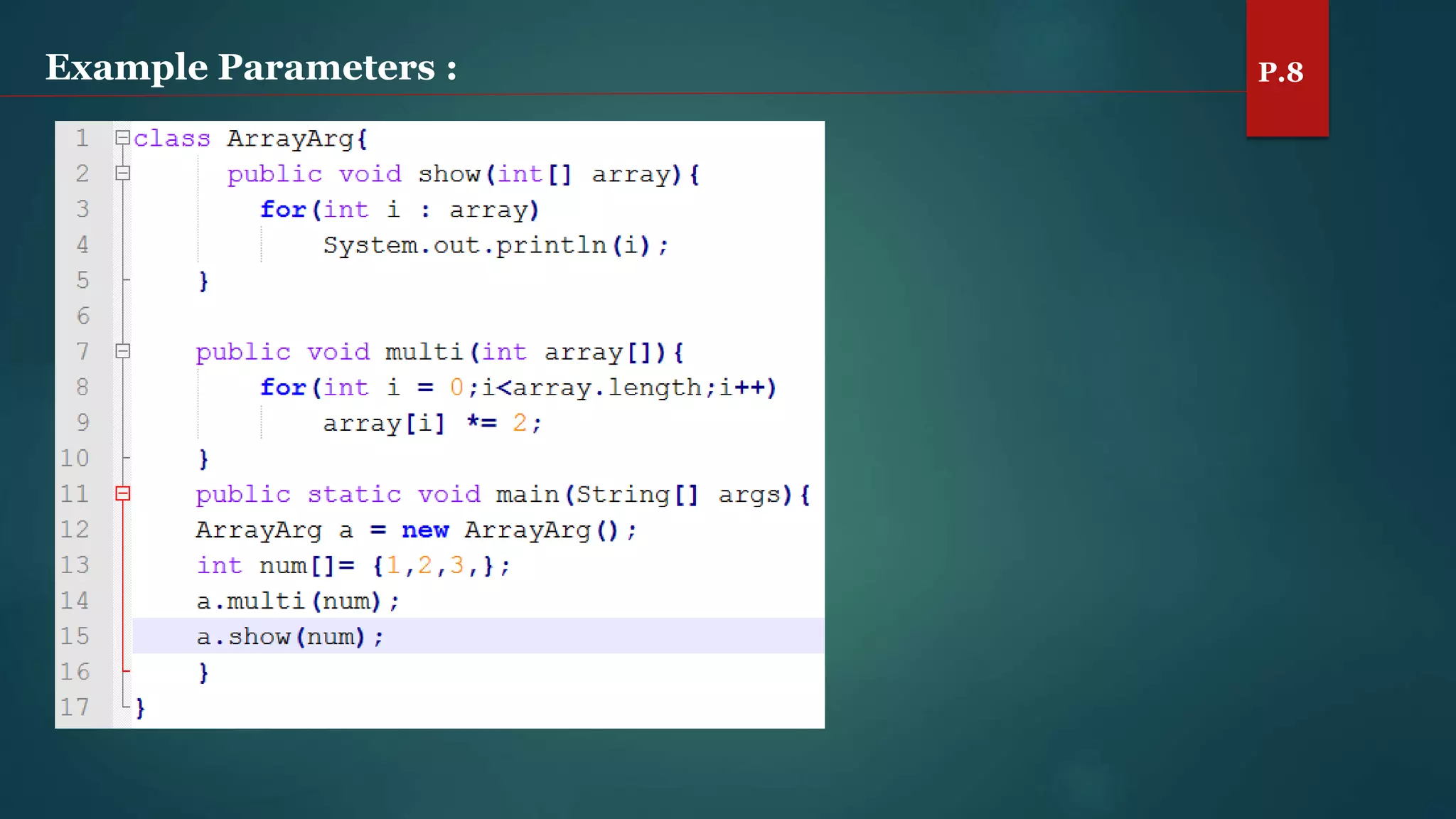
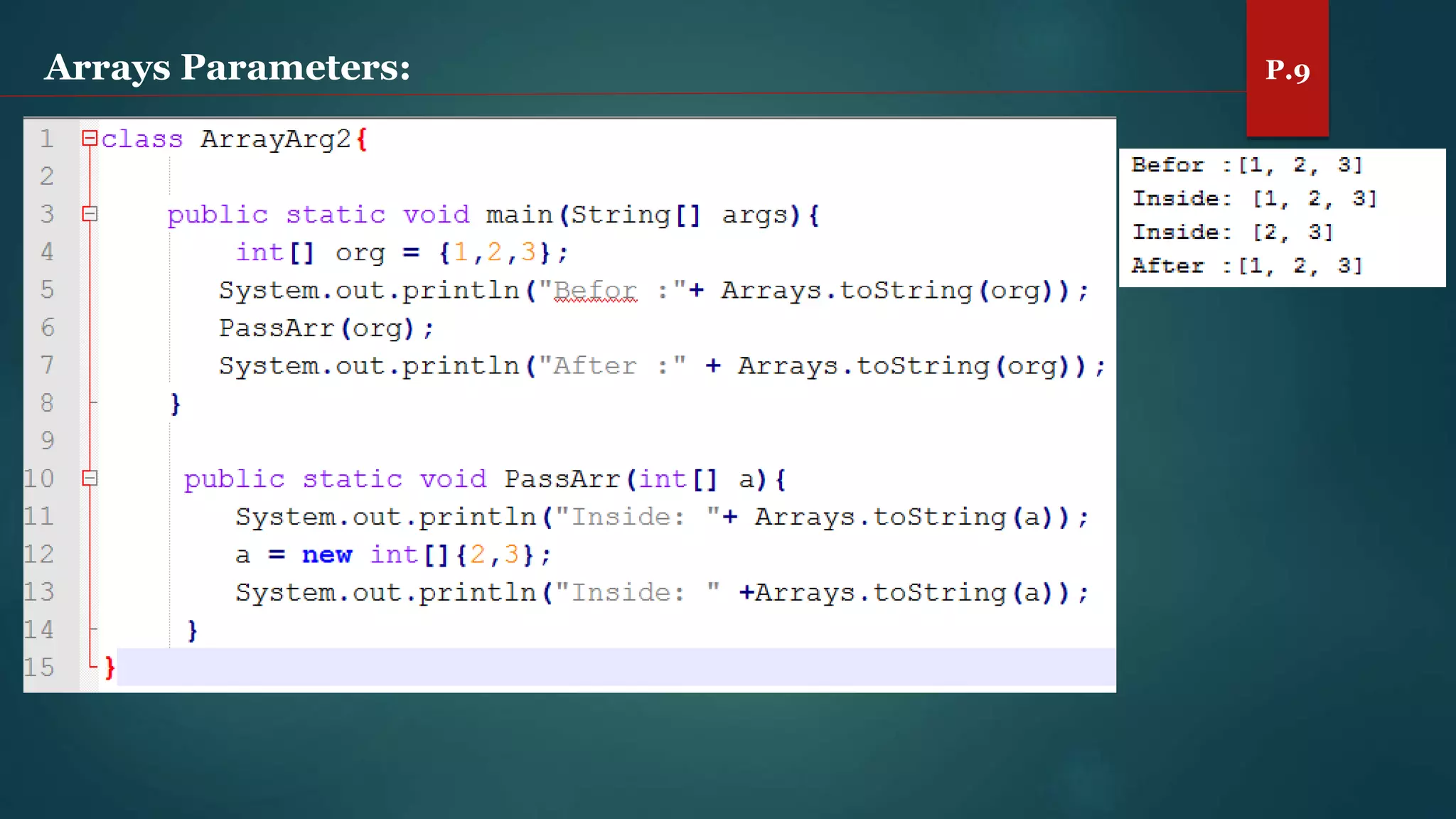
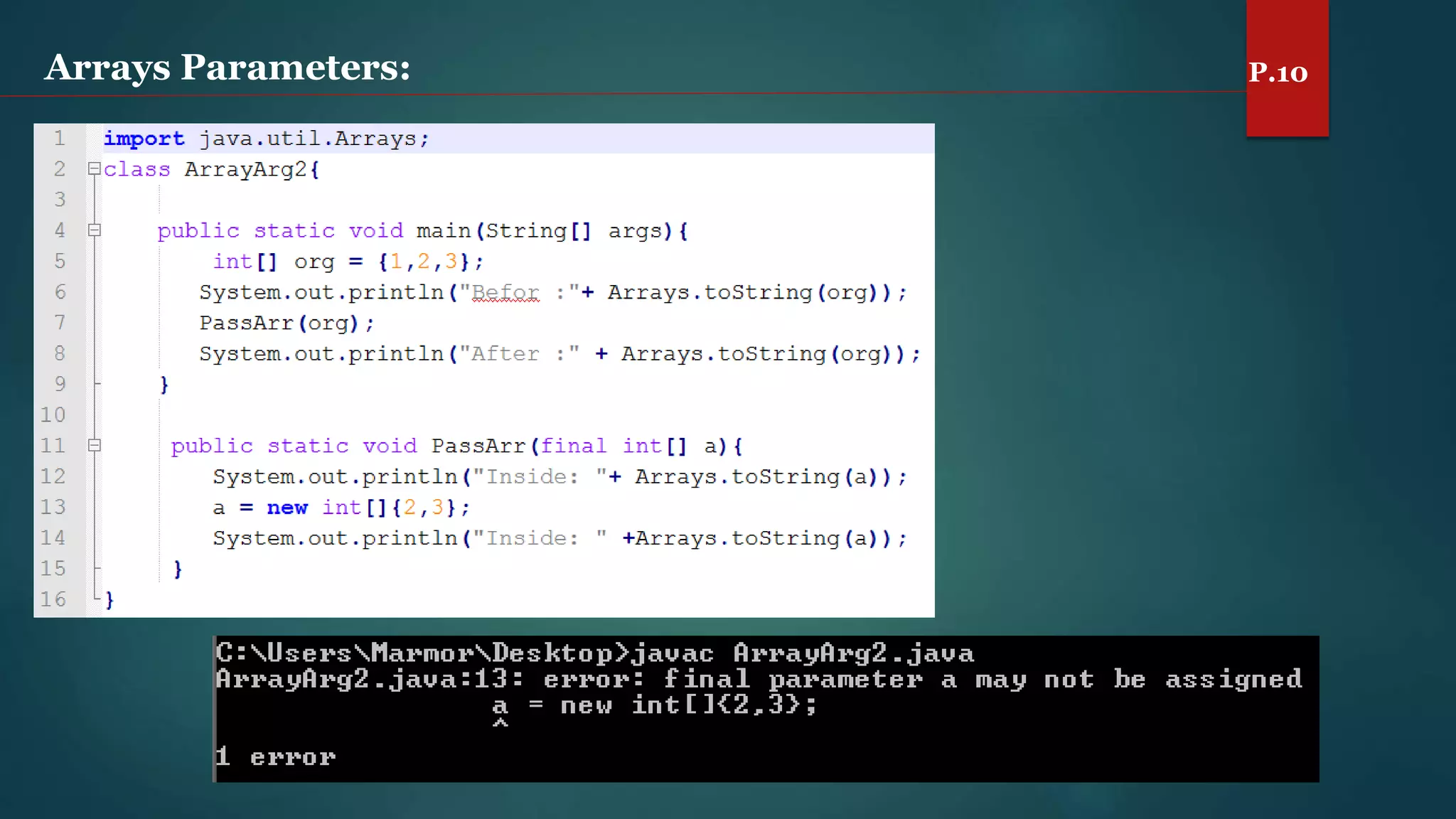
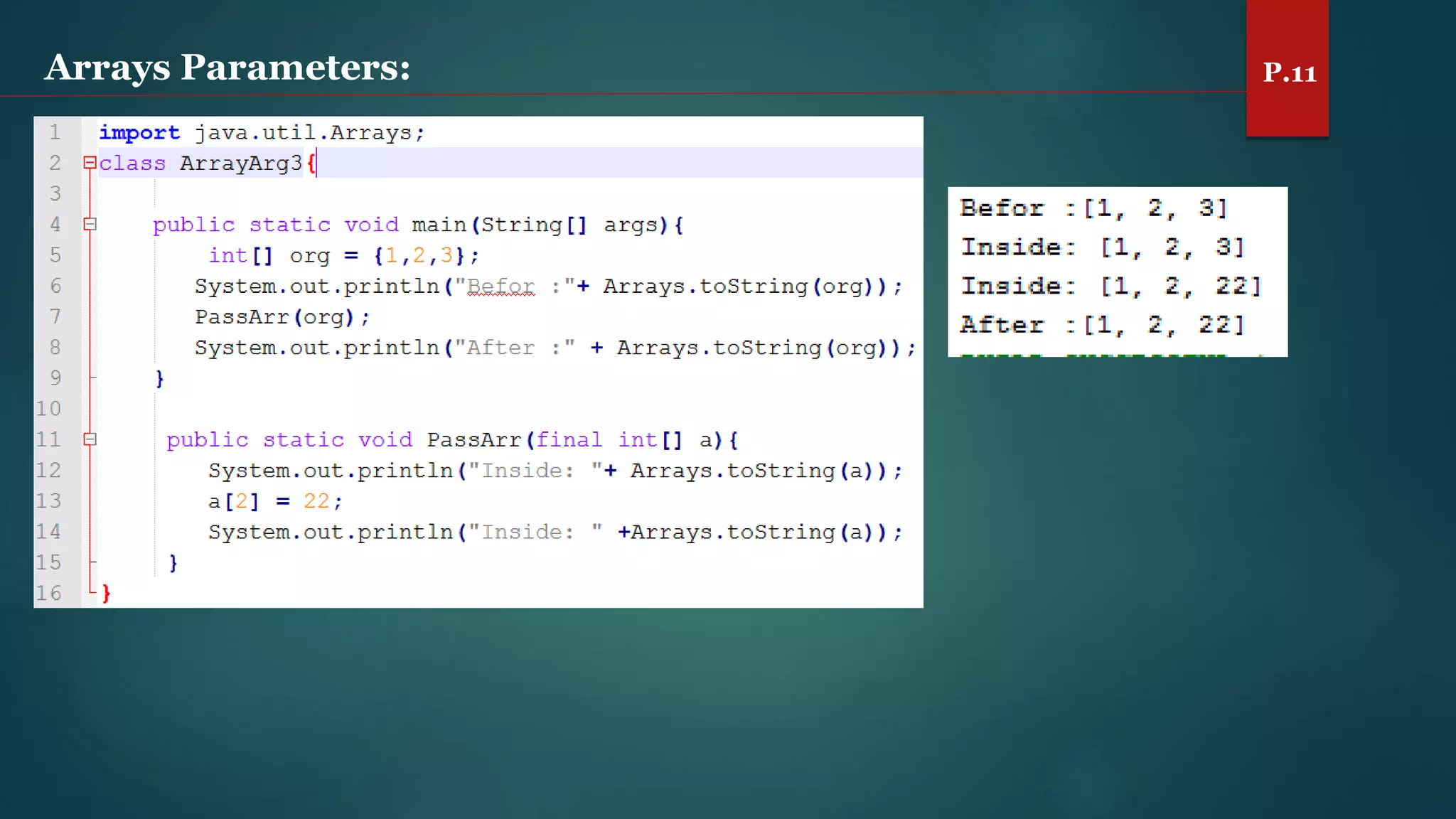
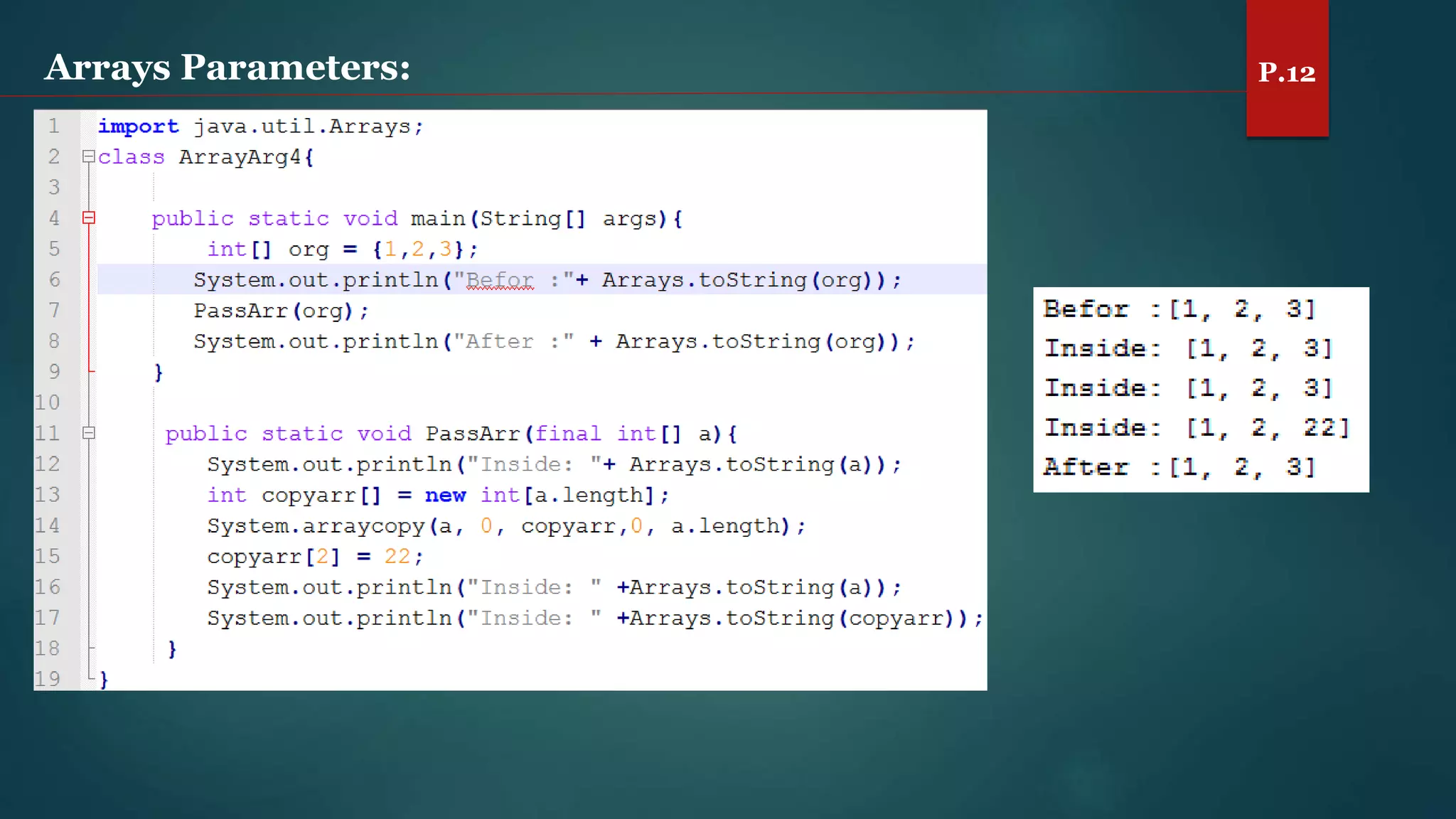
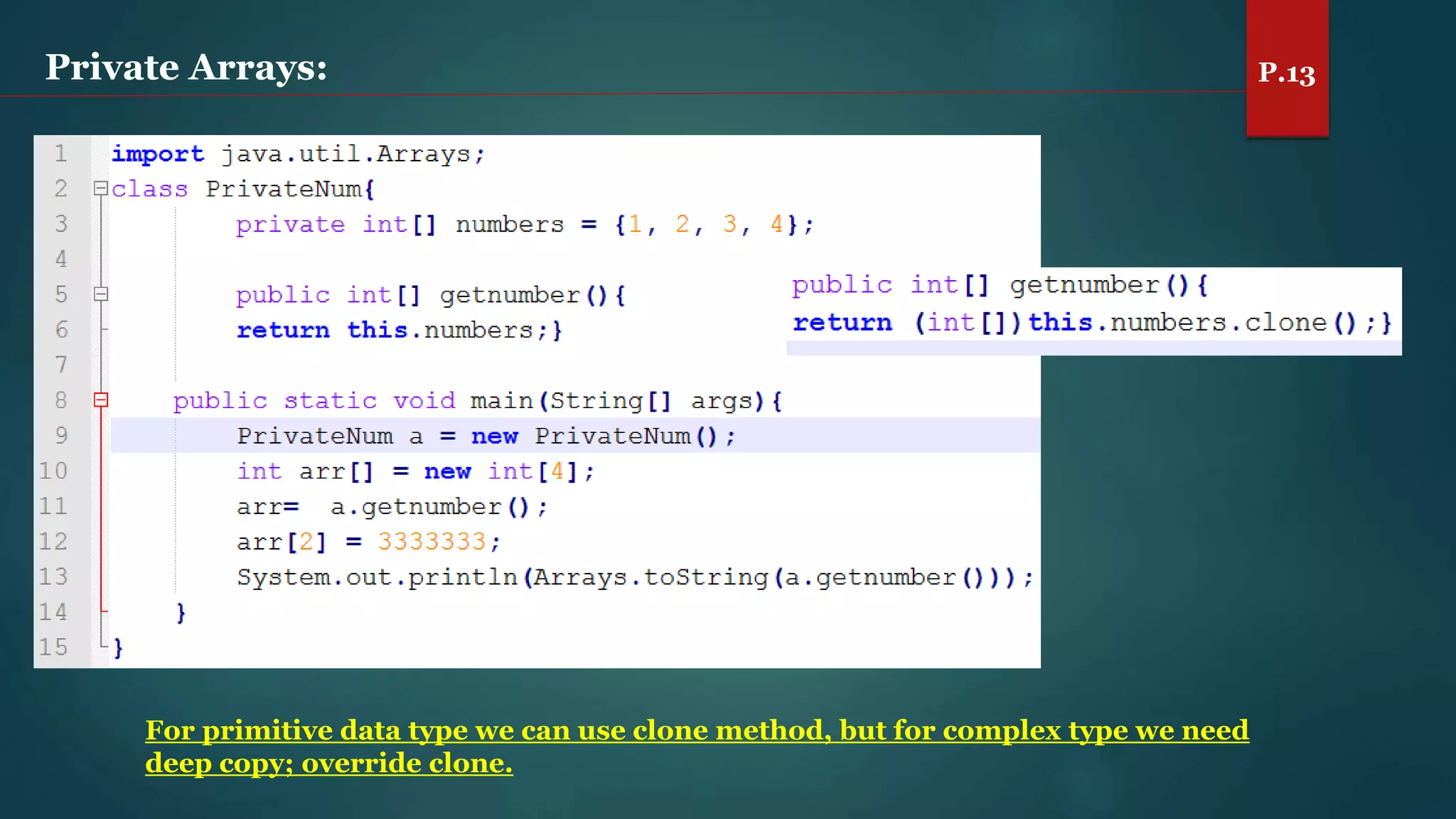
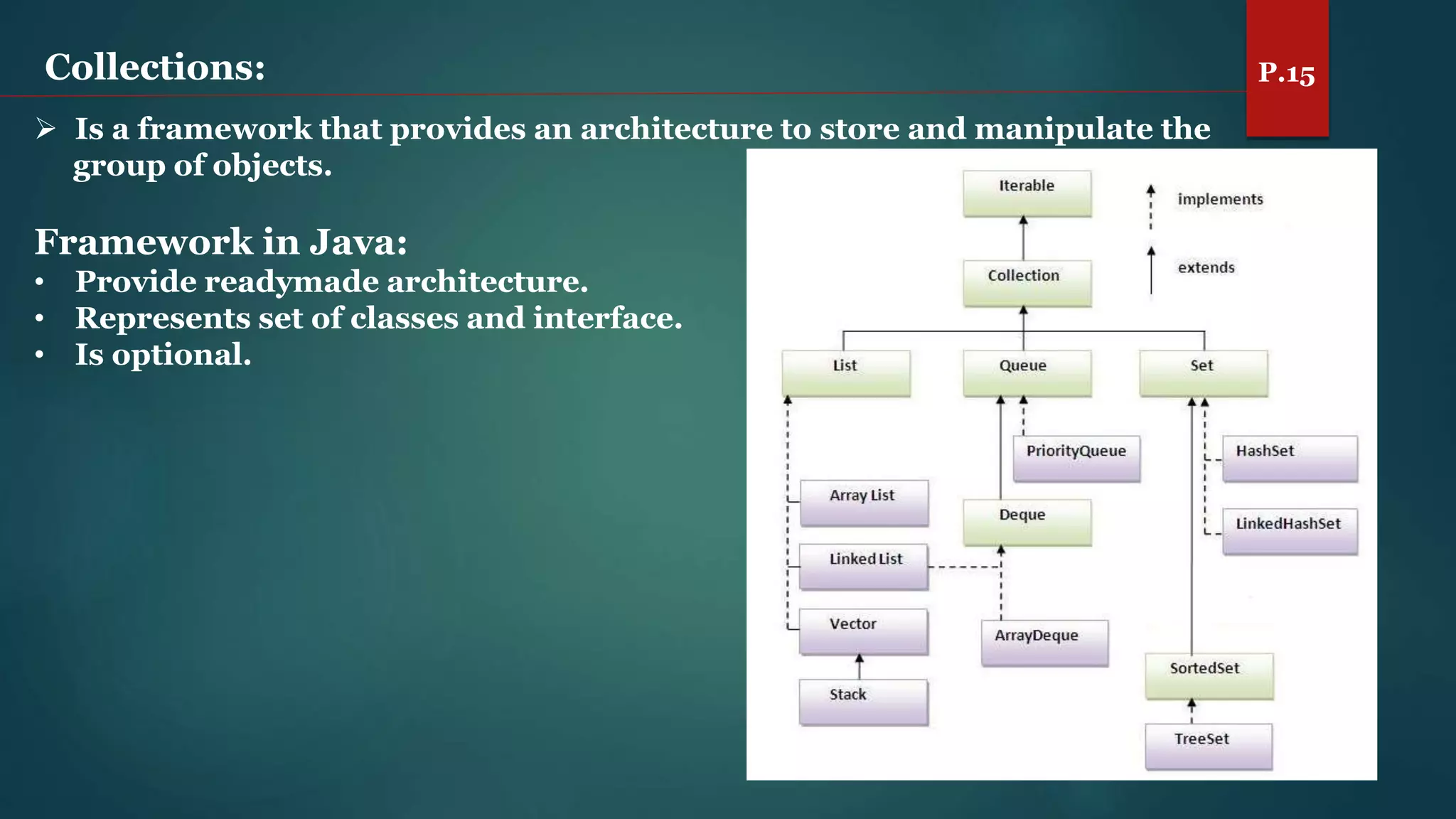
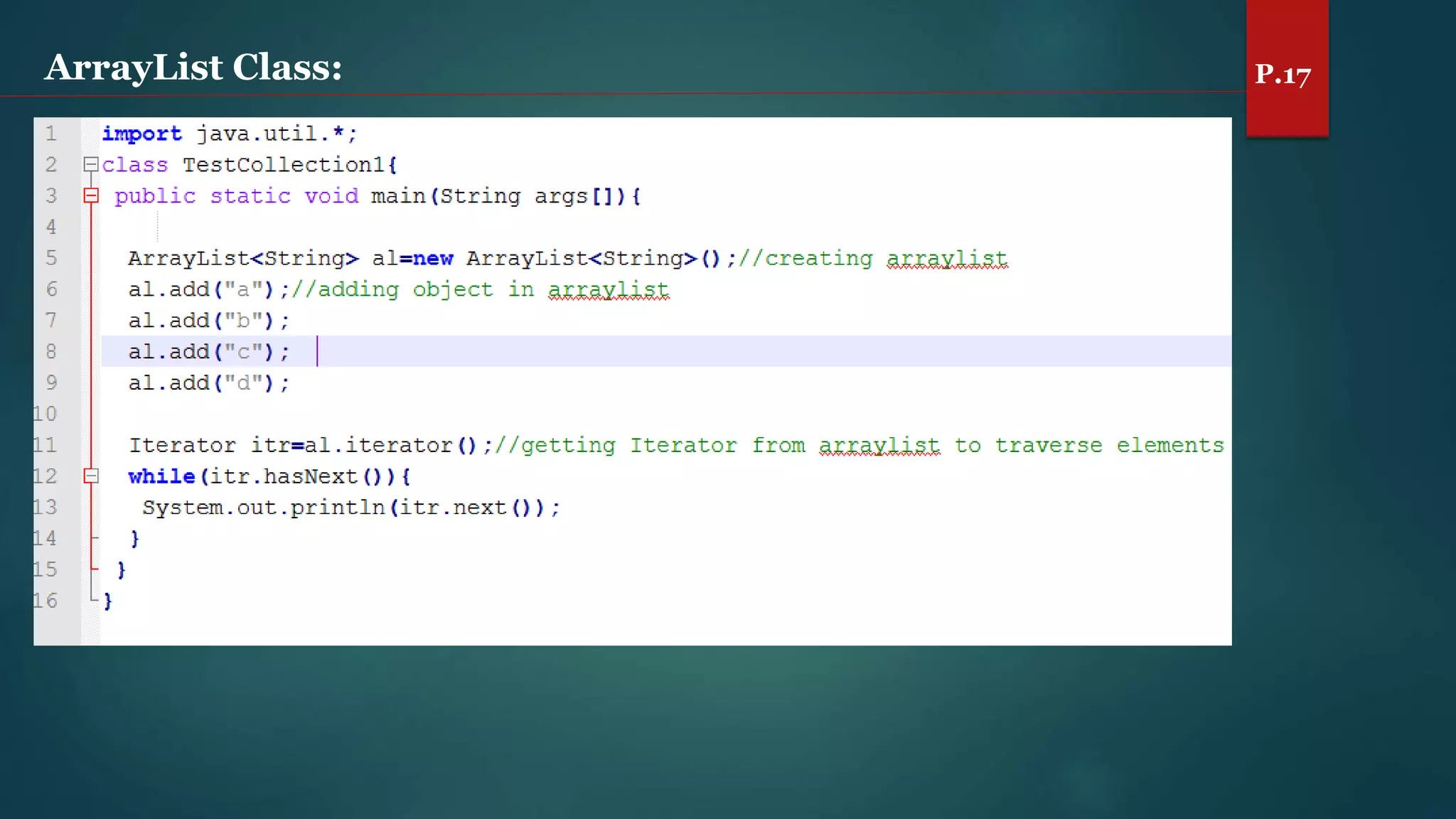
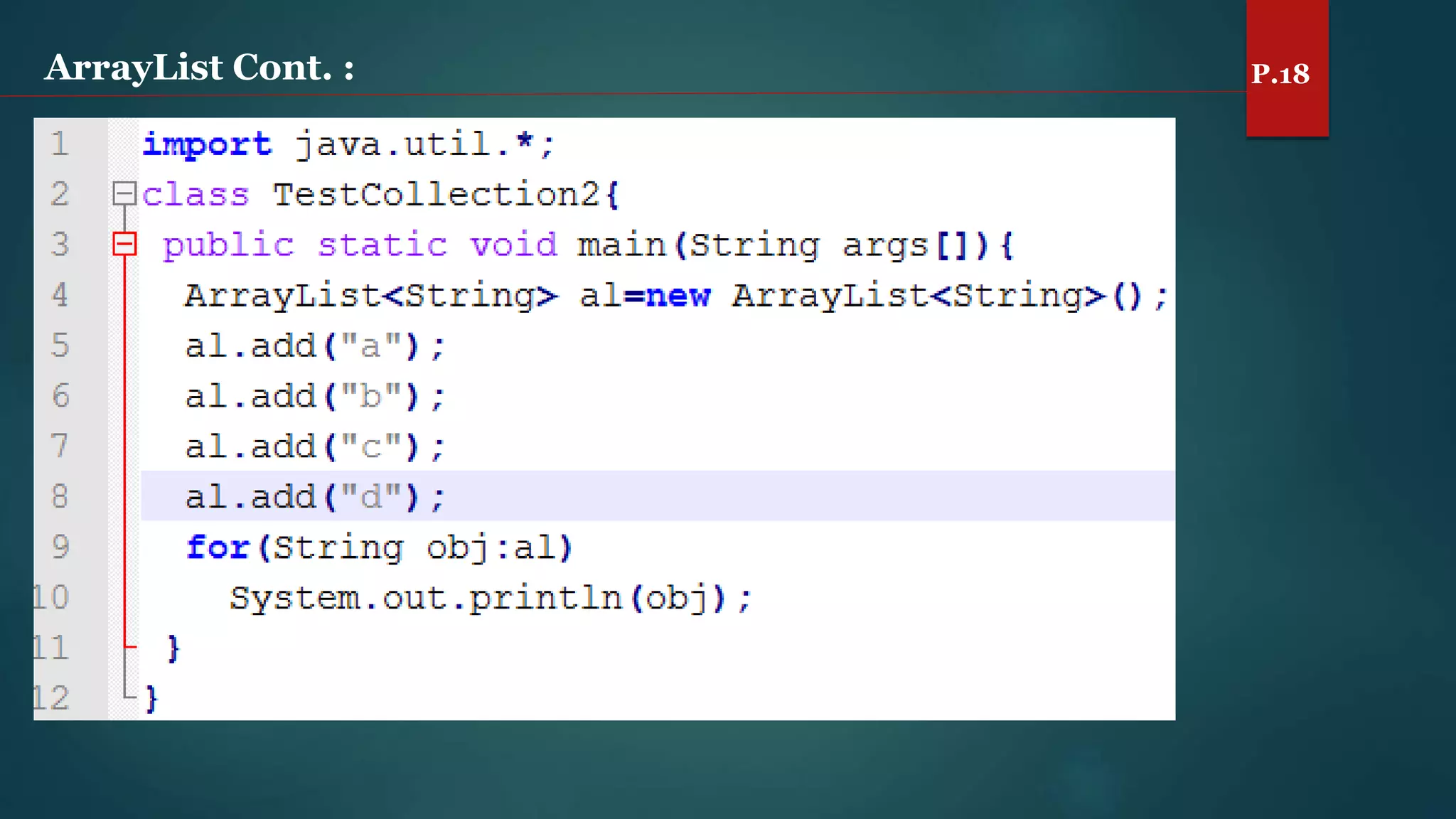
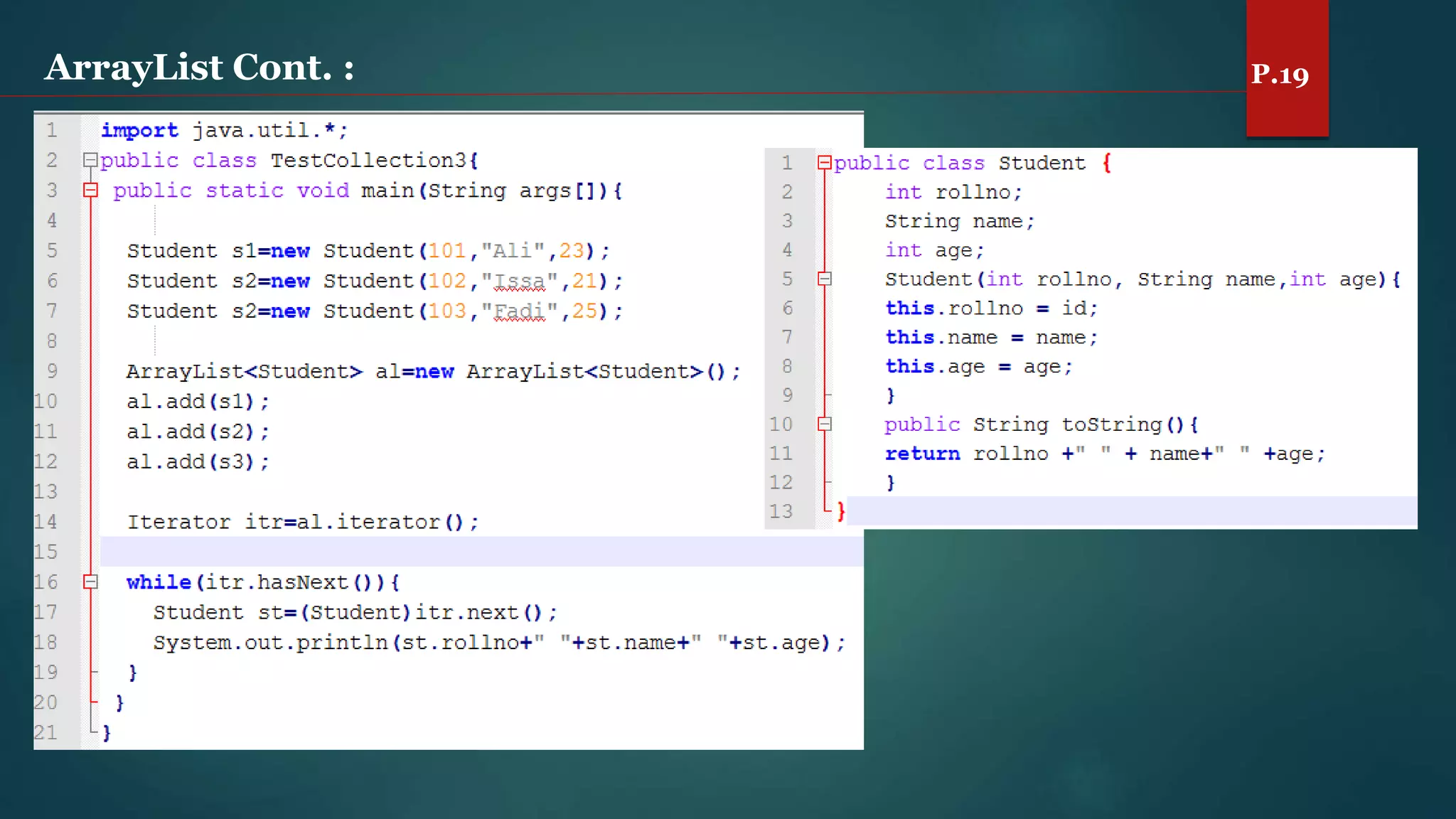
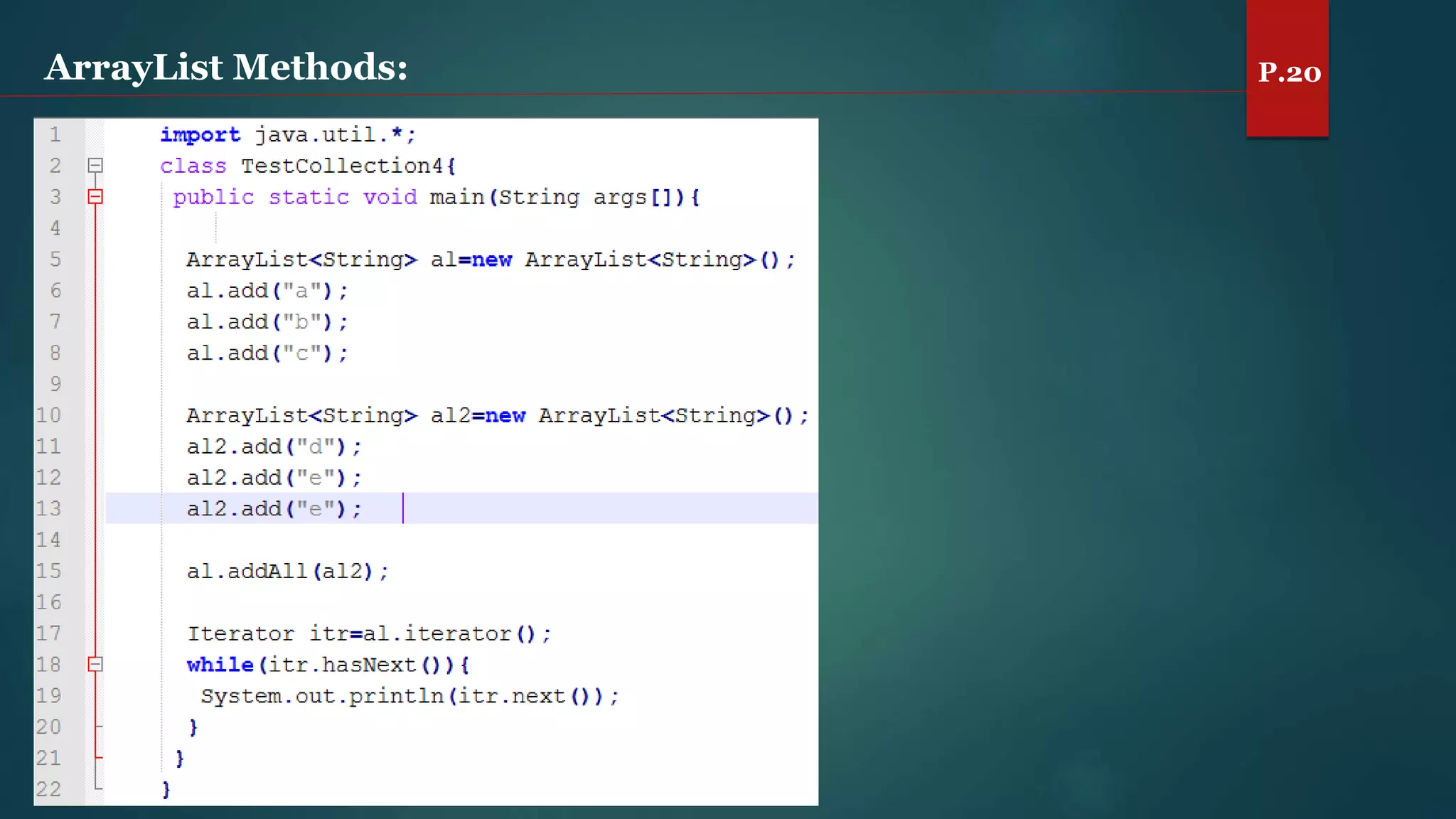
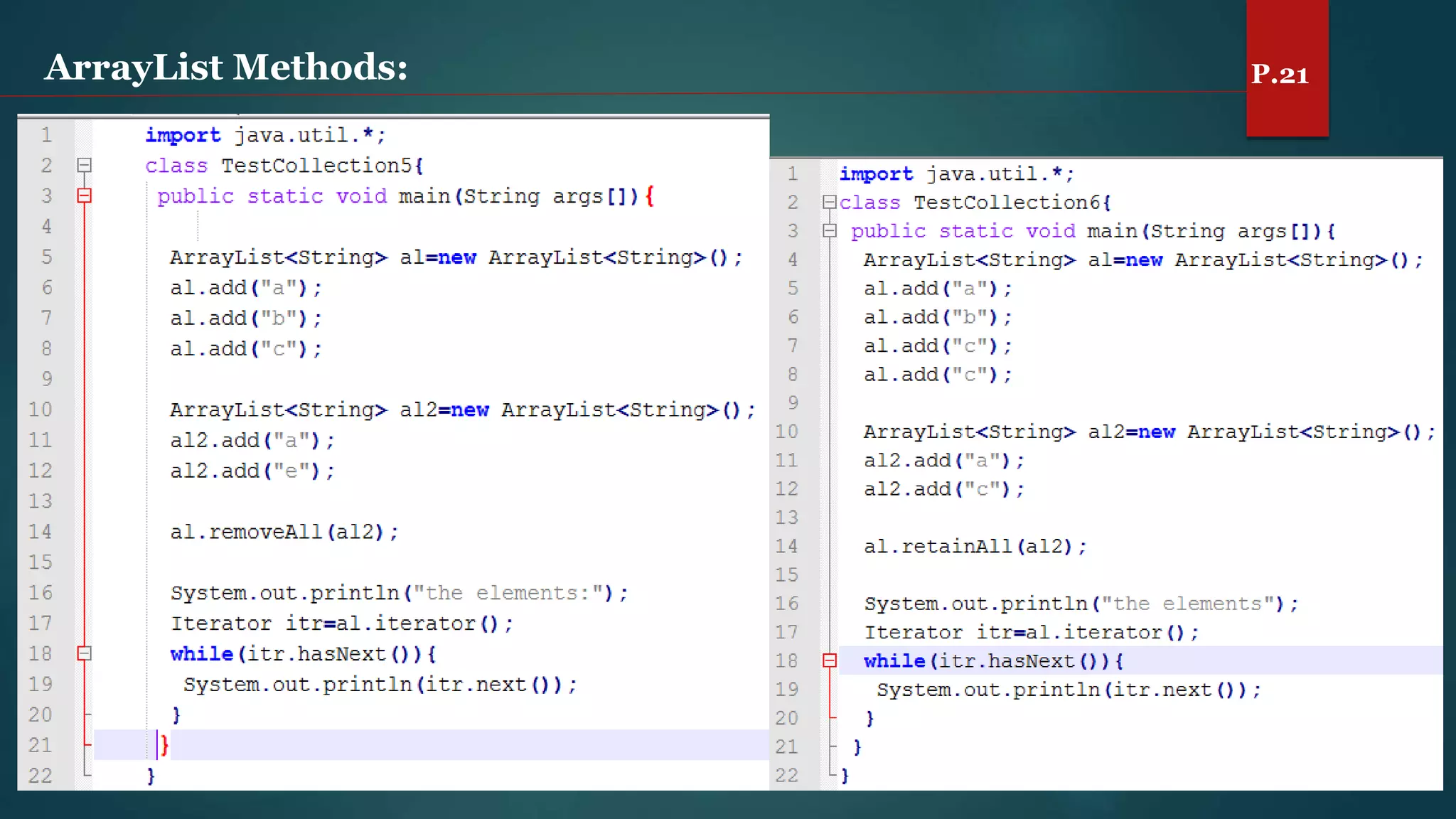
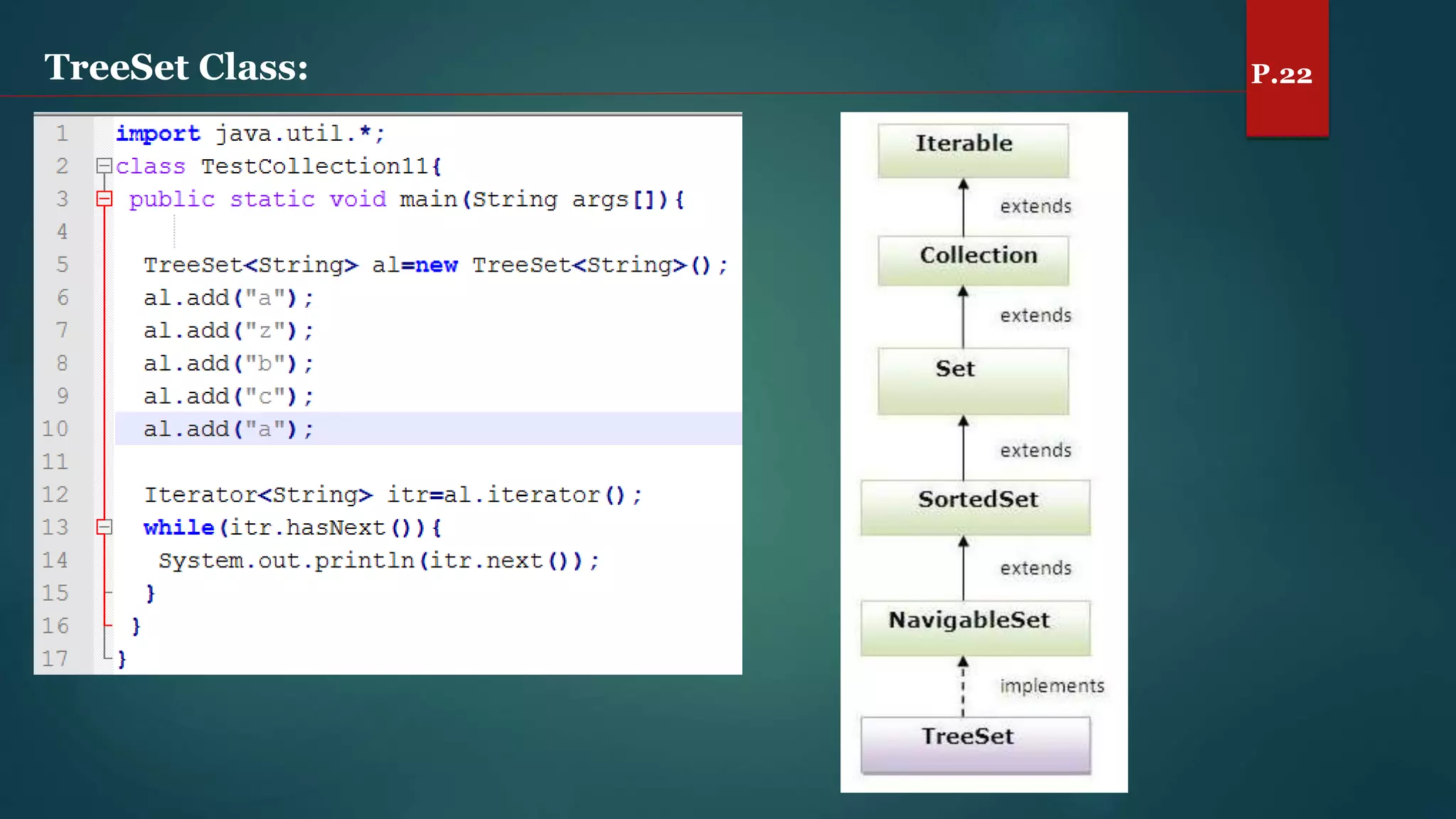
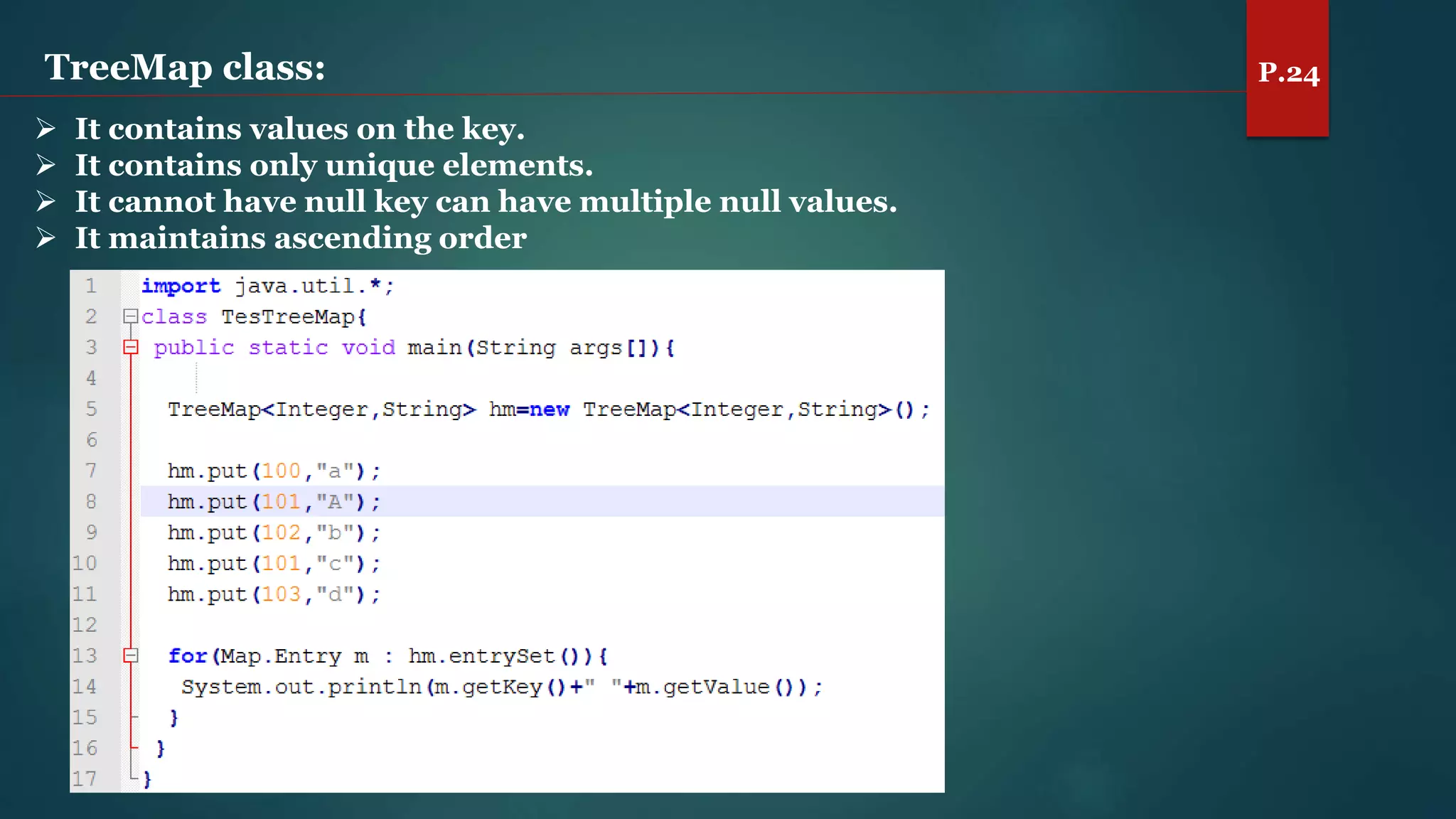
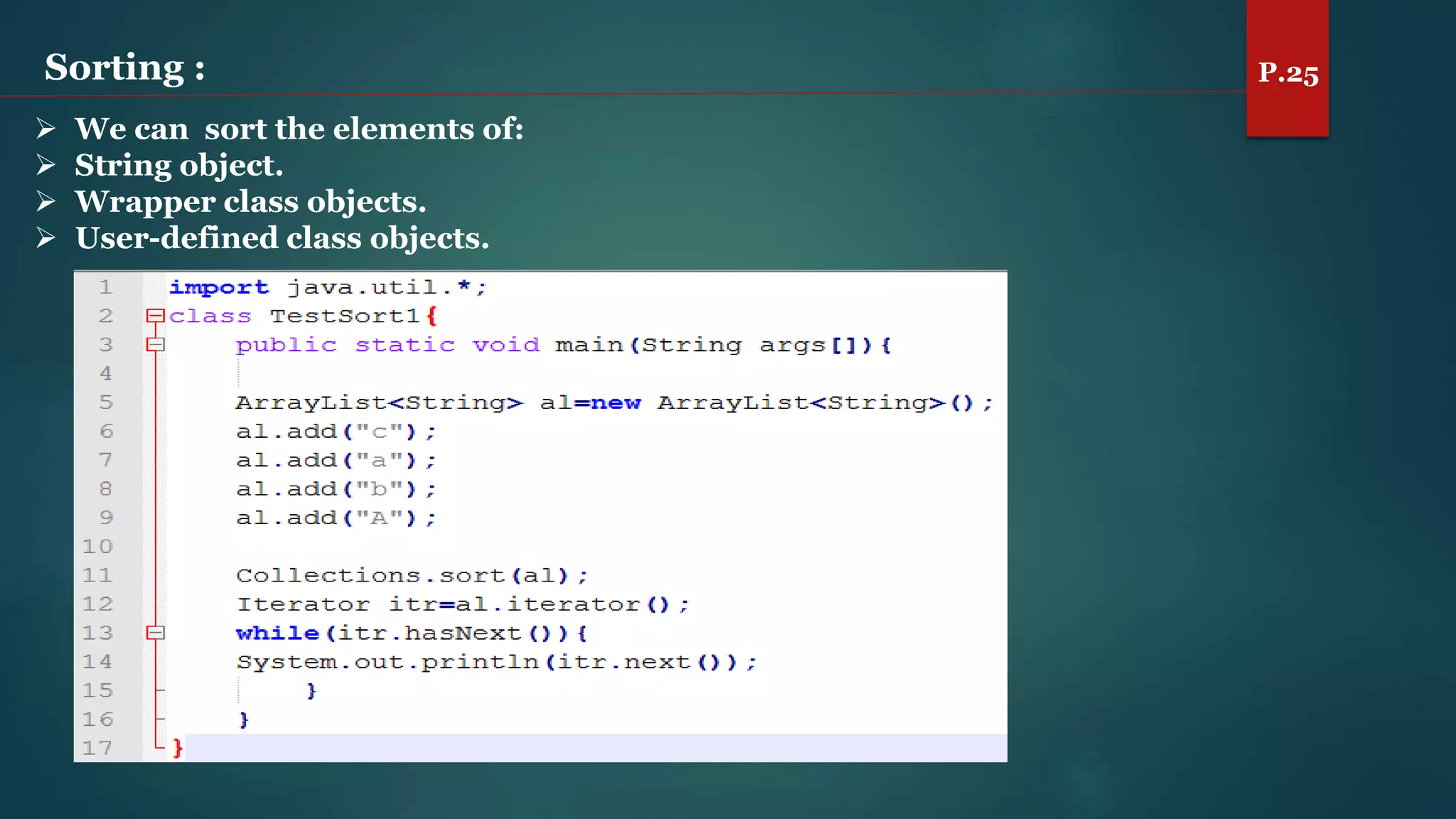
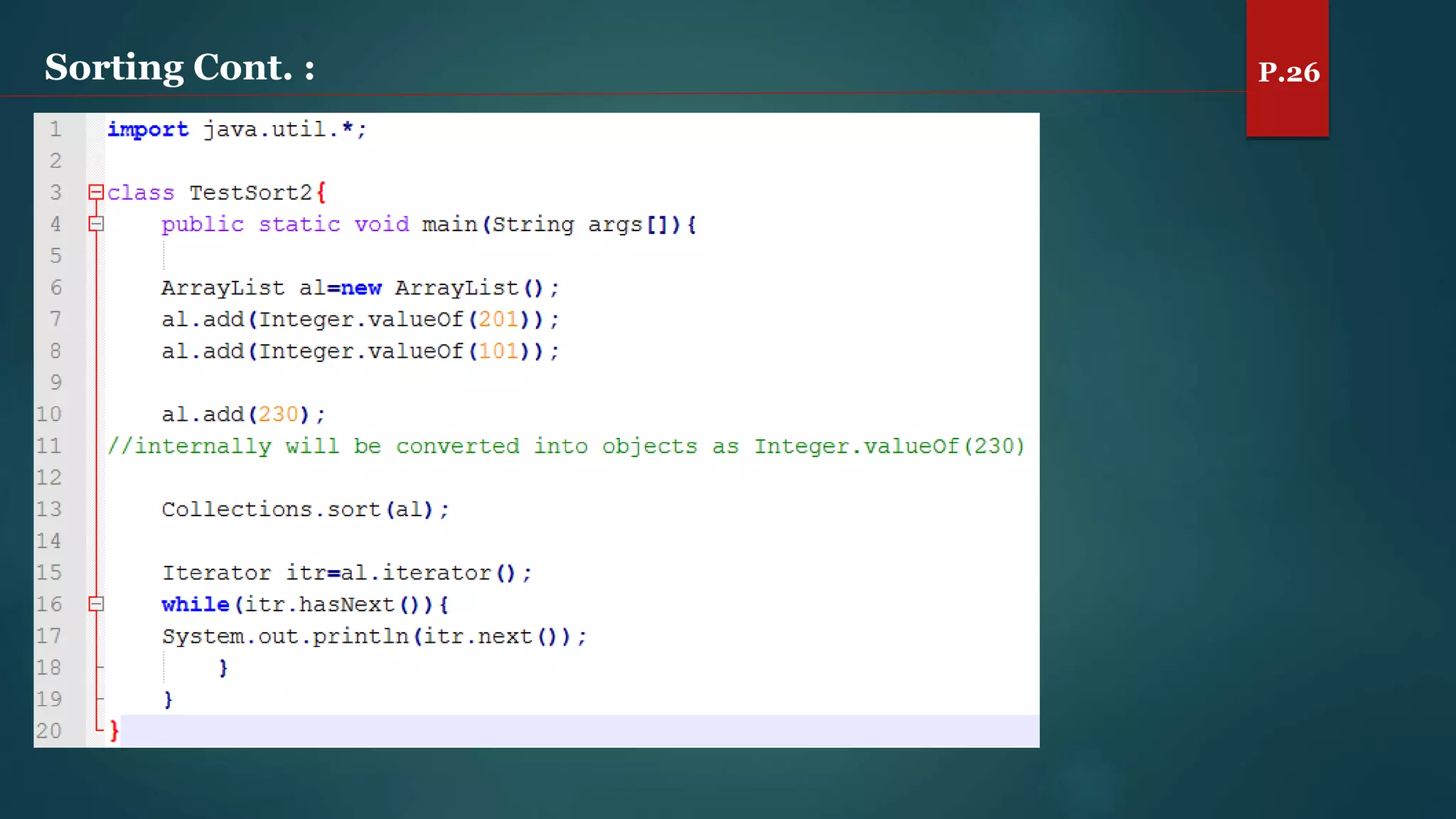
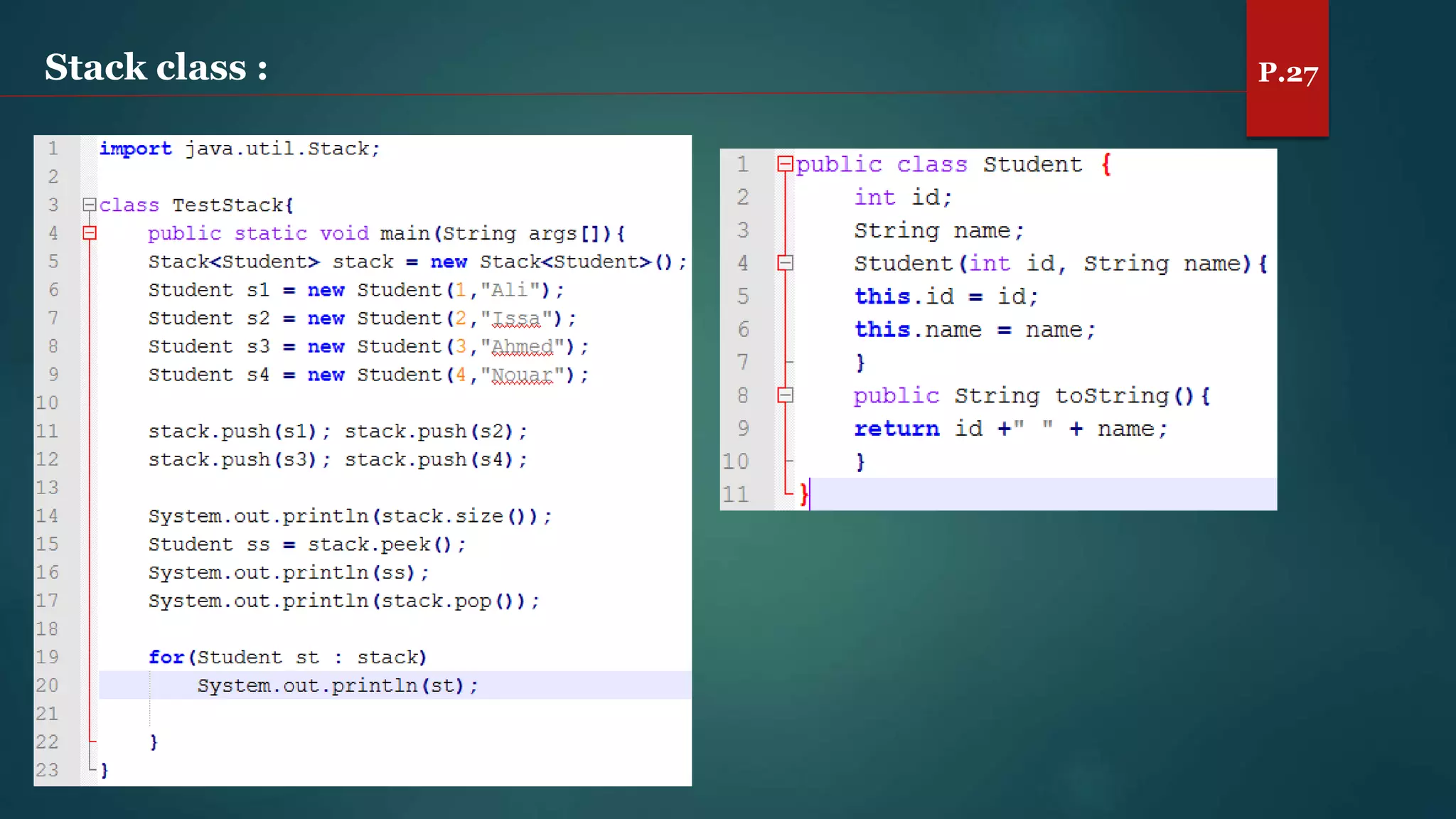
The document discusses arrays and the Java Collections Framework, explaining concepts such as array initialization, copying, and multidimensional arrays. It highlights the iterator interface methods, as well as various collection classes like ArrayList and TreeSet, detailing their functionality and properties. Additionally, it covers sorting elements and managing key-value pairs in map interfaces.