This document discusses binary arithmetic and how it works using boolean logic. It provides examples of adding binary numbers and what happens in overflow conditions when the results exceed the bit limit. The key concepts covered are:
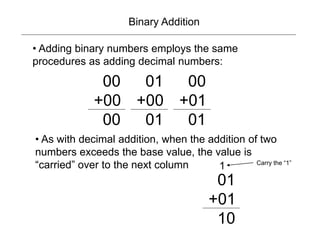
1) Binary addition employs the same process as decimal addition, carrying values to the next column when the sum exceeds the base.
2) Overflow occurs when the result of an addition does not fit in the allocated bit space, with part of the value lost. Programs can detect overflow as an error.
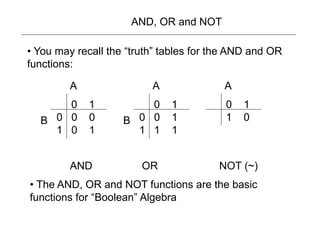
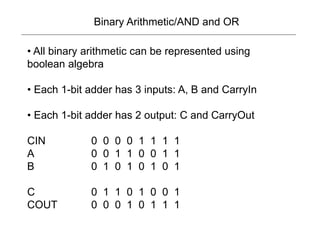
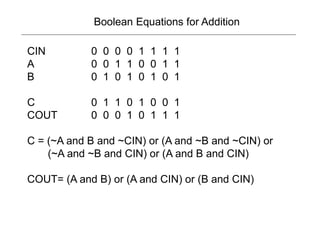
3) Binary operations can be represented using boolean logic functions like AND, OR and NOT. Single bit adders use these functions with inputs A, B, and a carry in to calculate outputs for the