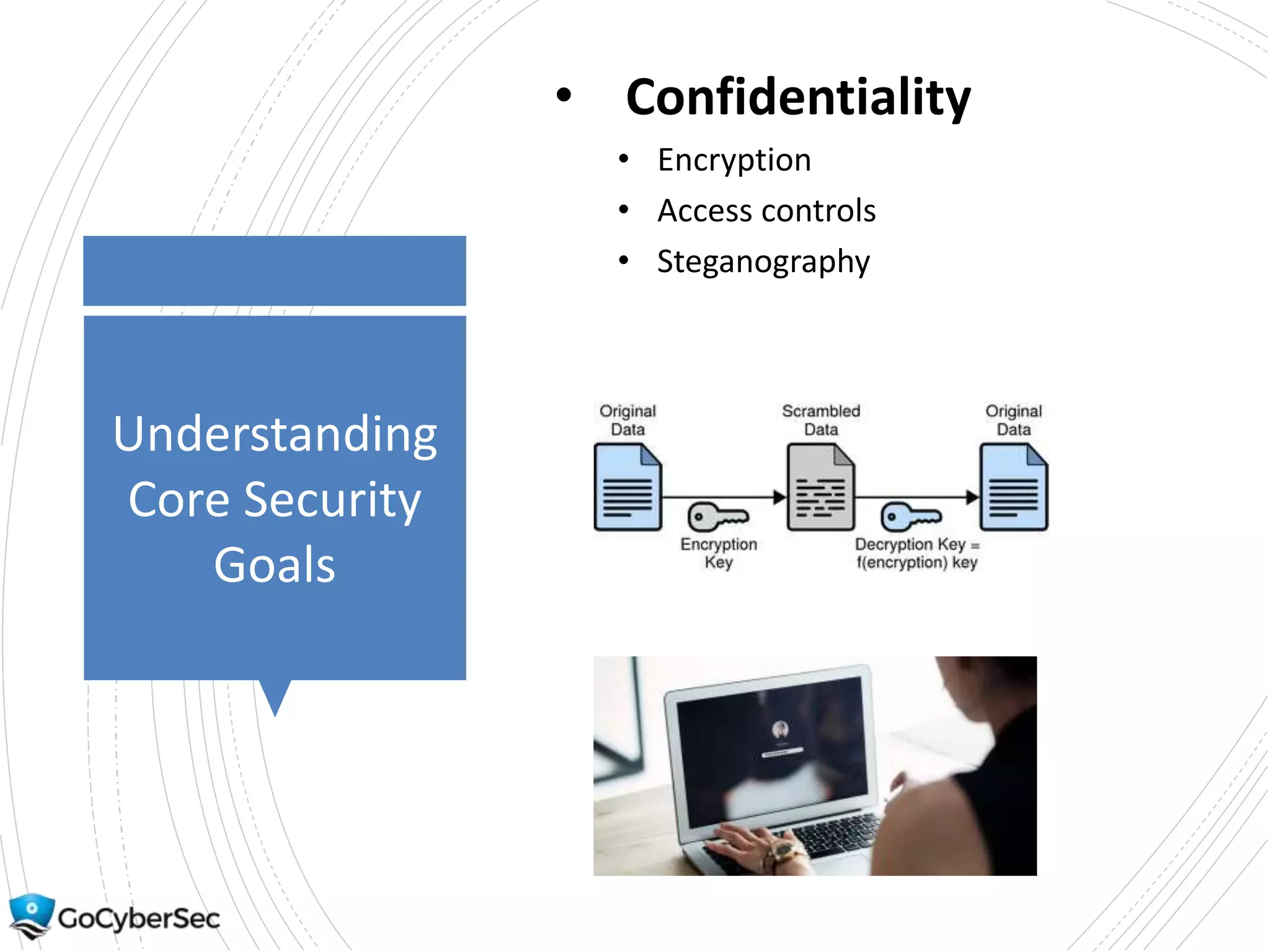
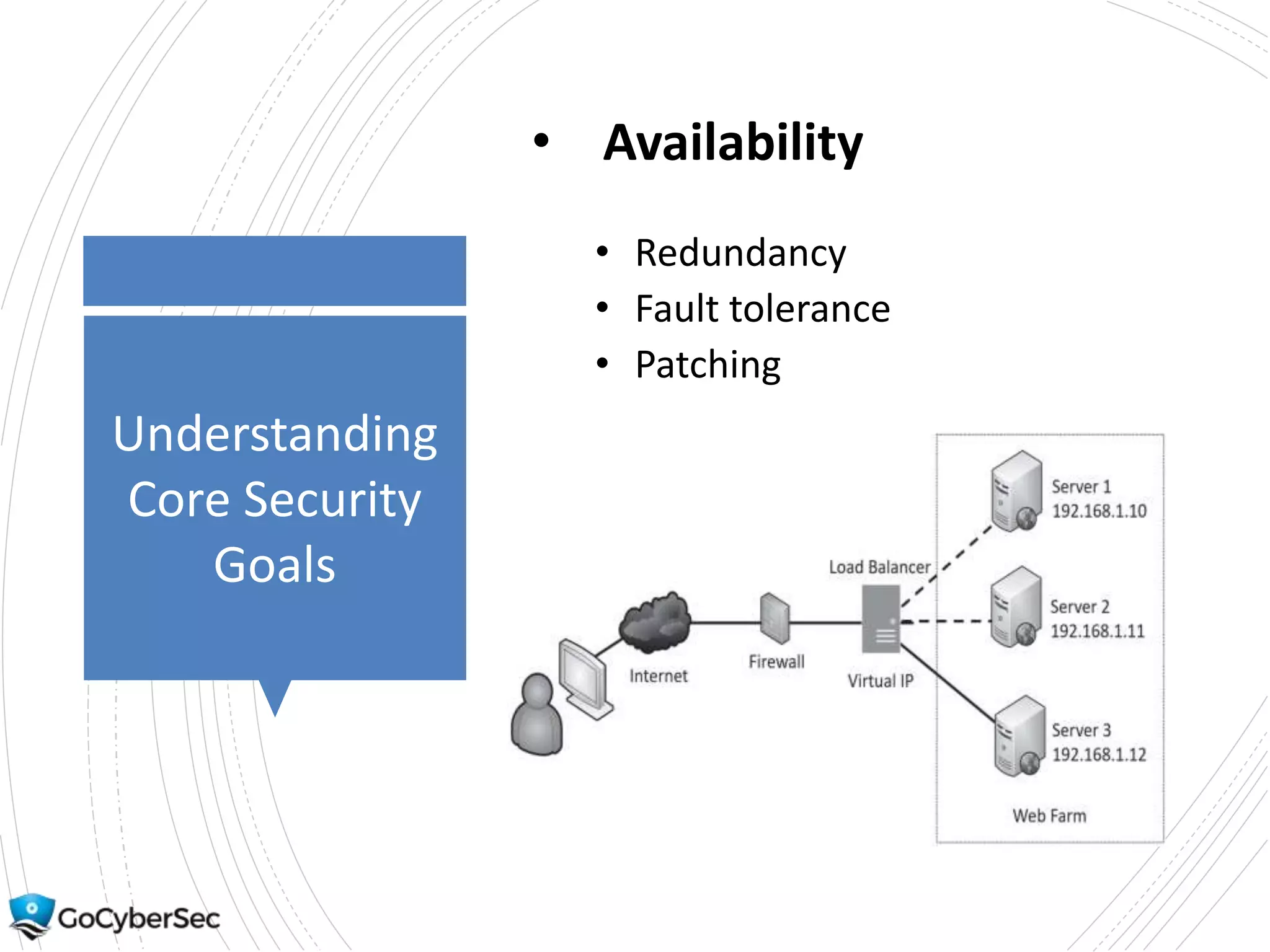
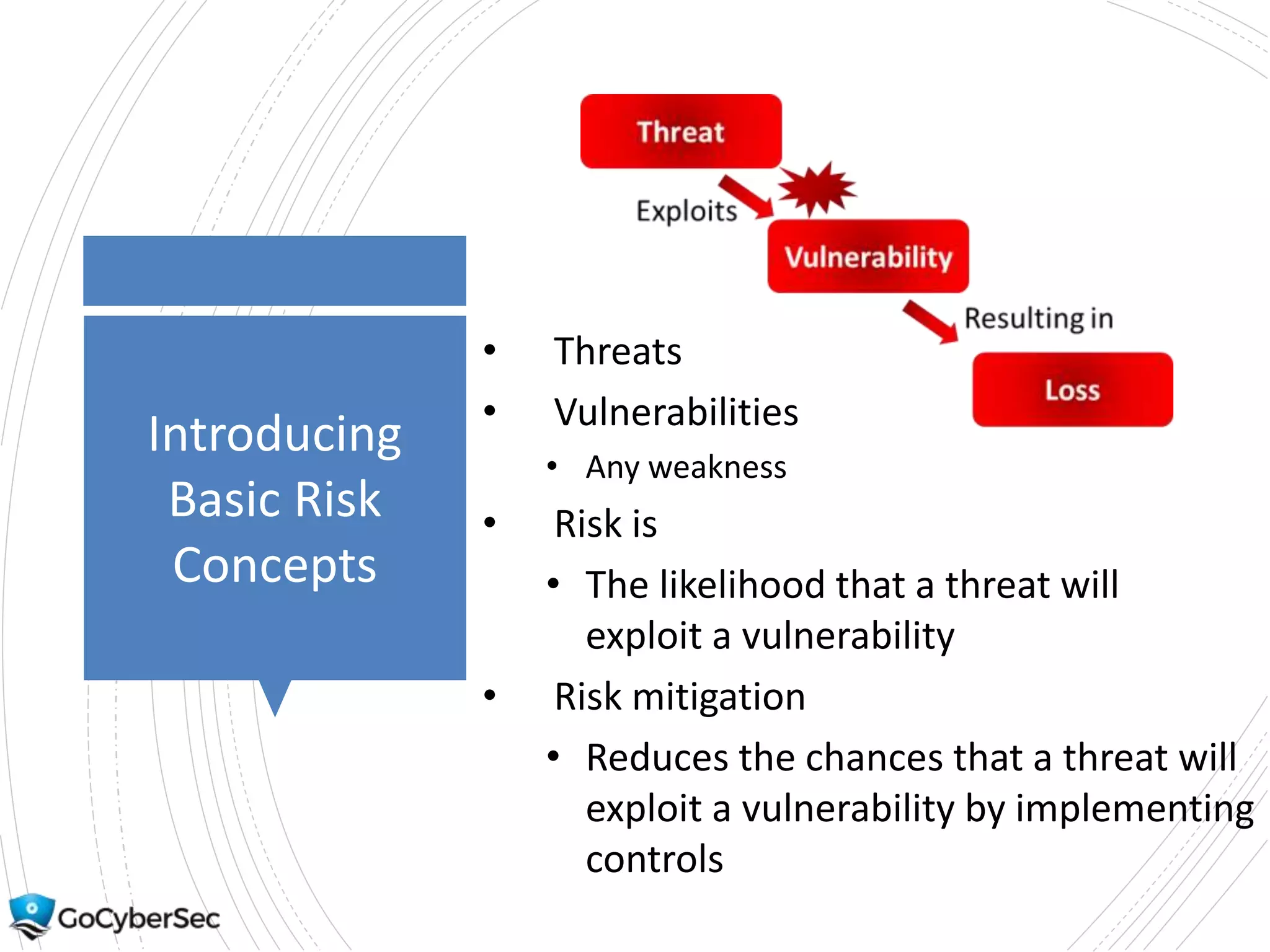
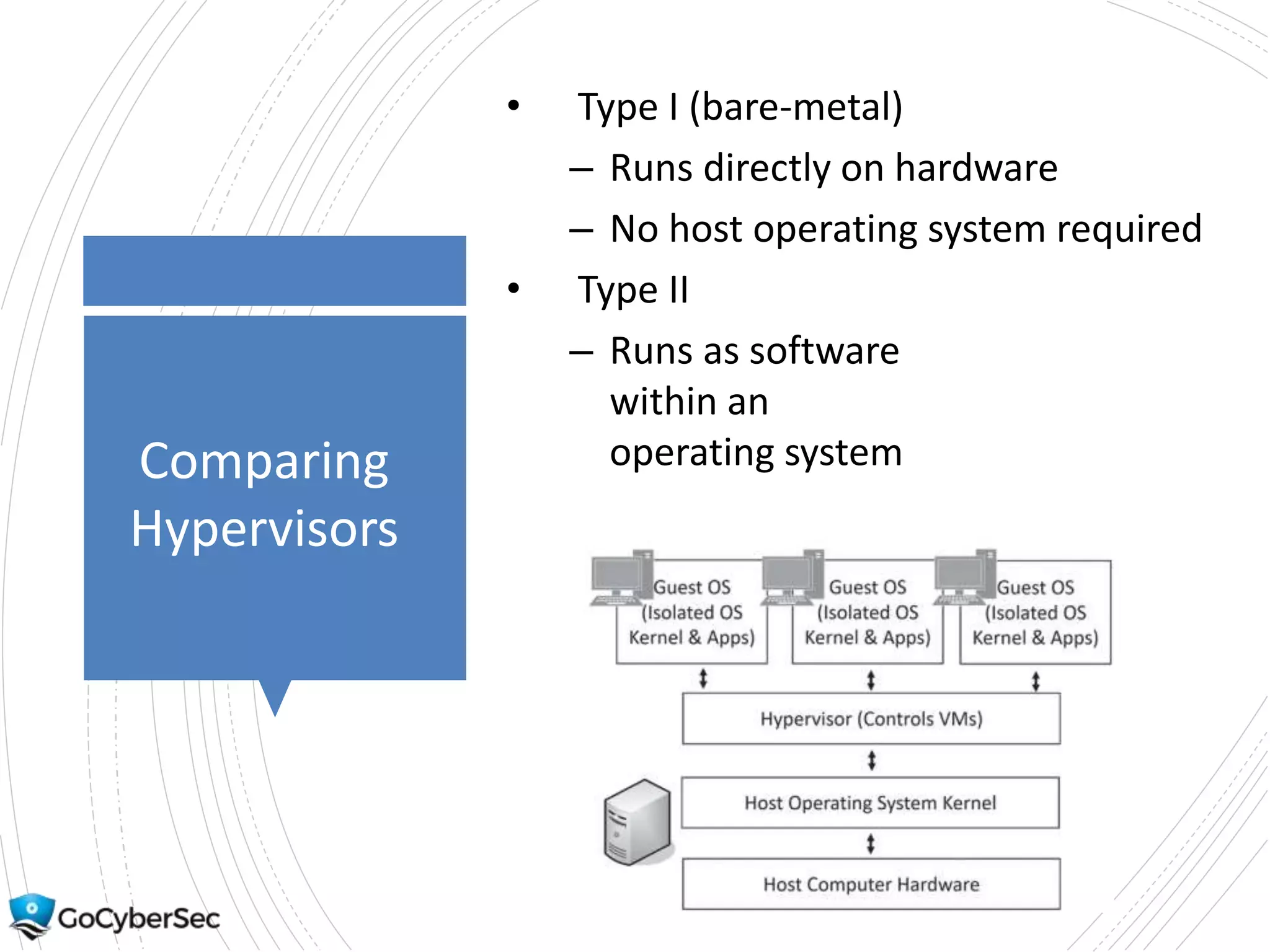
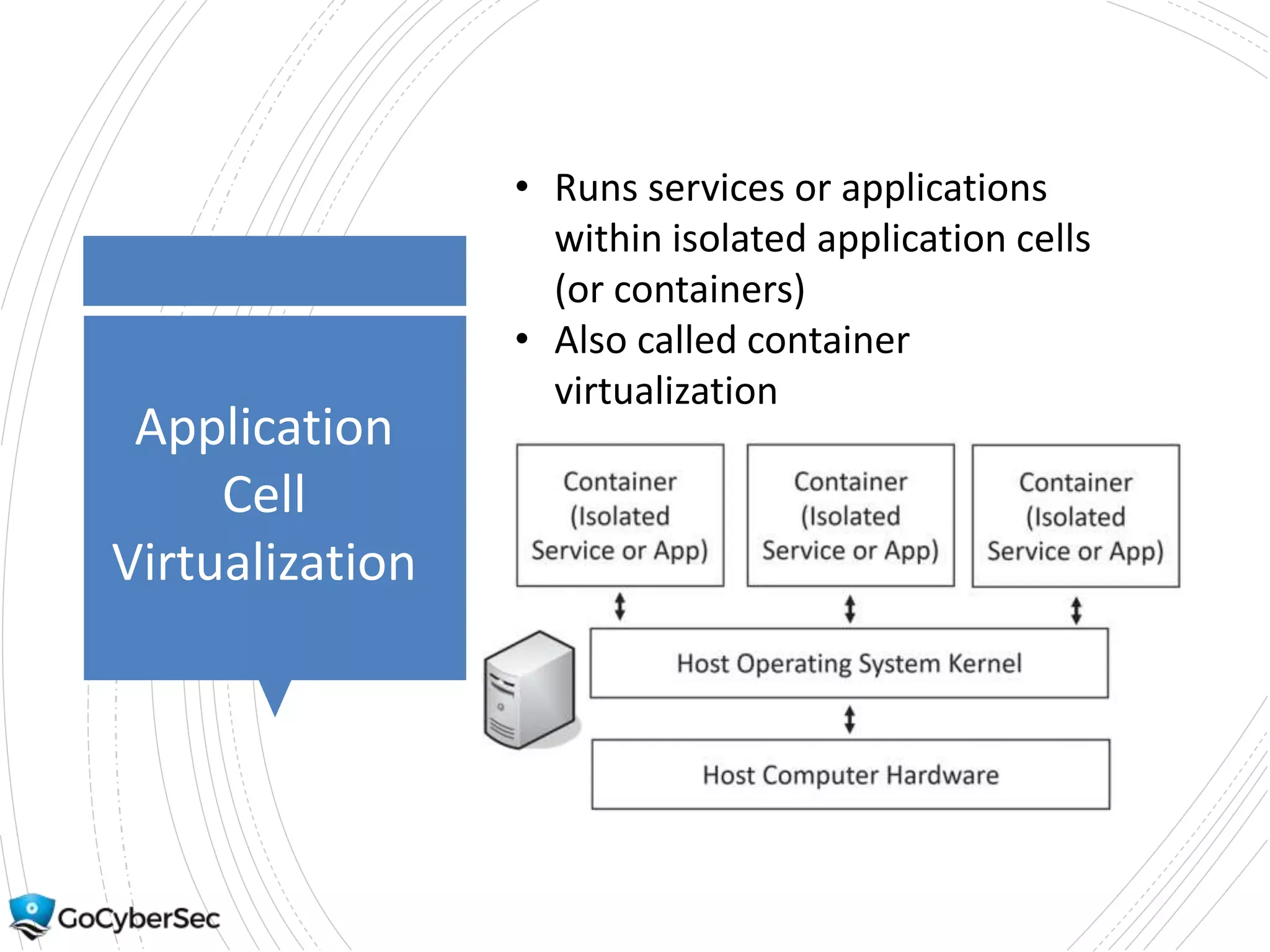
This chapter discusses core security concepts like the CIA triad of confidentiality, integrity and availability. It introduces risk concepts such as threats, vulnerabilities and risk mitigation. It covers different types of controls including technical, administrative and physical controls. The chapter also discusses virtualization topics such as hypervisors, snapshots and risks. Finally, it demonstrates some basic command line tools for Windows and Linux like ping, ipconfig and ifconfig.