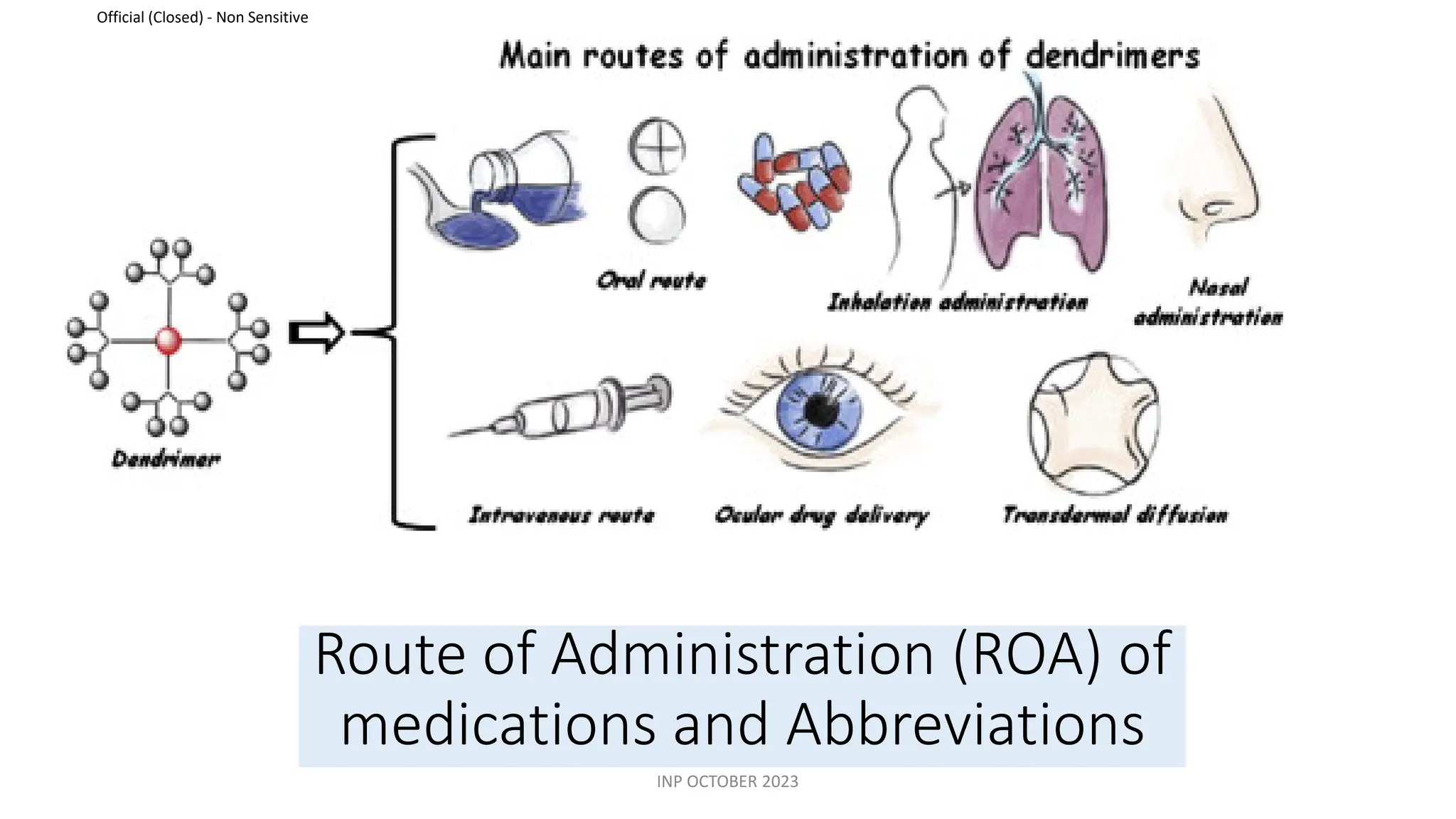
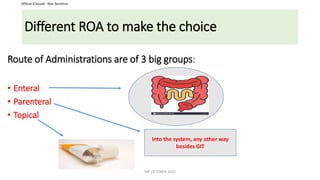
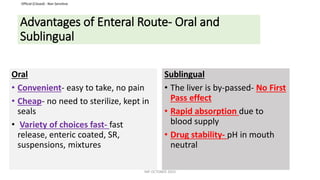
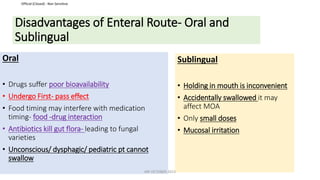
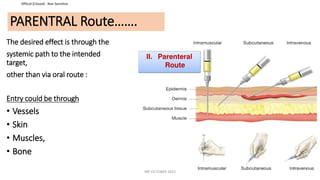
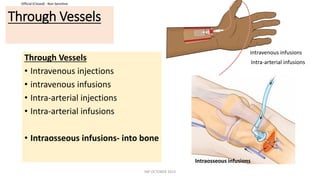
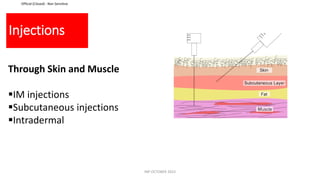
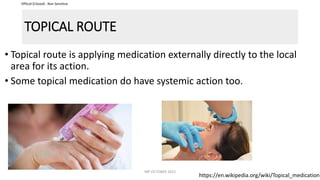
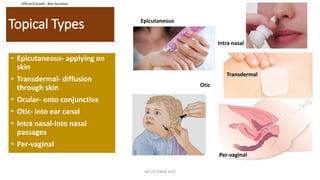
This document discusses routes of administration (ROA) of medications and provides information on different ROAs including enteral, parenteral, and topical routes. It defines ROA as the means by which a drug is brought into contact with the body. The choice of ROA depends on the pharmacokinetics of the drug and the patient's condition. Common ROAs include oral, sublingual, intravenous, intramuscular, and topical applications. The advantages and disadvantages of different ROAs are presented.