This document provides an overview of arrays in programming. It discusses:
- How arrays are sequences of objects of the same type indexed from 0.
- Directly accessing arrays via index values.
- Initializing arrays with values and trailing zeros.
- Passing arrays to functions passes the memory address, allowing modification.
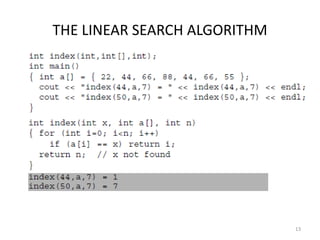
- Common sorting and searching algorithms for arrays like linear search, bubble sort, and binary search.
- Multidimensional arrays can store arrays within arrays.






![float a[7] = { 55.5,66.6, 77.7 };
• This array is declared to have 7 elements of type float;
then its initializer list initializes the first 3 elements with
the given values and the remaining 4 elements with the
value 0.
PROCESSING ARRAYS
7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4-220923101428-651326bf/85/4-Array-pptx-7-320.jpg)



![• Explanation:
• When an array is passed to a function, as in the call
sum(a,size) in previous example, the value of array name
a is actually the memory address of the first element
(a[0]) in the array.
• The function uses that address value to access and
possibly modify the contents of the array. So passing an
array to a function is similar to passing a variable by
reference: the function can change the values of the
array’s elements.
11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4-220923101428-651326bf/85/4-Array-pptx-11-320.jpg)
![• Printing the Memory Location of an Array
• This program prints the value of the address stored in an
array name.
• Its value is the memory address of the first byte of the
first element a[0] in the array.
12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4-220923101428-651326bf/85/4-Array-pptx-12-320.jpg)