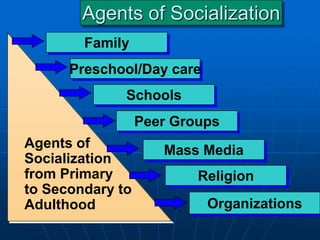
The document discusses various agents of socialization that influence individuals, including both informal agents like family and peers, as well as formal agents like schools and mass media. It focuses on the role of the family as the first and most important socialization agent, establishing one's identity, values and goals. However, it notes the family has changed with trends like the decline of the nuclear family structure. Other agents like religion, schools, peer groups and mass media also socialize individuals by transmitting norms, knowledge and creating social connections. Mass media in particular has taken on a new role with the rise of internet addiction among some groups.