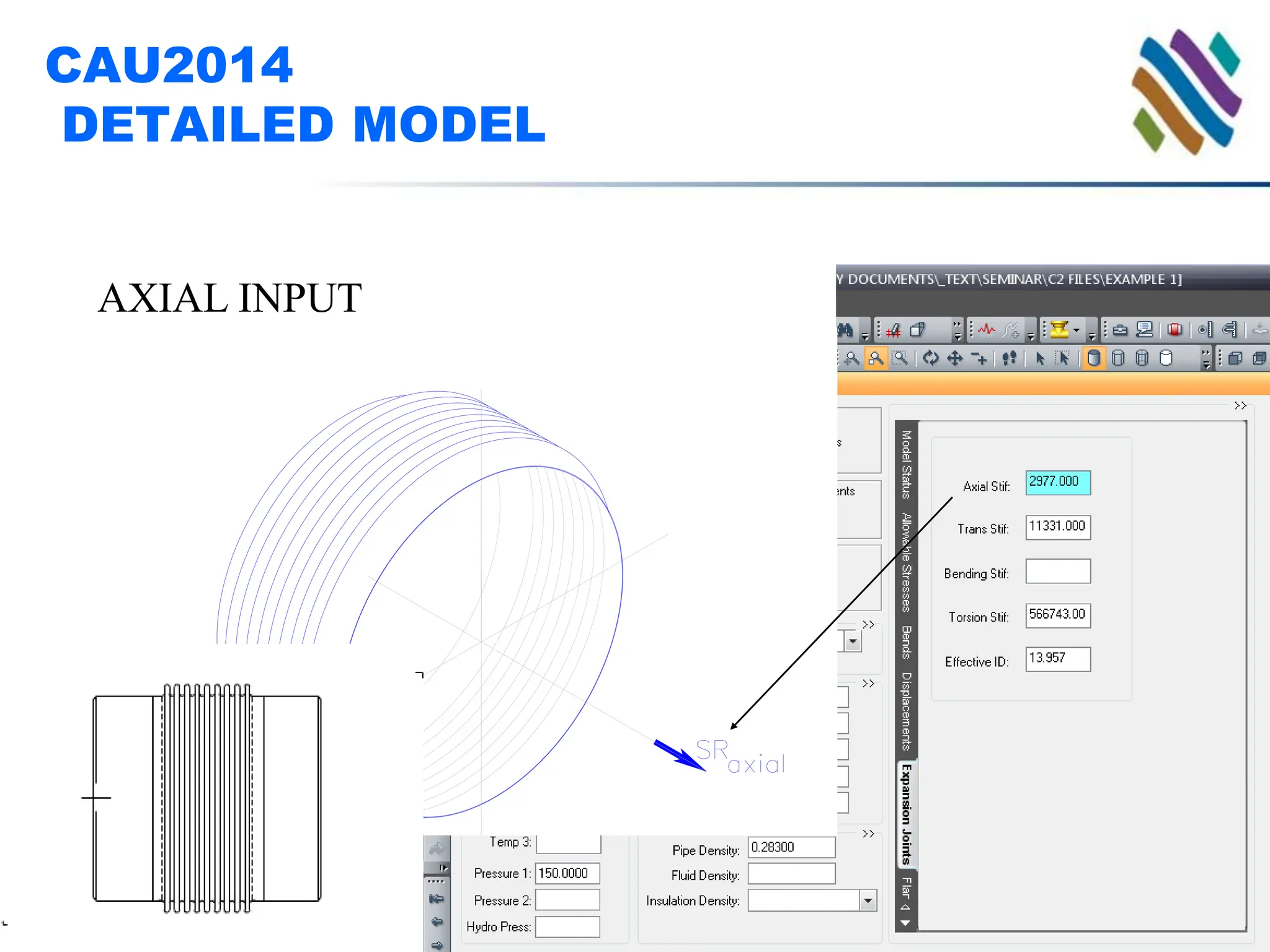
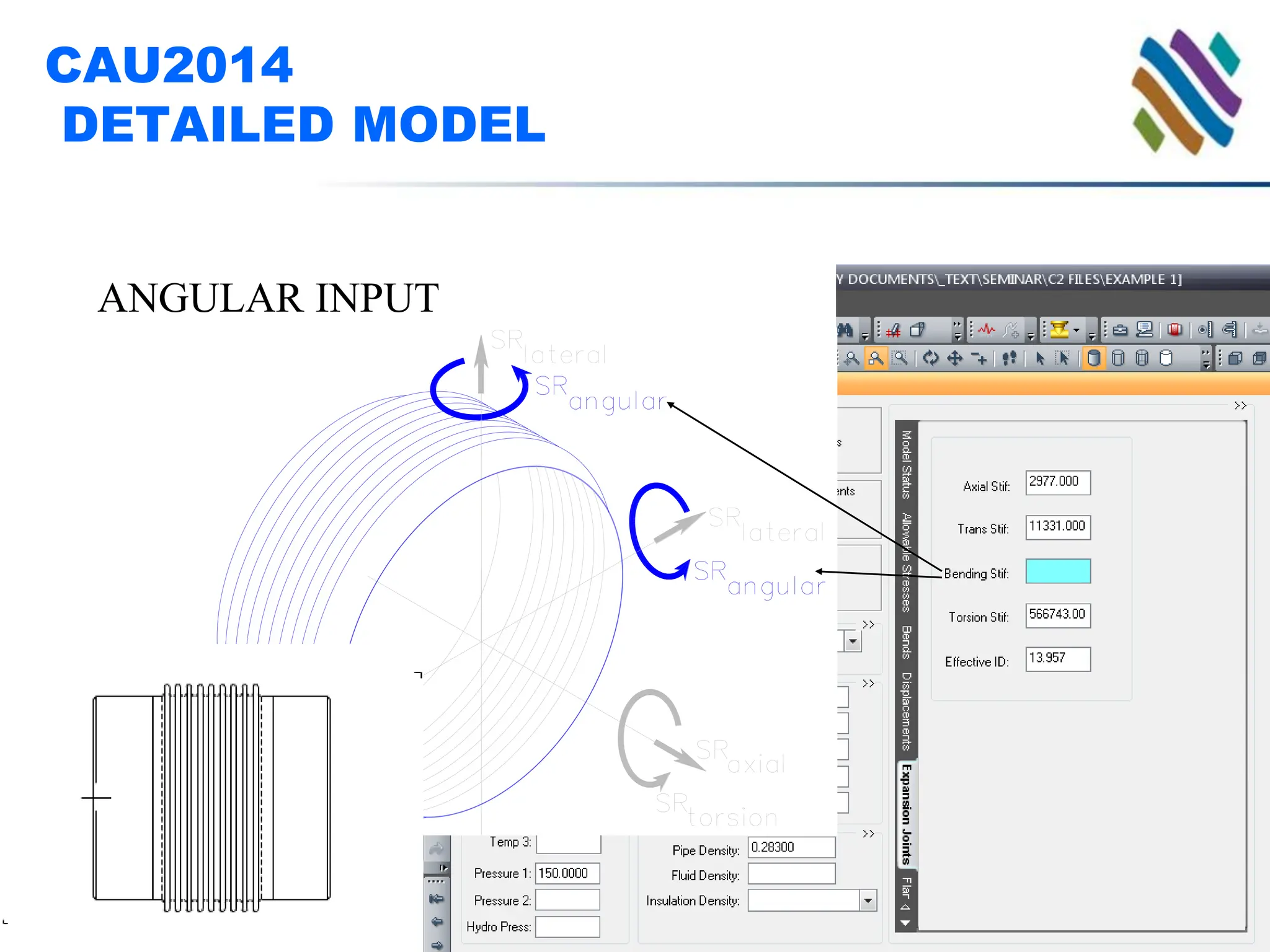
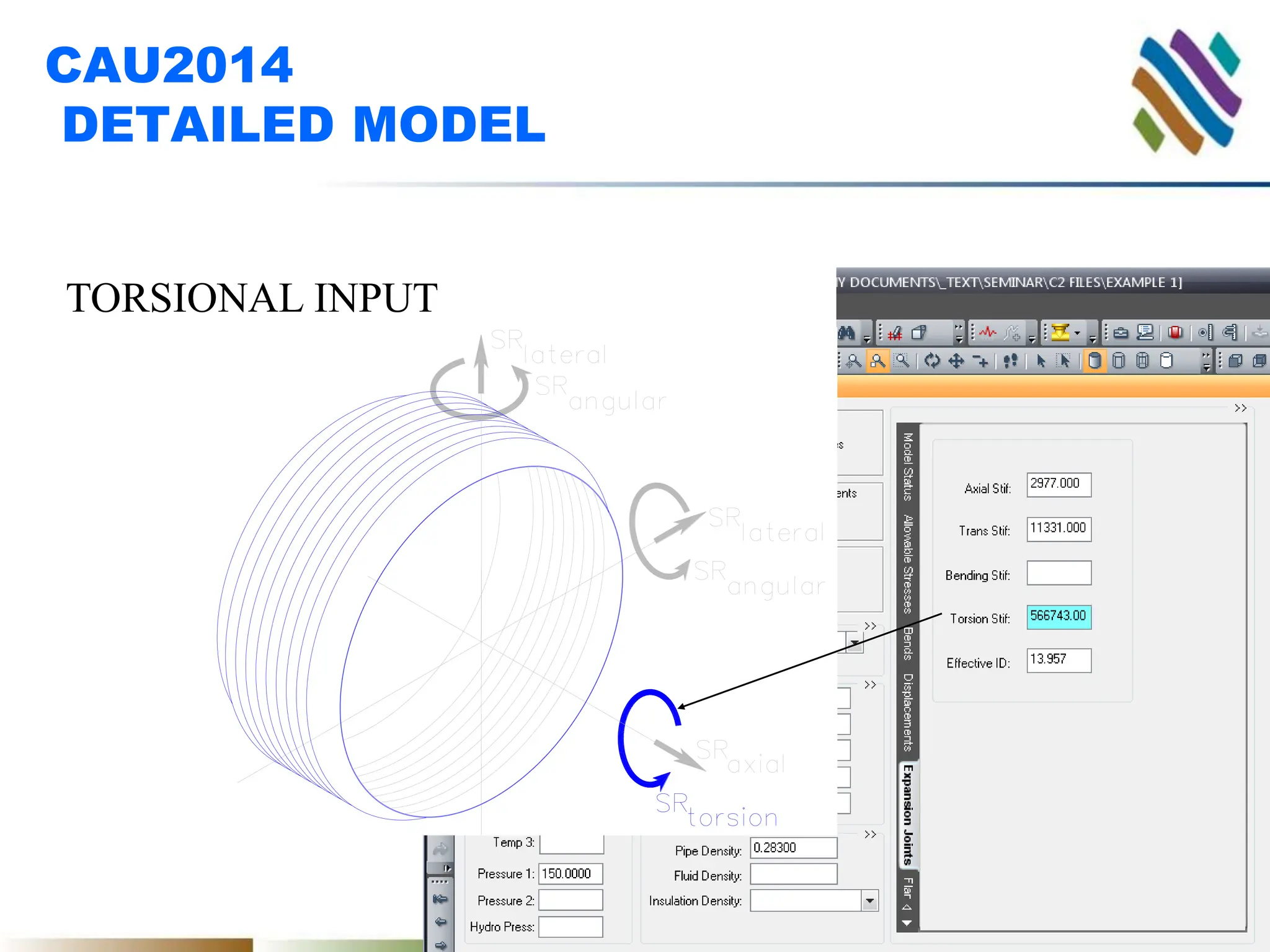
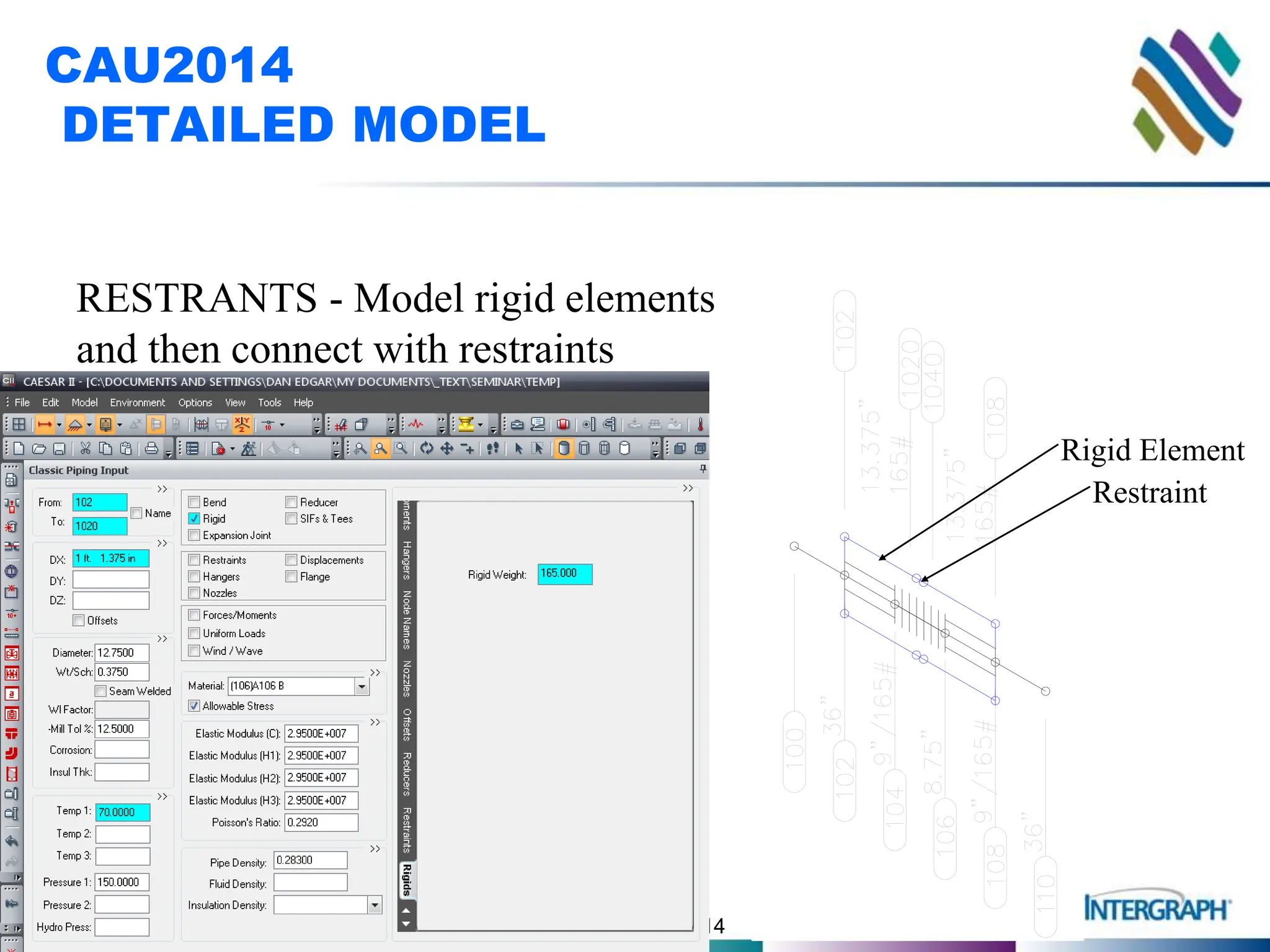
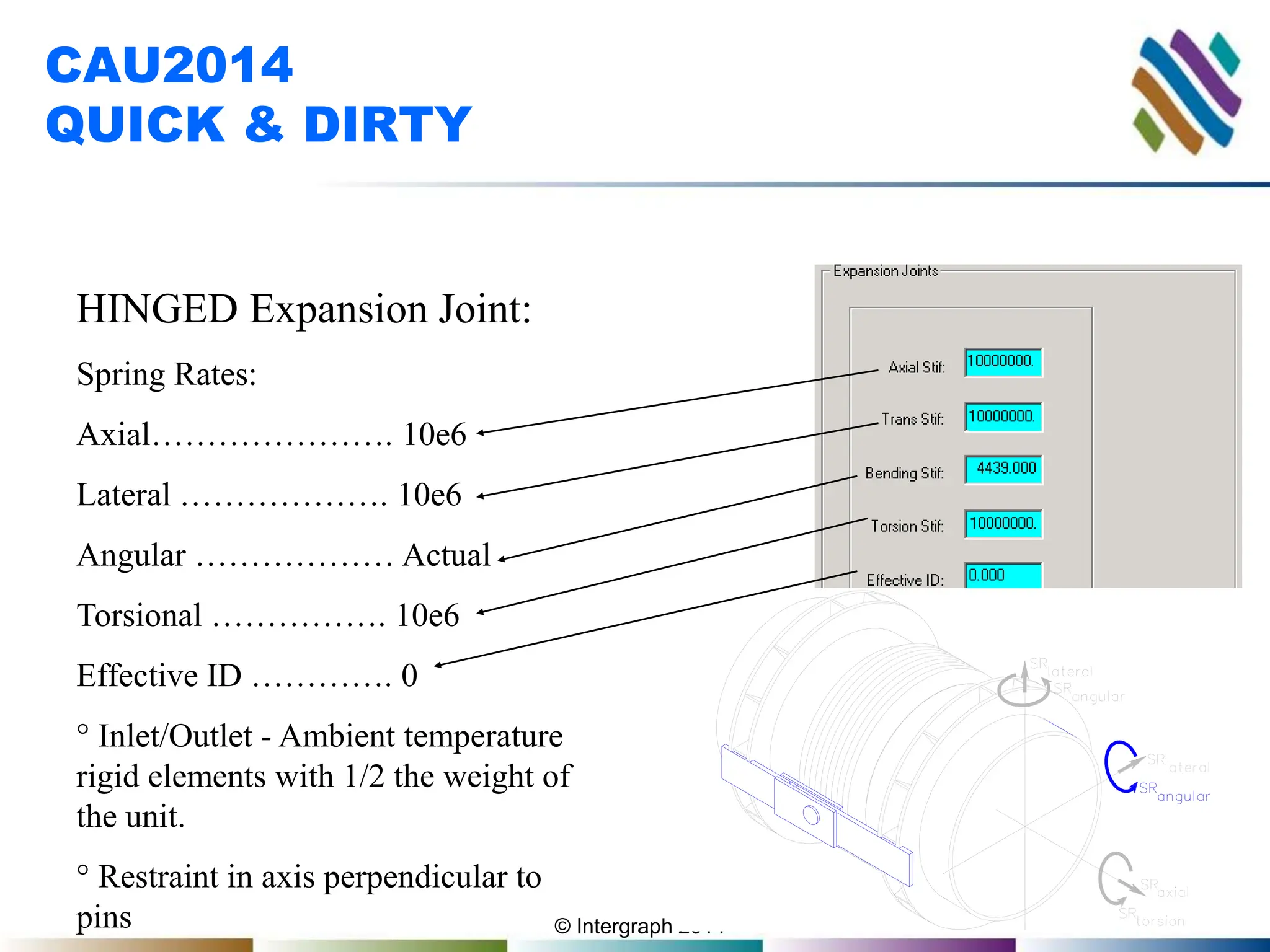
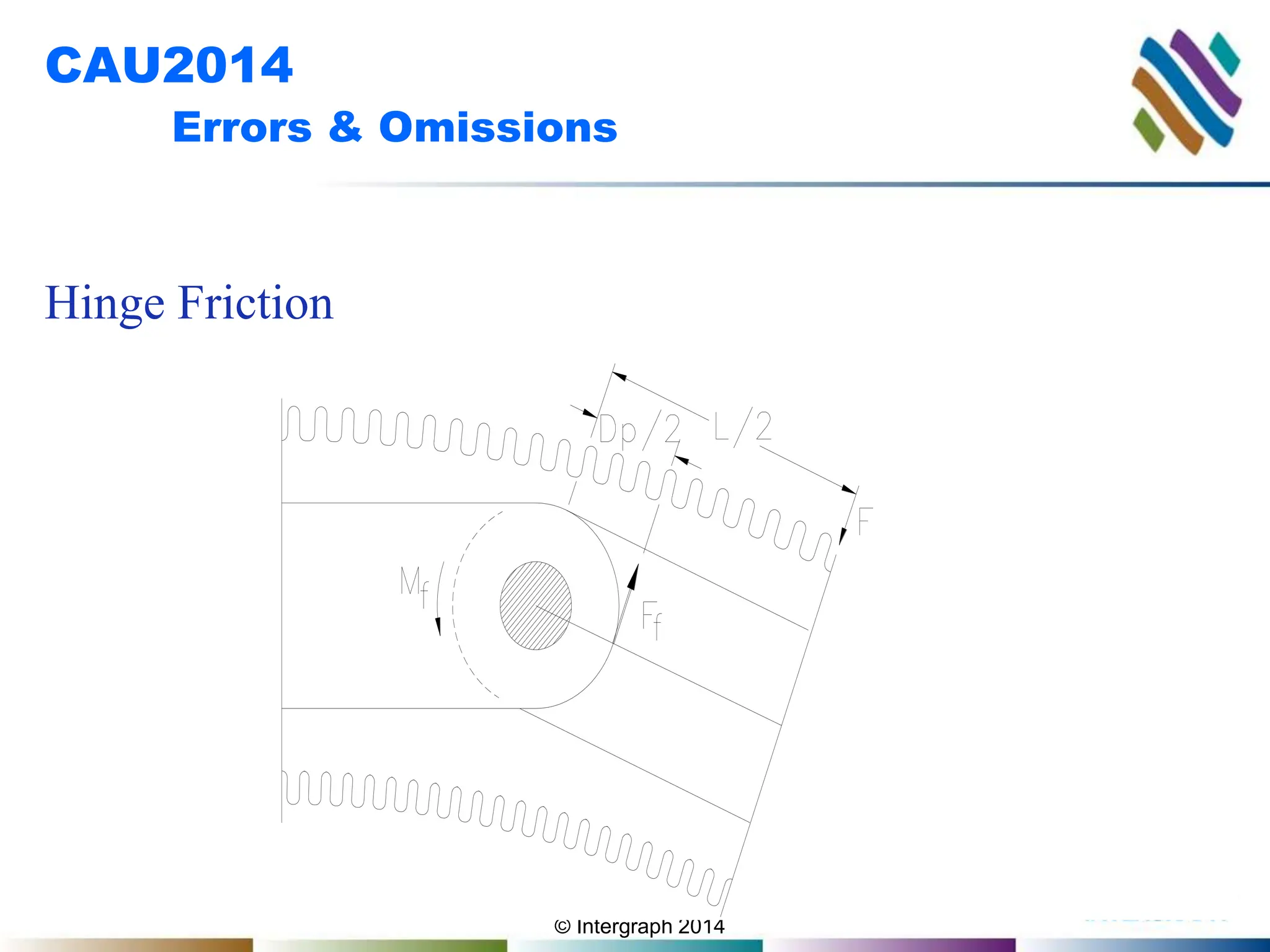
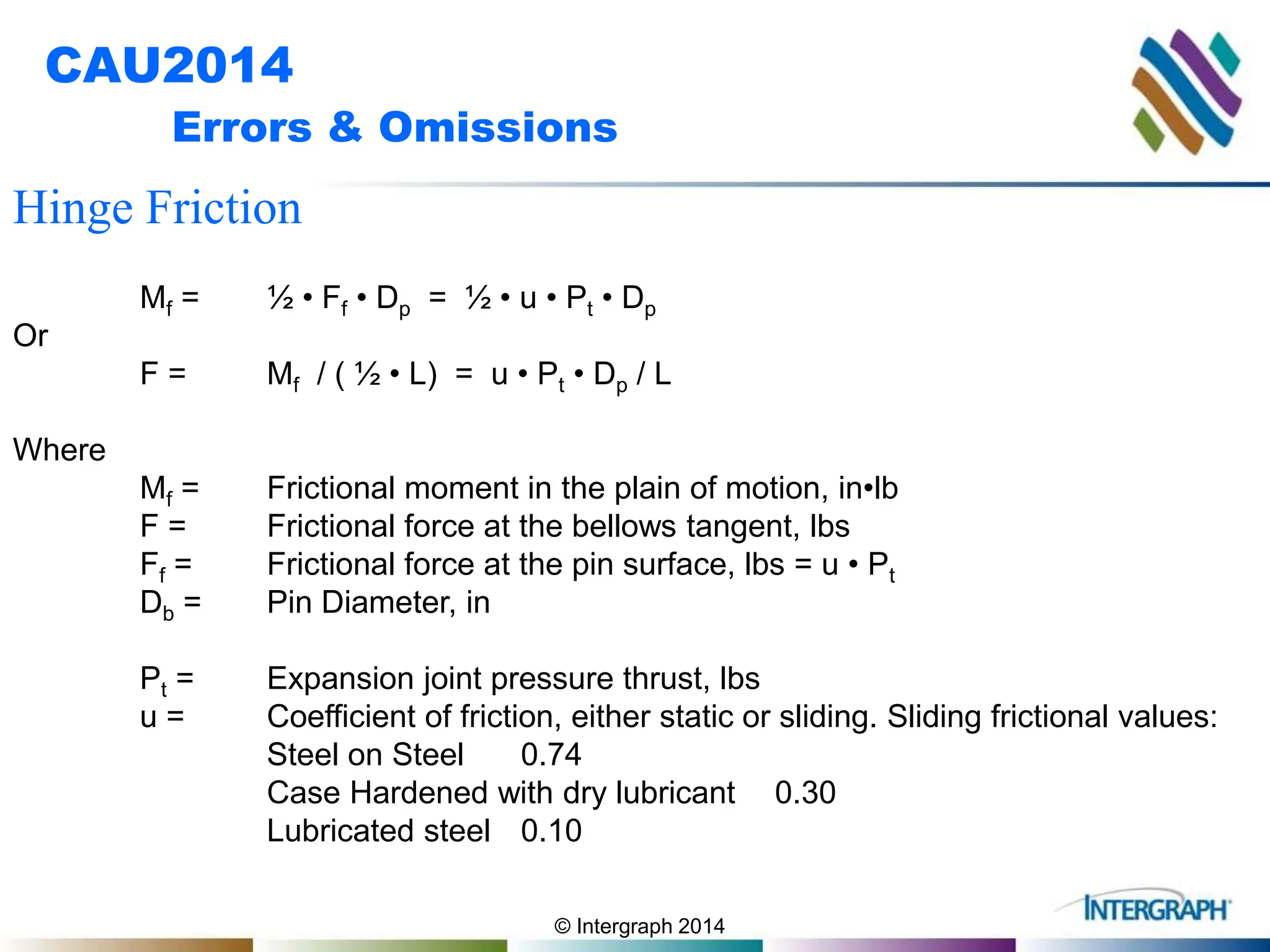
The document outlines guidelines and techniques for modeling expansion joints using CAESAR II software, focusing on detailed modeling inputs for bellows, hardware, and restraints. It also discusses quick modeling approaches, common errors, and addressing issues like rotation and rigidity errors in the modeling process. Furthermore, it provides information on calculating hinge friction and other critical variables relevant to expansion joint performance.