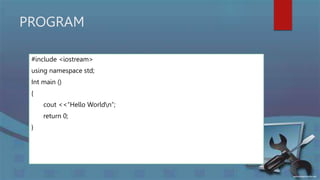
The document outlines key concepts in programming, including its definition, ethical considerations, and types of programming languages such as procedural, functional, object-oriented, scripting, and logic. It also covers the role of compilers and the importance of understanding number systems in computing. Additionally, it mentions programming basics using C++ and includes examples of syntax and identifier rules.