The document summarizes a meeting to analyze Nigeria's 2014 health budget allocation. Key points include:
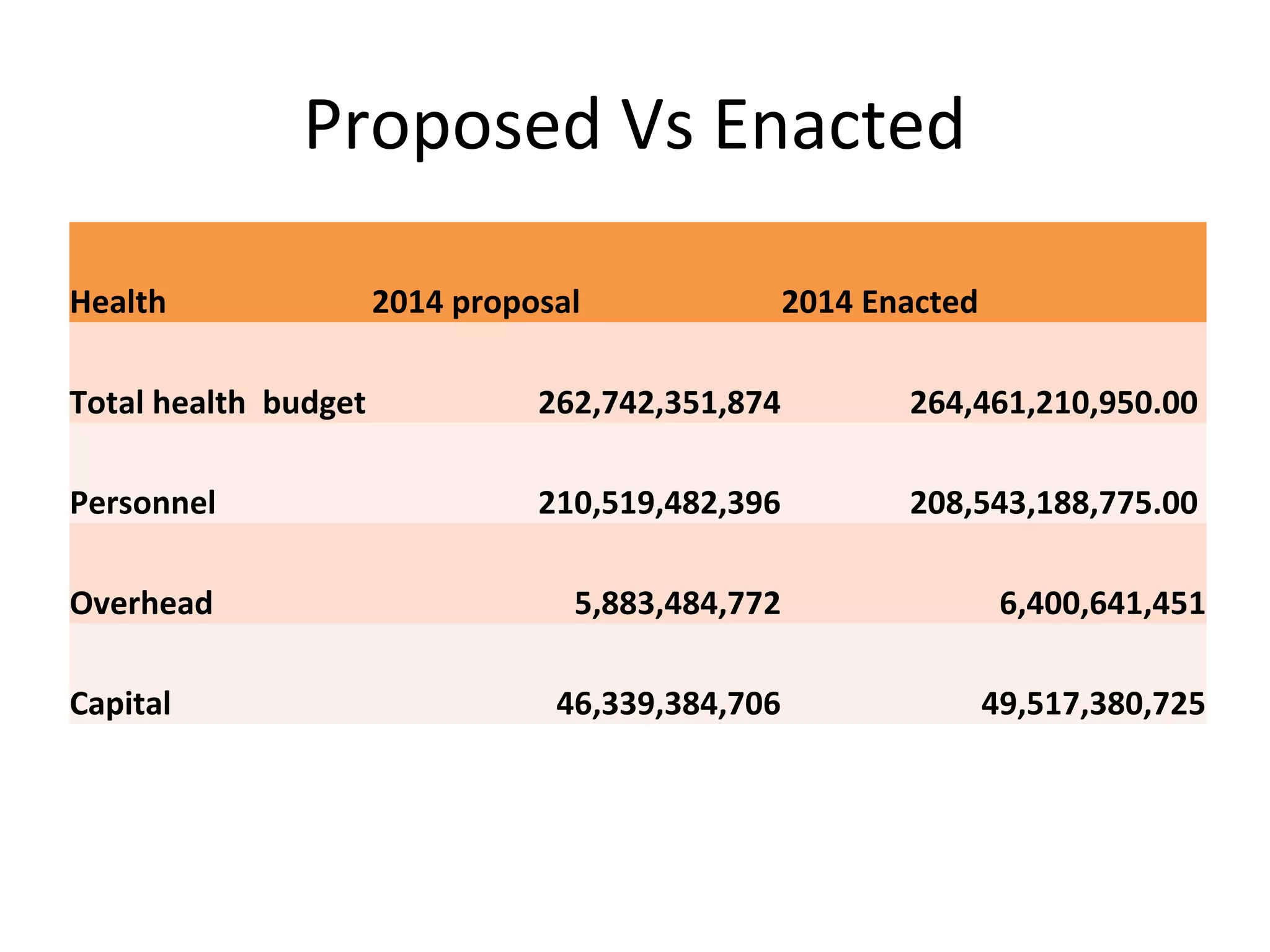
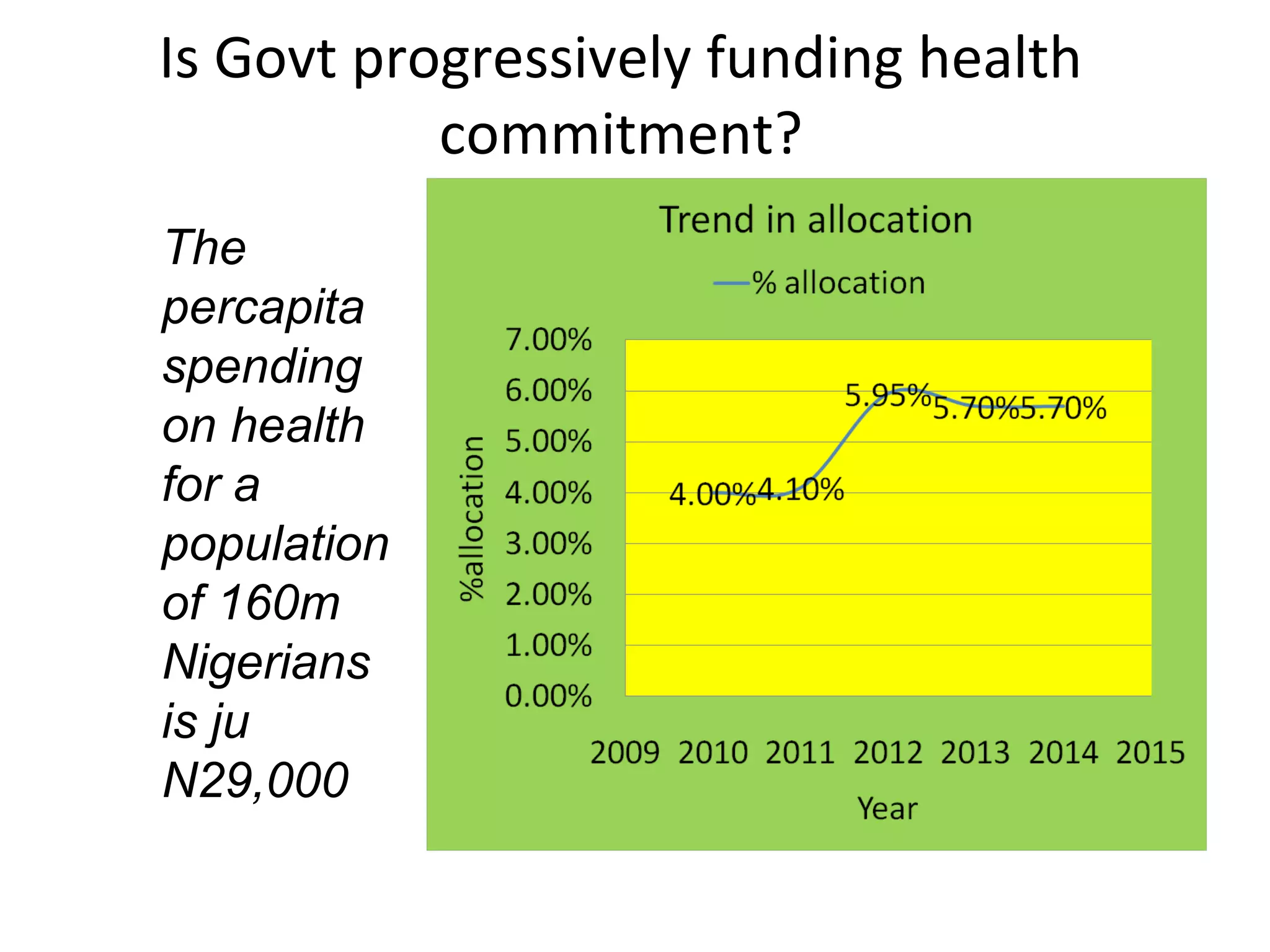
- The total health budget was N264 billion, a N2 billion increase from the proposed amount. However, per capita spending on health remains low at N29,000.
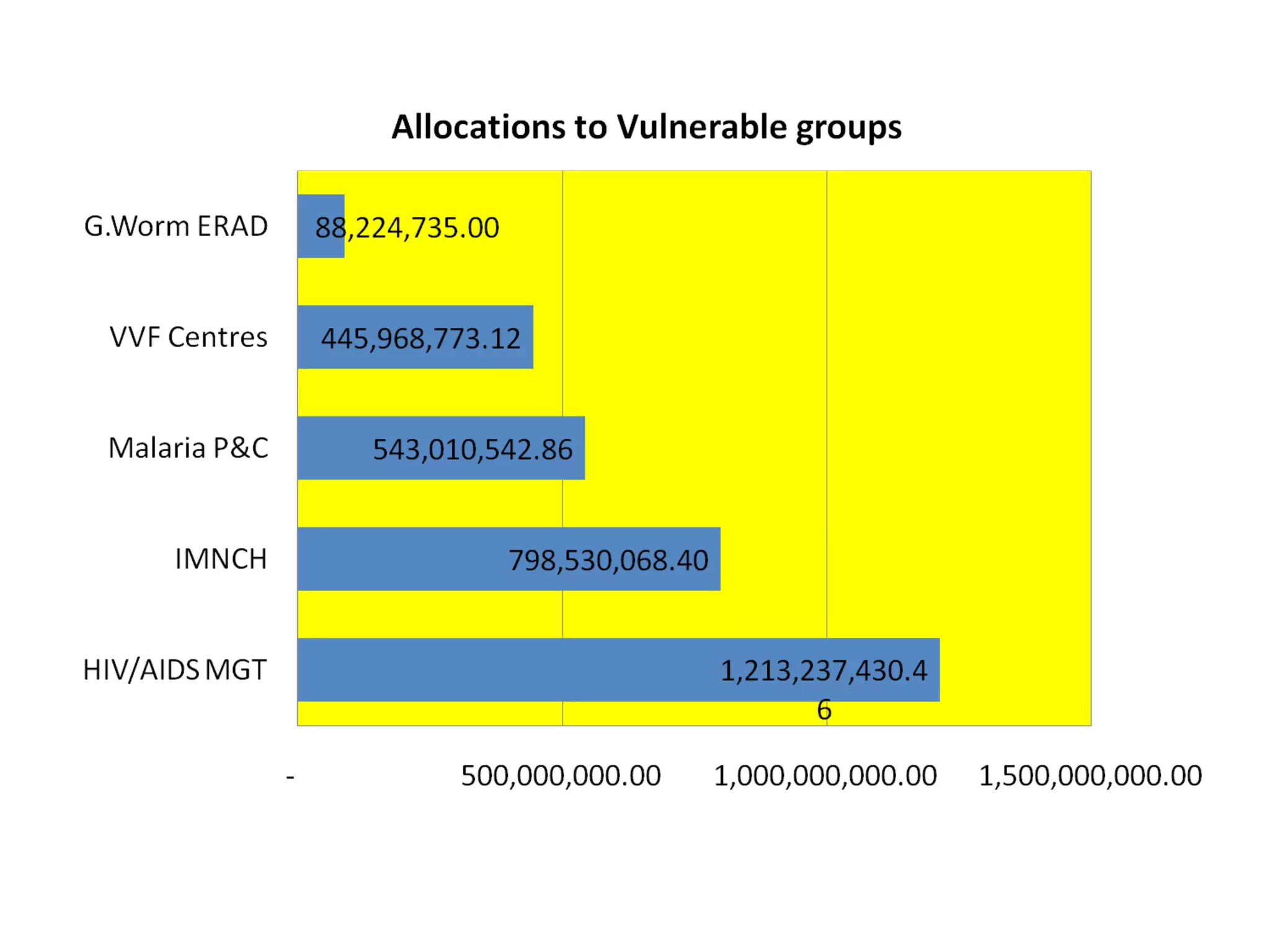
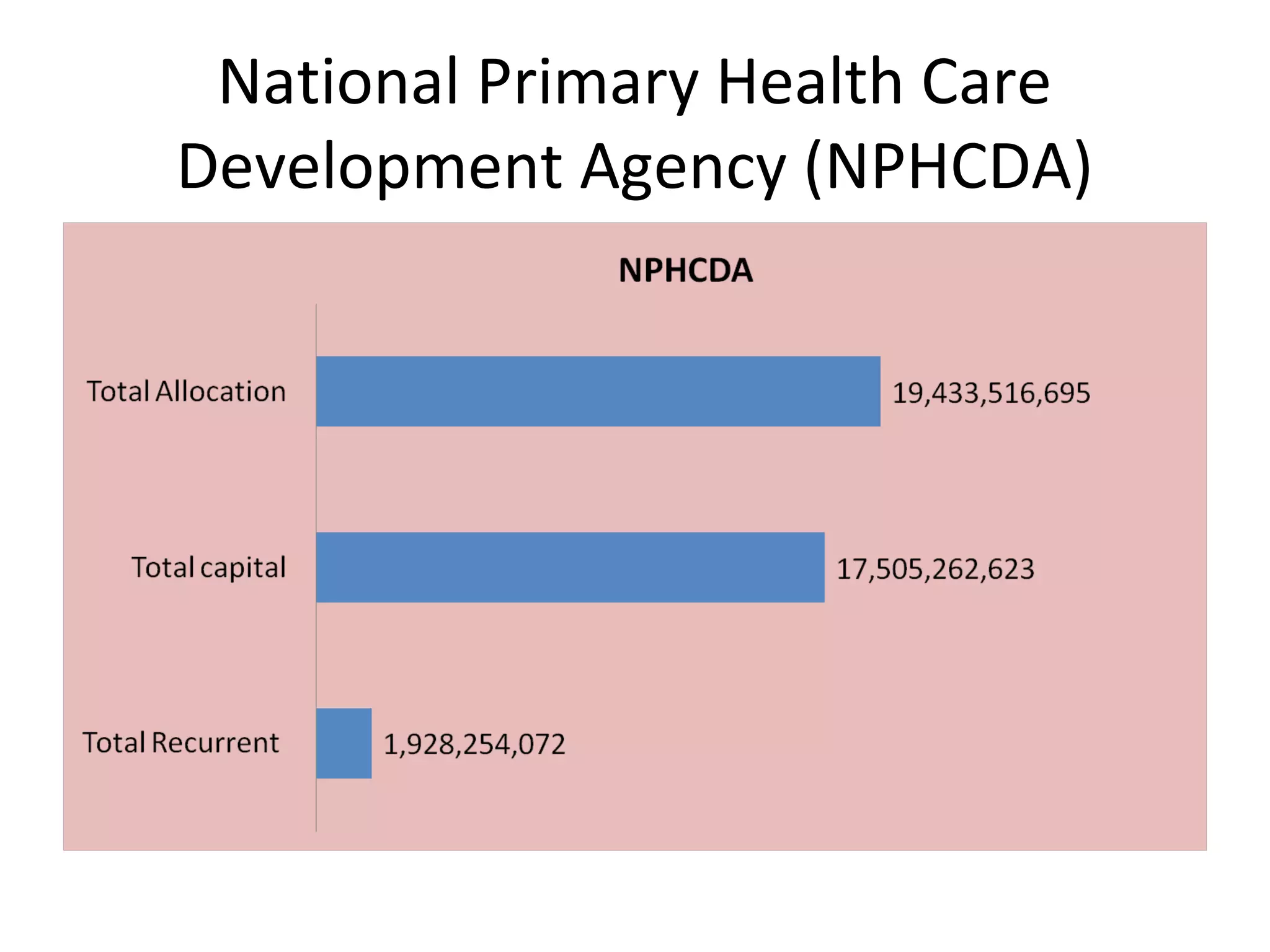
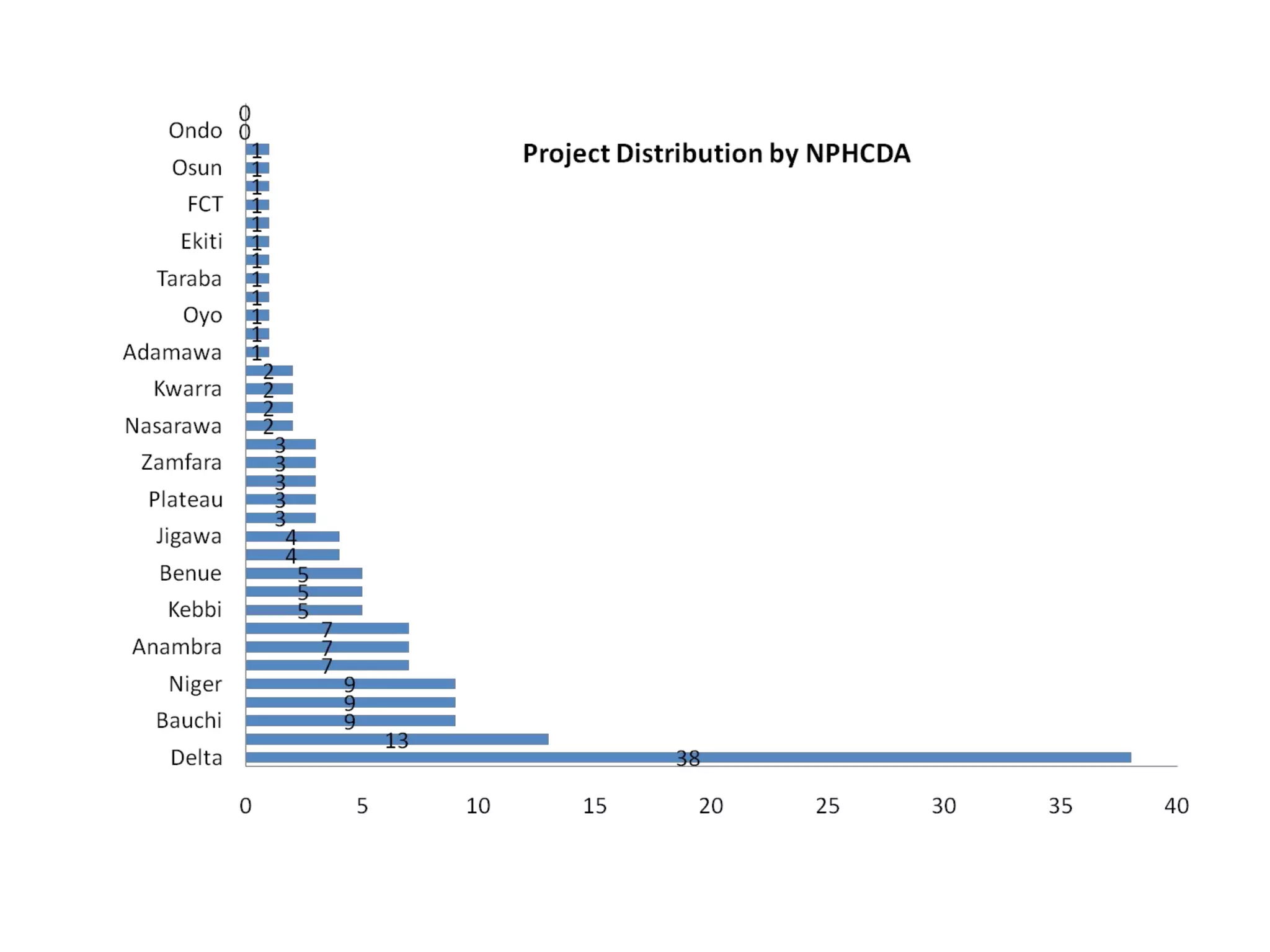
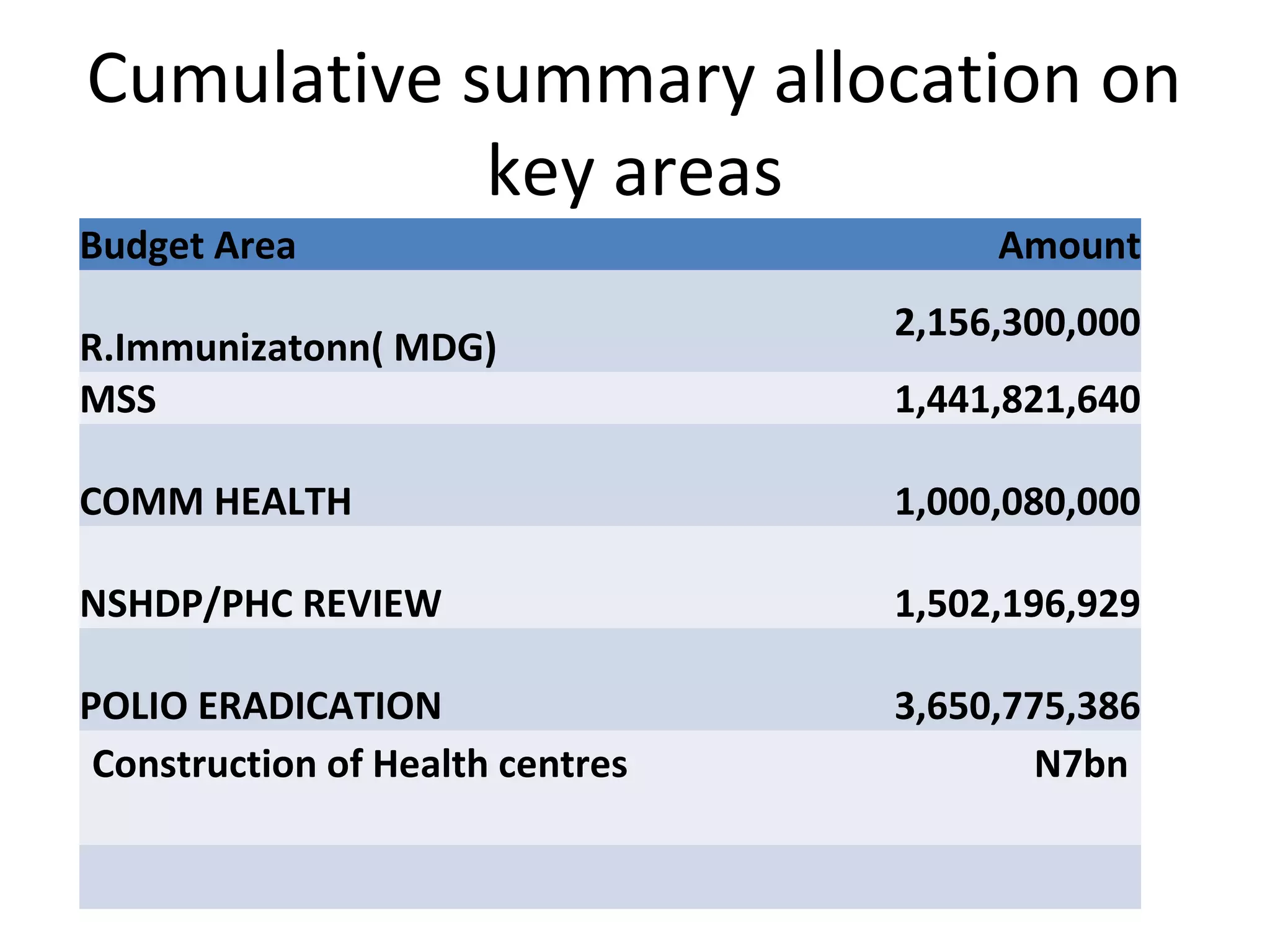
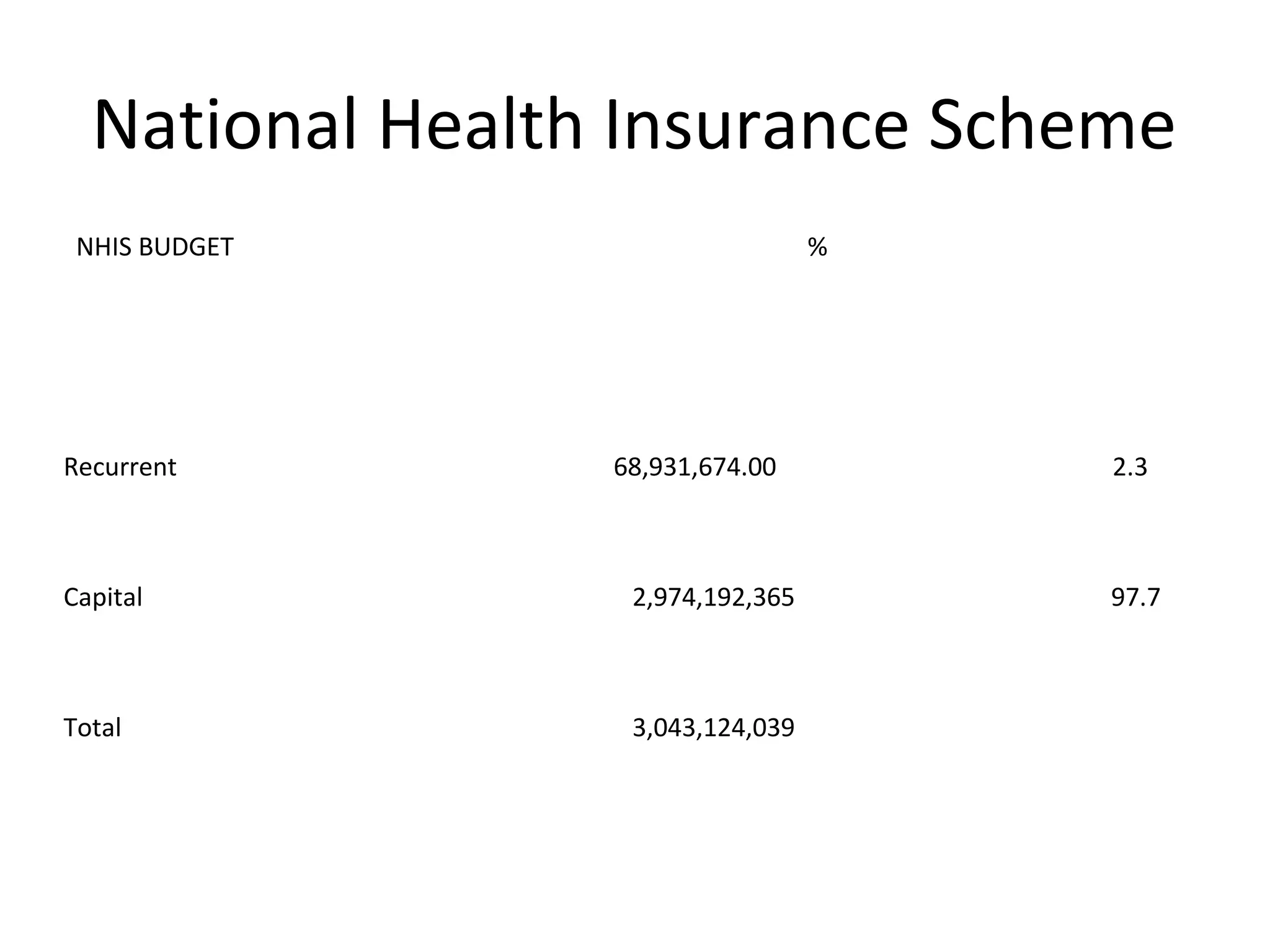
- Allocations to the National Primary Health Care Development Agency (NPHCDA) and Federal Ministry of Health (FMOH) focus on programs for women and children's health. However, funding remains inadequate compared to population needs.
- Additional funds from SURE-P were allocated, but long-term funding relies too heavily on infrastructure over service provision and training. Advocacy is needed to influence priority setting and budget planning.