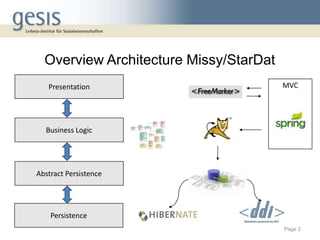
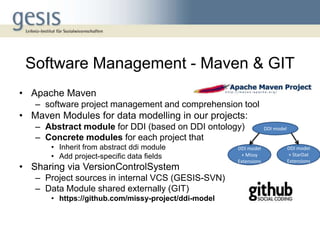
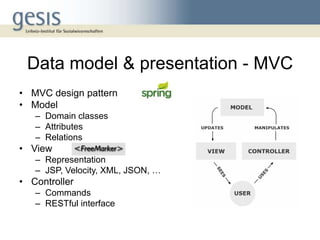
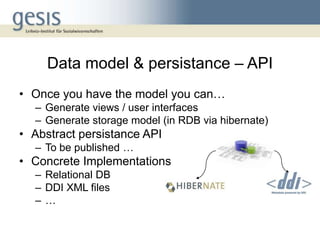
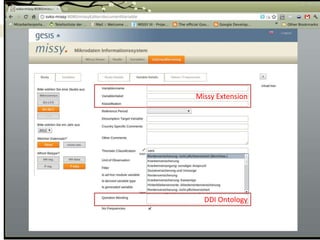
The document discusses using a model-view-controller (MVC) architecture to manage data modeling projects. It describes using an abstract data module based on the DDI ontology with concrete modules for each project that inherit and extend the abstract module. A RESTful interface is proposed to access resources identified by URIs. The abstract data model is implemented as domain classes with attributes and relations according to MVC and can generate views, storage models, and abstract persistence APIs. Extending the DDI ontology allows projects to add custom fields while maintaining compatibility. Sharing source code and data modules between projects via version control is described.