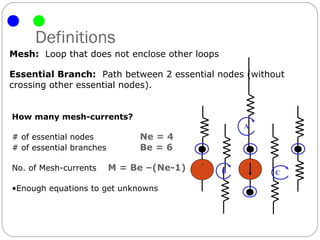
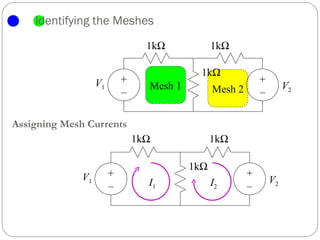
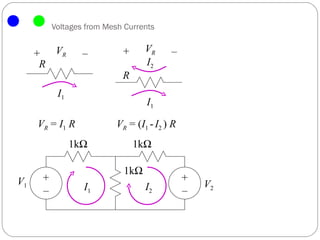
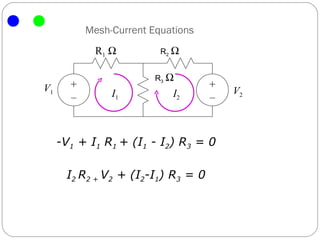
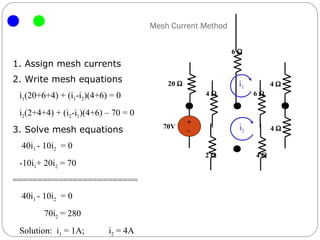
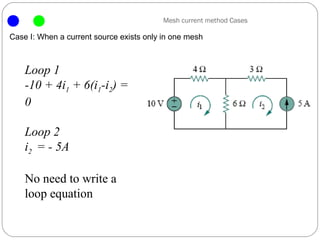
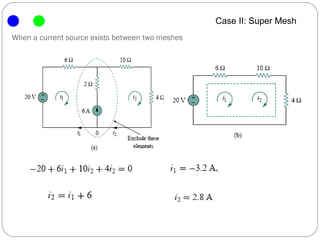
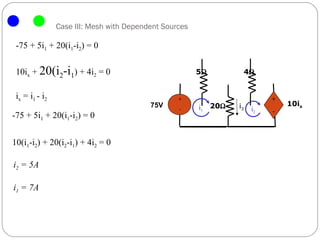
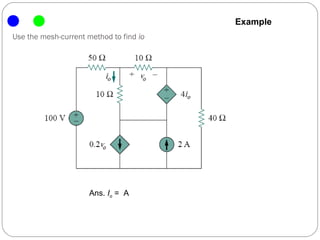
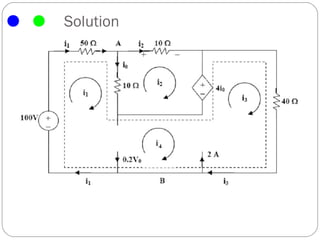
The document introduces the mesh-current method for solving electric circuits. It defines key terms like mesh and essential branch. The steps of the mesh-current method are: 1) identify meshes, 2) assign a current to each mesh, 3) write Kirchhoff's voltage law equations for each mesh in terms of the mesh currents, and 4) solve the resulting system of equations. Examples are provided to demonstrate how to apply the method to circuits with different elements like dependent sources.