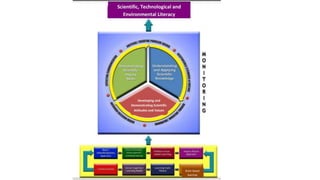
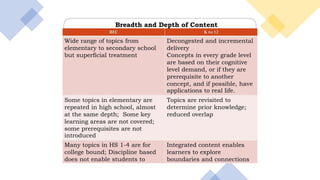
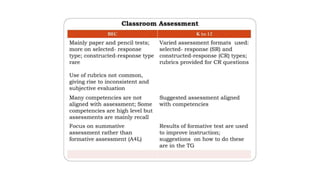
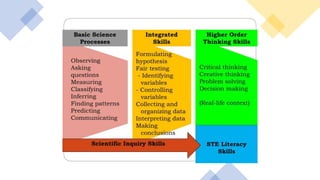
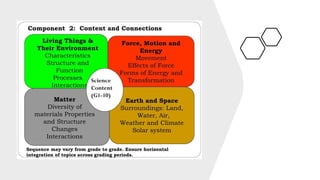
The document discusses the Philippine science education system. It aims to develop scientific literacy to prepare students to be informed citizens who can make judgments regarding scientific applications. The science curriculum recognizes the role of science in everyday life and promotes linking science and technology with cultural heritage. The K to 12 science curriculum envisions developing students who are problem solvers, responsible, innovative, informed decision makers, and effective communicators through learning science, skills, and attitudes using multi-disciplinary and issue-based approaches. Trends in math and science studies like TIMSS and PISA evaluate education systems worldwide to help improve teaching and learning in these areas.