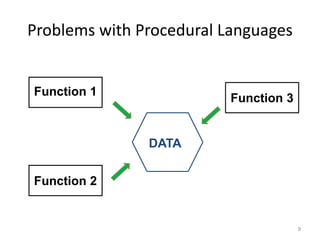
This document provides an overview of different programming paradigms and the evolution of programming languages. It discusses the procedural paradigm and some of its problems, including lack of data ownership, difficulty maintaining data integrity, and resource deallocation issues. The next session will cover object-oriented programming concepts as an alternative paradigm.



![Sample C program
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
#define SIZE 5
struct bot { int xpos; int ypos; };
struct bot initialize(struct bot b);
int main()
{
struct bot robots[SIZE];
int x;
srandom((unsigned)time(NULL));
for(x=0;x<SIZE;x++)
{ 7
robots[x] = initialize(robots[x]);
printf("Robot %d: Coordinates:
%d,%dn", x+1,robots[x].
xpos,robots[x].ypos);
}
return(0);
}
struct bot initialize(struct bot b)
{
int x,y;
x = random();
y = random();
x%=20;
y%=20;
b.xpos = x;
b.ypos = y;
return(b); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1ppvsoo-221005051659-1f104941/85/1_PP_vs_OO-ppt-7-320.jpg)