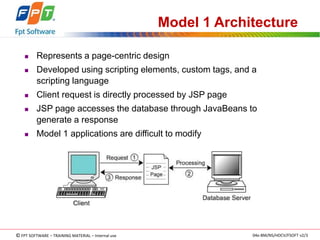
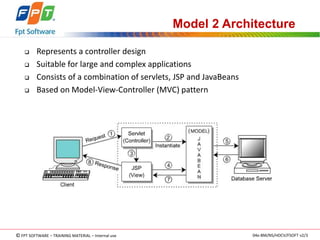
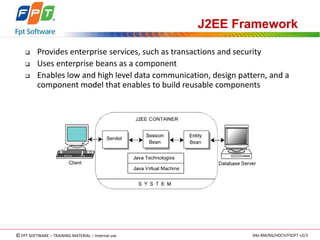
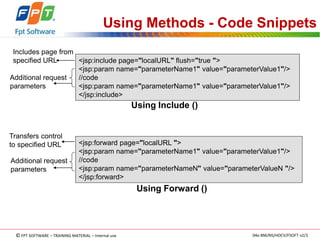
The document discusses JSP application models and frameworks. It describes the Model 1 and Model 2 architectures. Model 1 uses scripting elements and is page-centric, while Model 2 follows the MVC pattern and is suitable for complex applications. The J2EE framework provides enterprise services and uses components like servlets, session beans, and entity beans. Exceptions can occur during translation or at request time, and unhandled exceptions are forwarded to an error page.