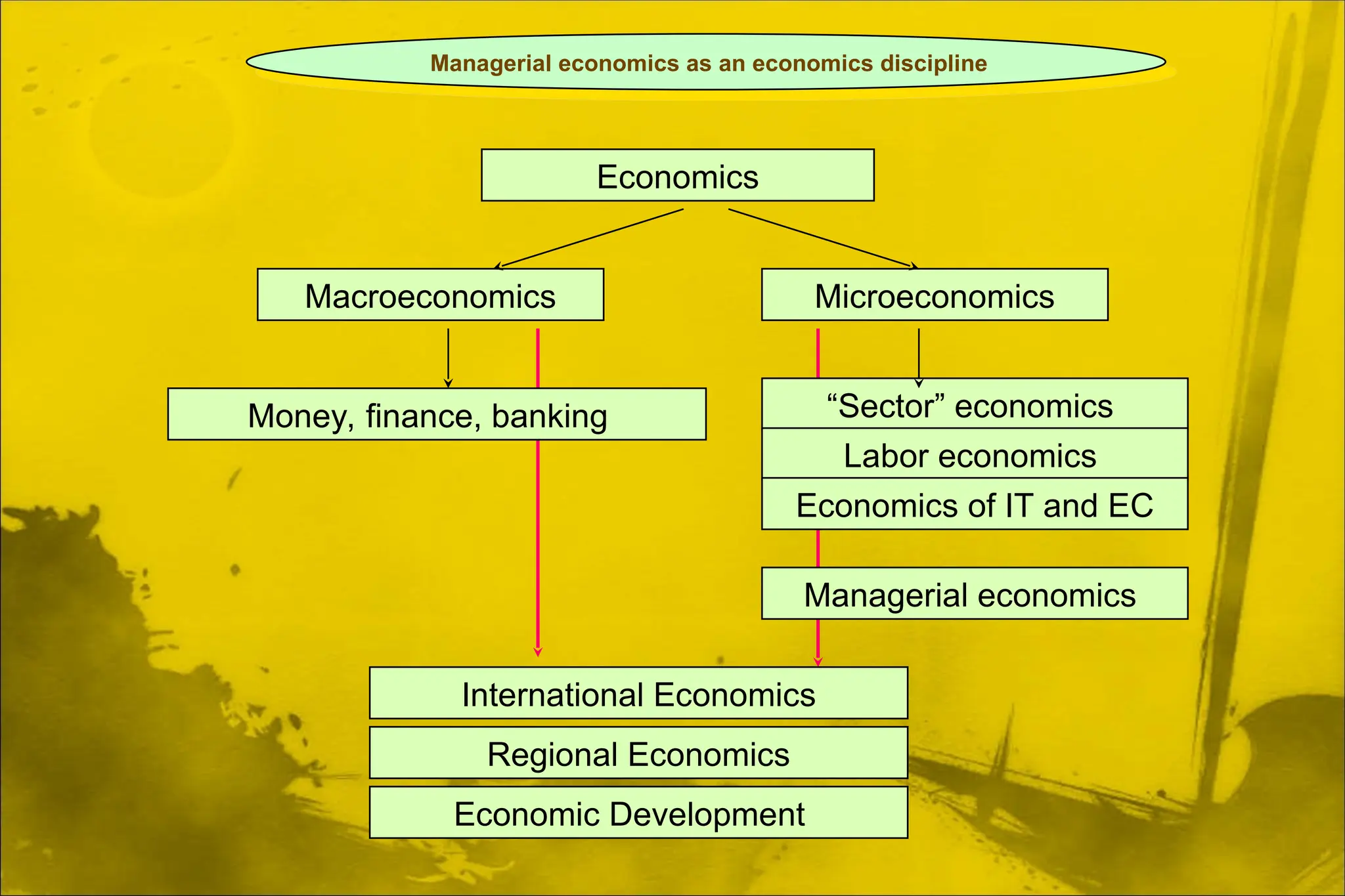
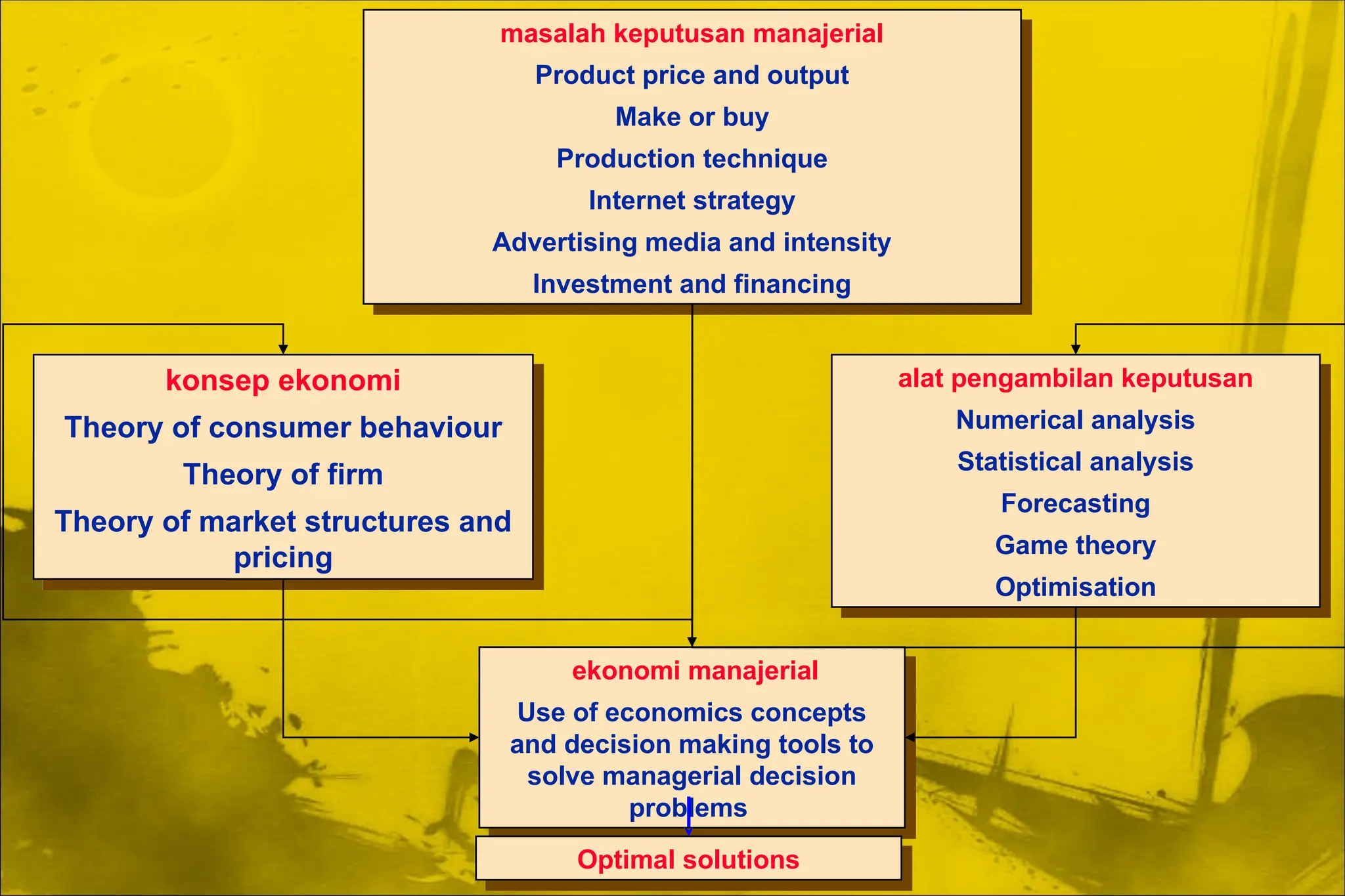
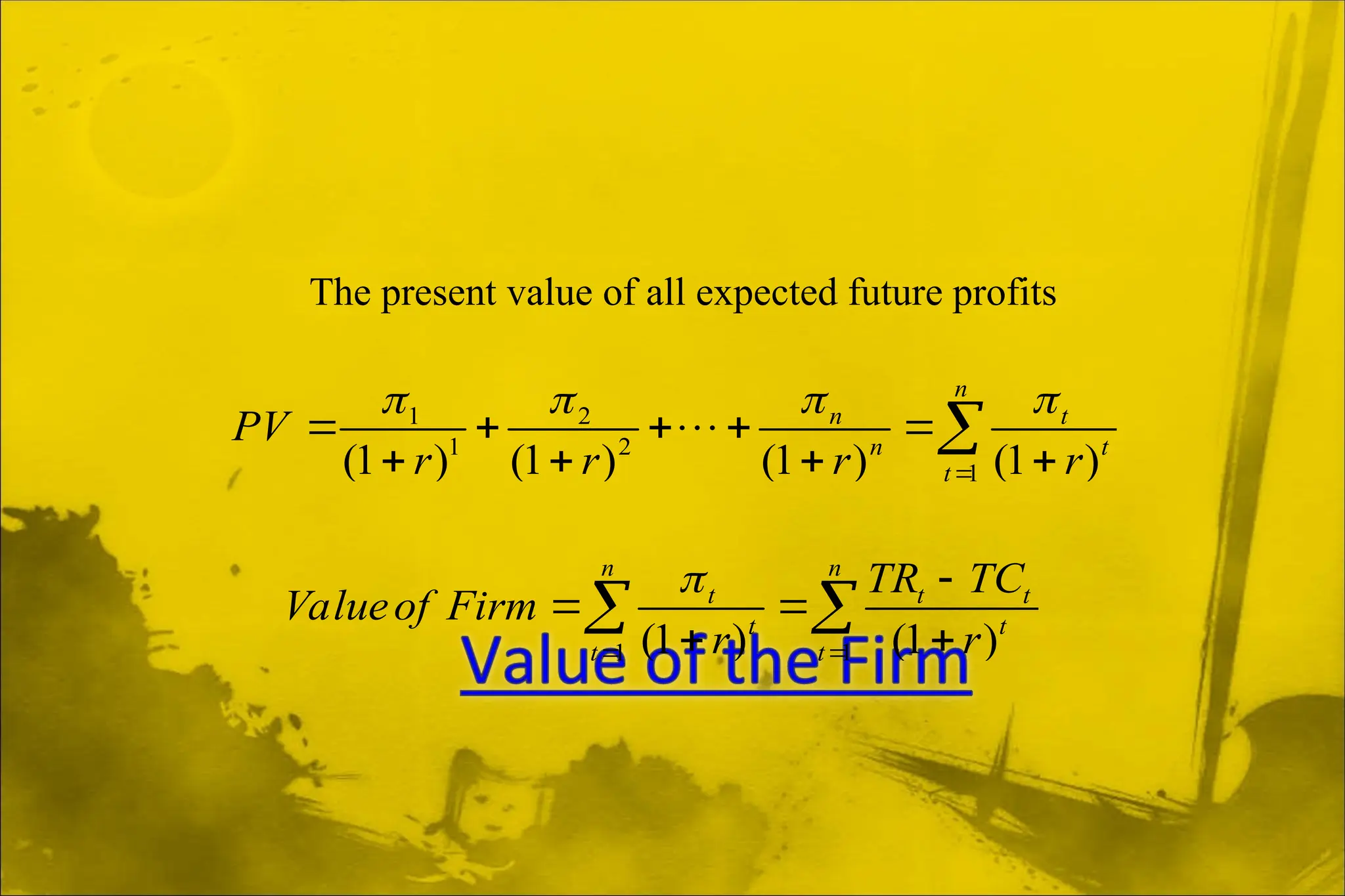
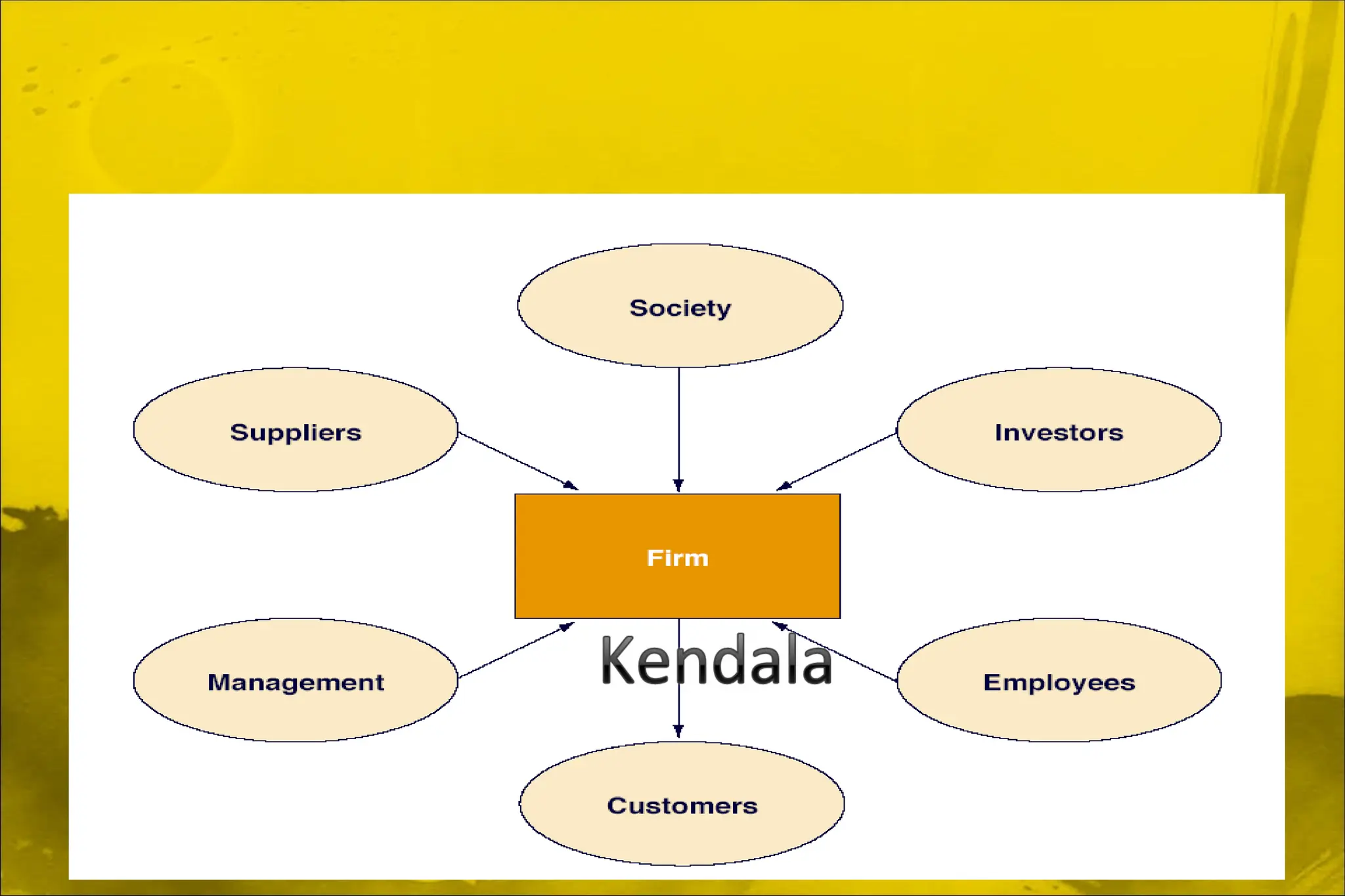
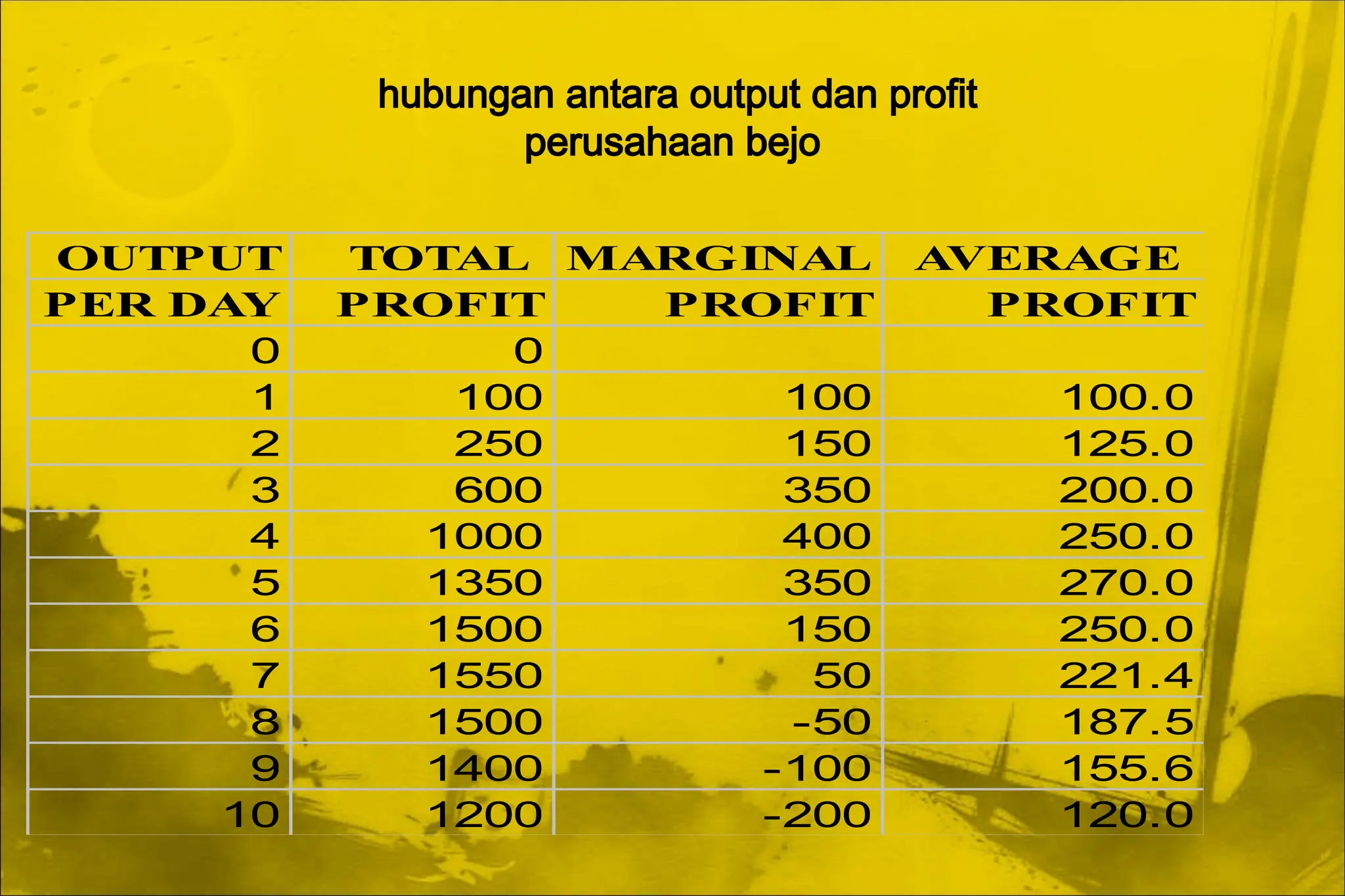
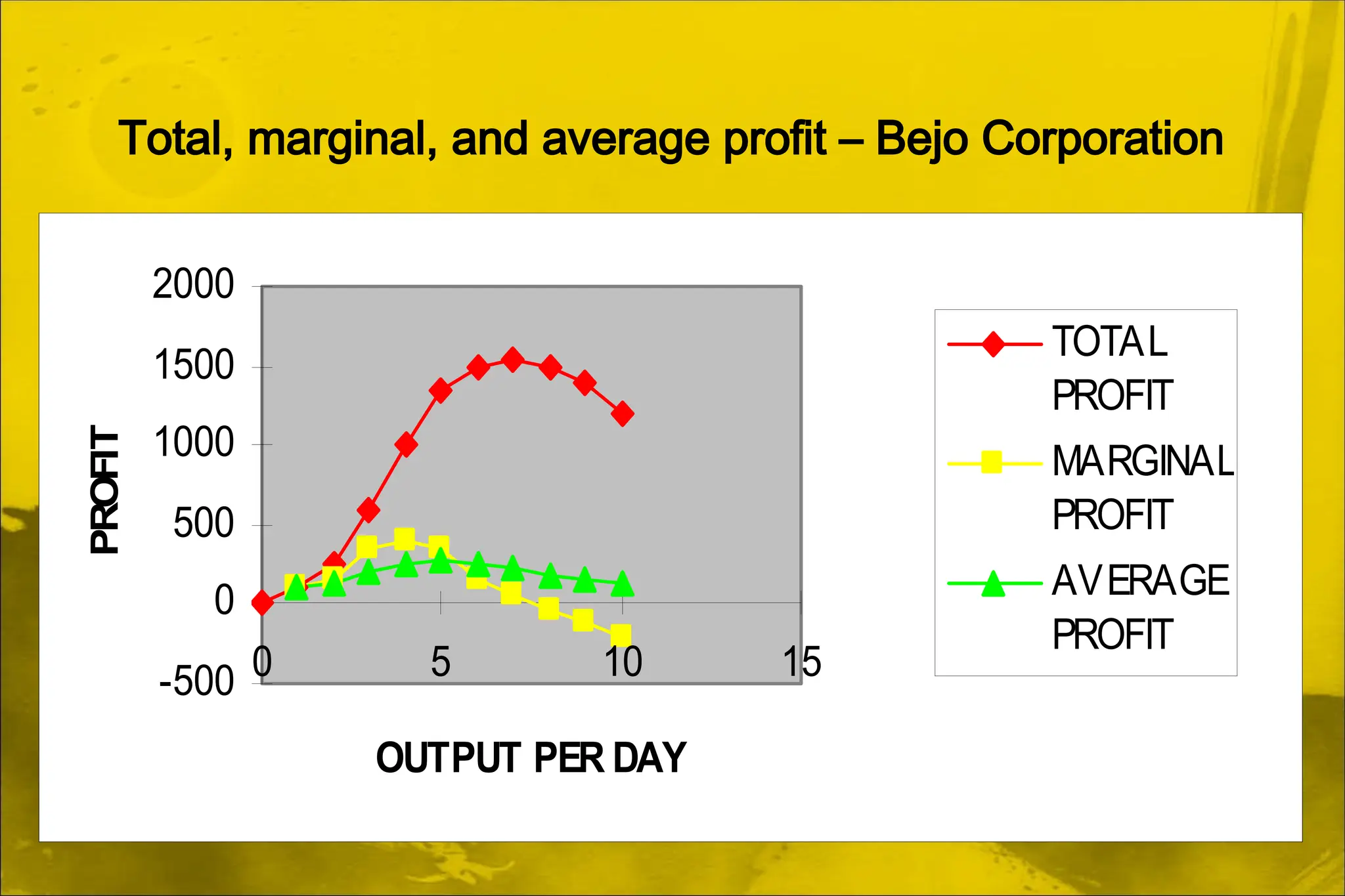
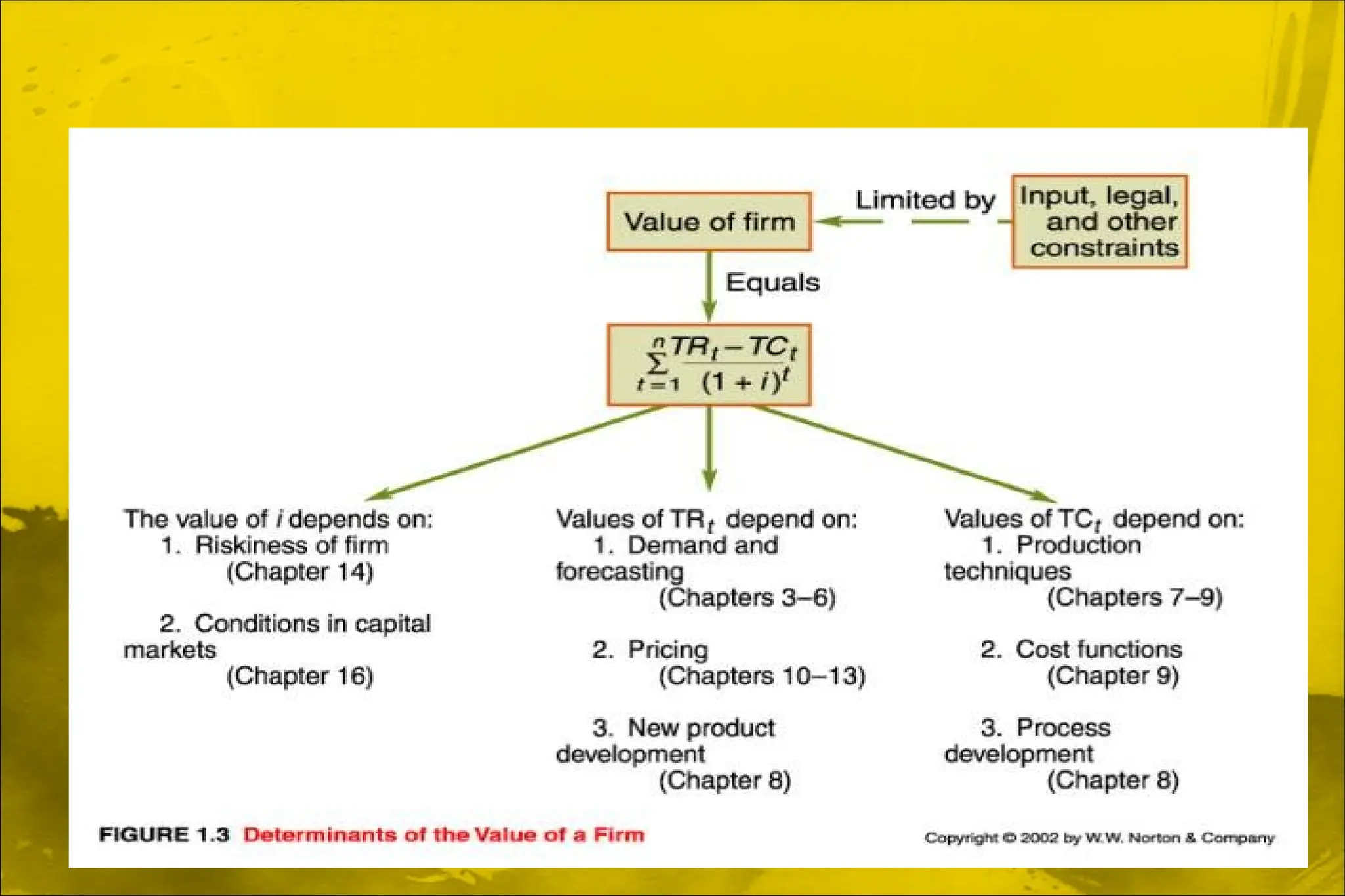
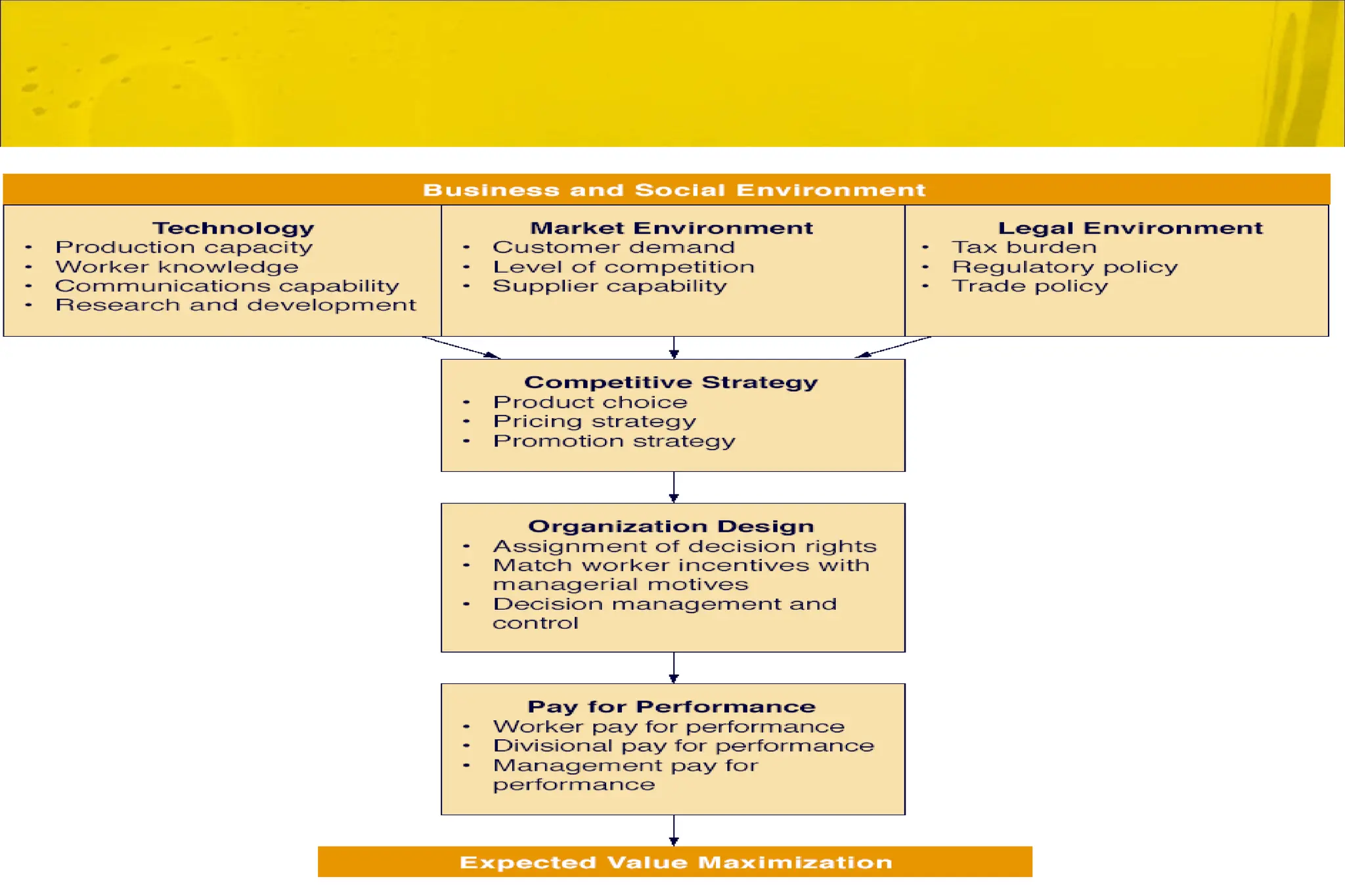
Dokumen ini membahas aplikasi teori ekonomi dan alat pengambilan keputusan dalam manajemen untuk mencapai tujuan organisasi secara lebih efektif. Ini mencakup konsep-konsep seperti maksimisasi keuntungan, perilaku konsumen, dan proses pengambilan keputusan. Manajerial ekonomi berperan penting dalam memecahkan masalah keputusan manajerial melalui analisis dan optimasi.