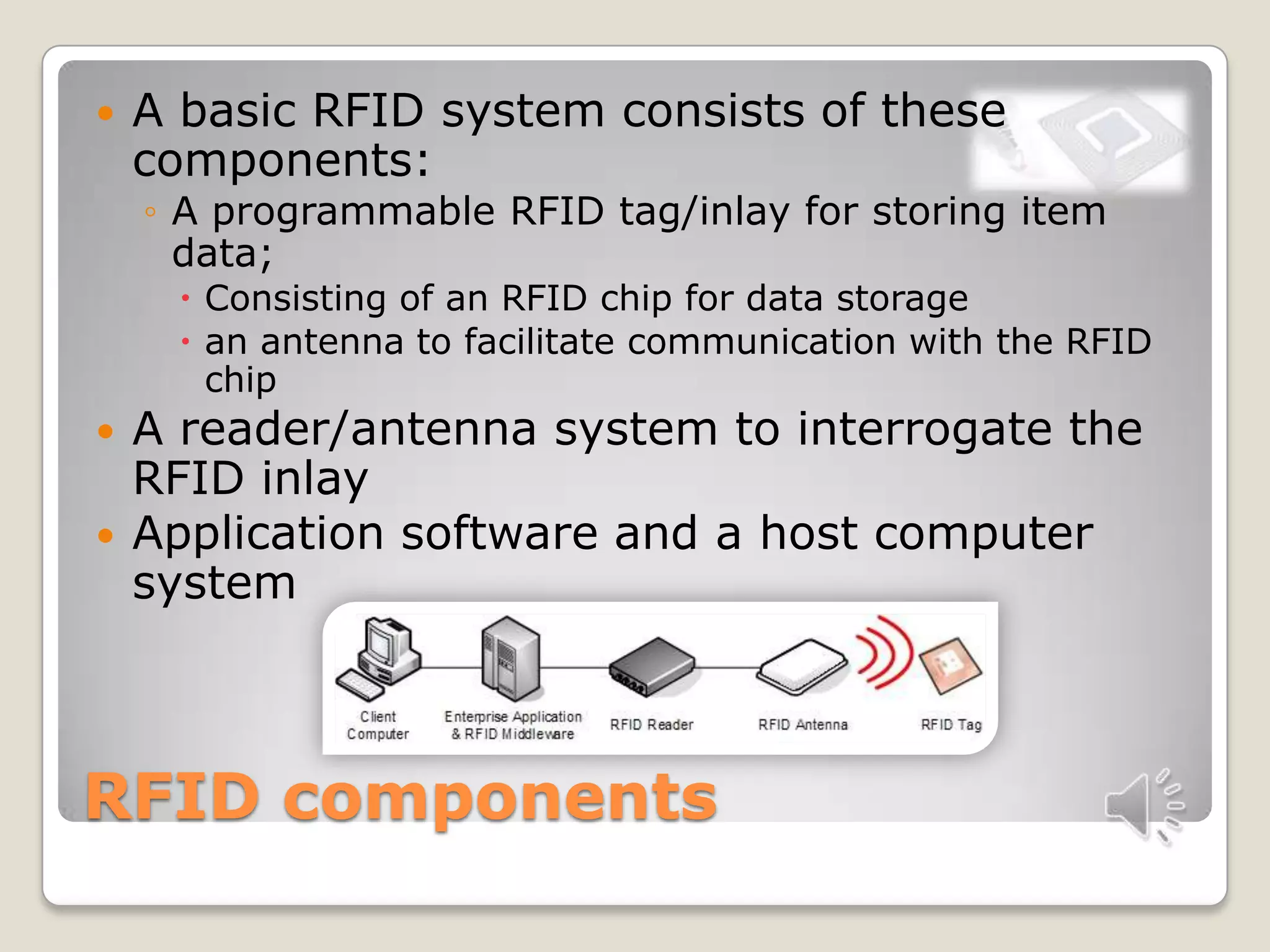
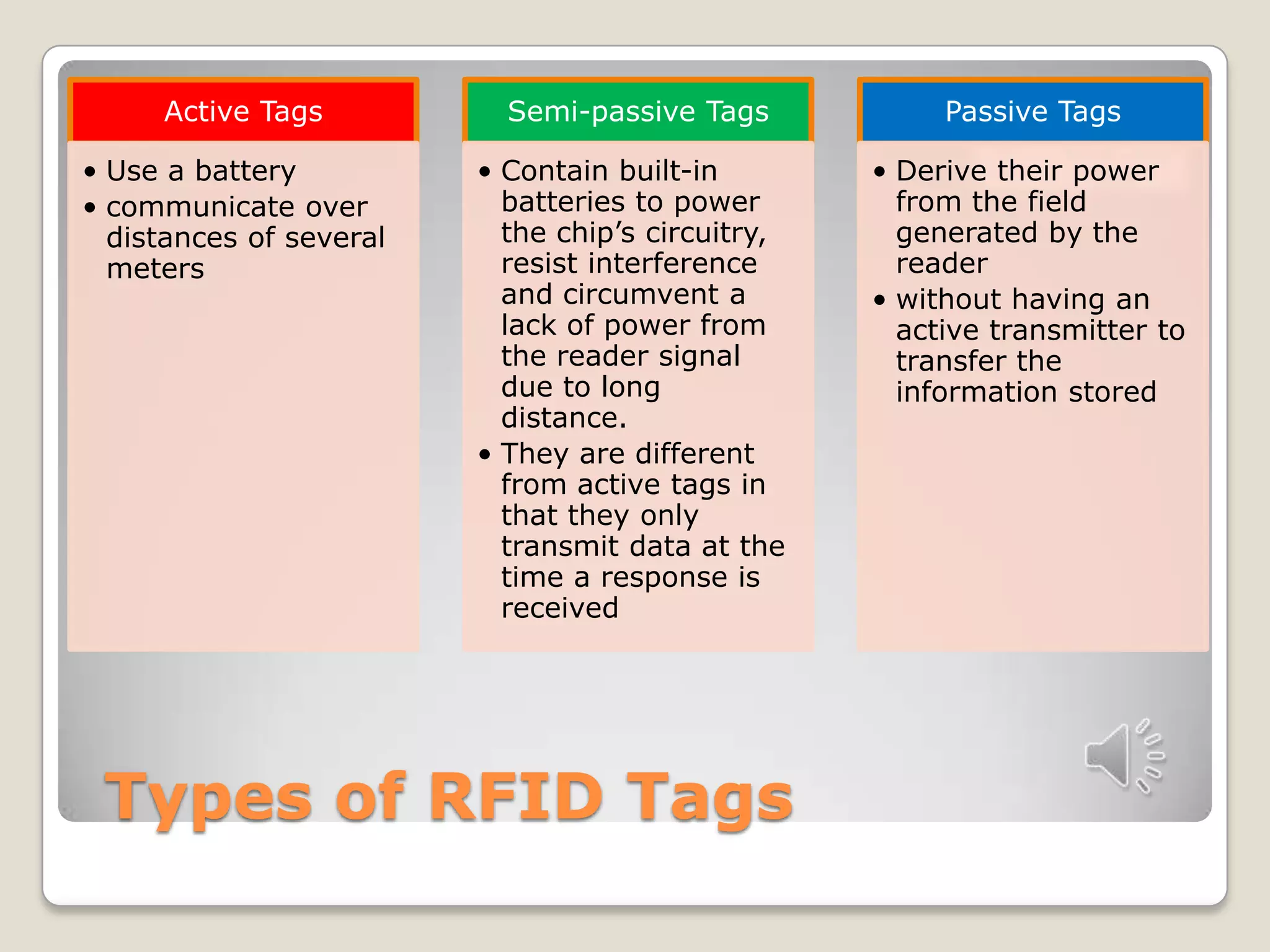
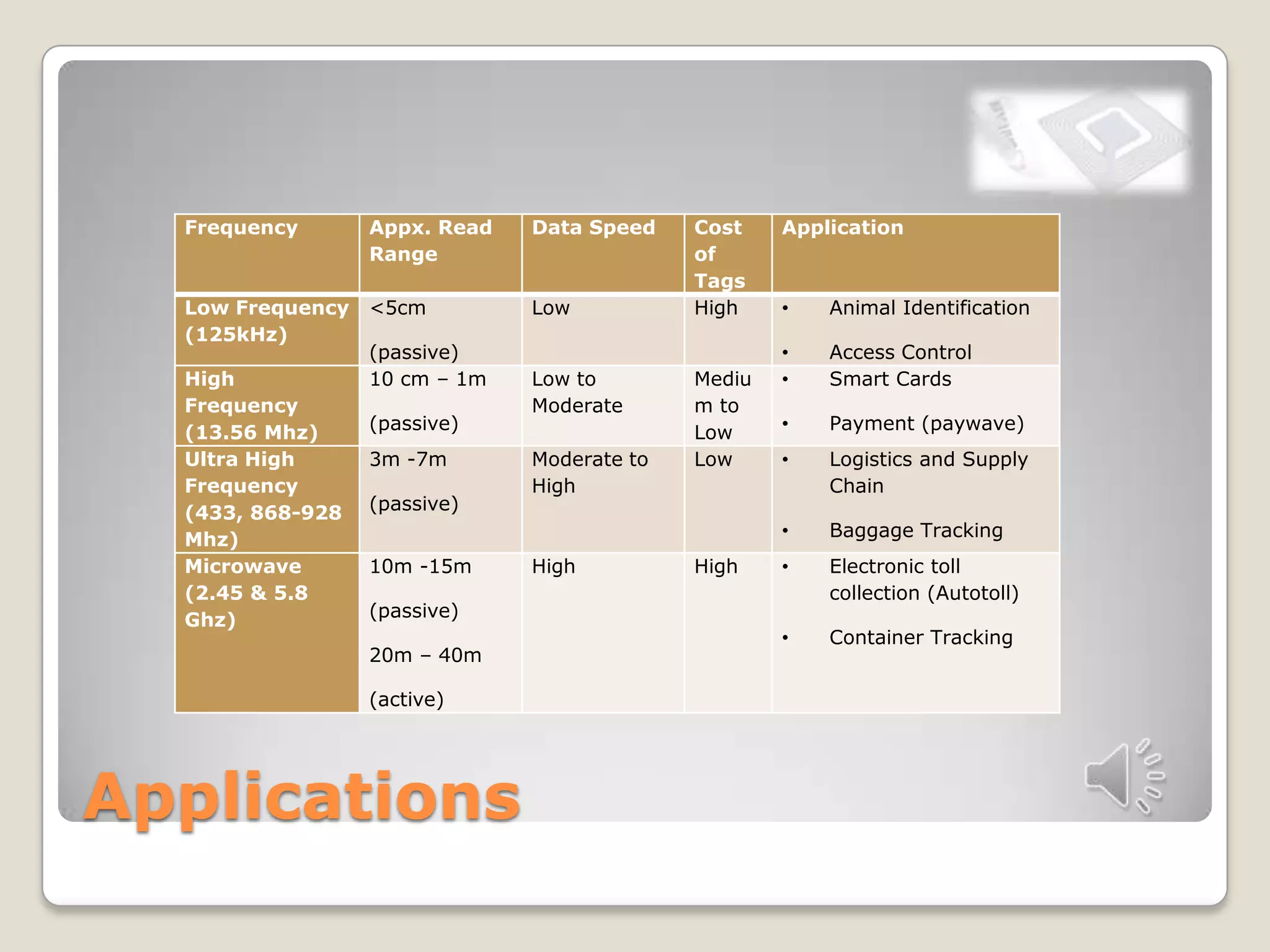
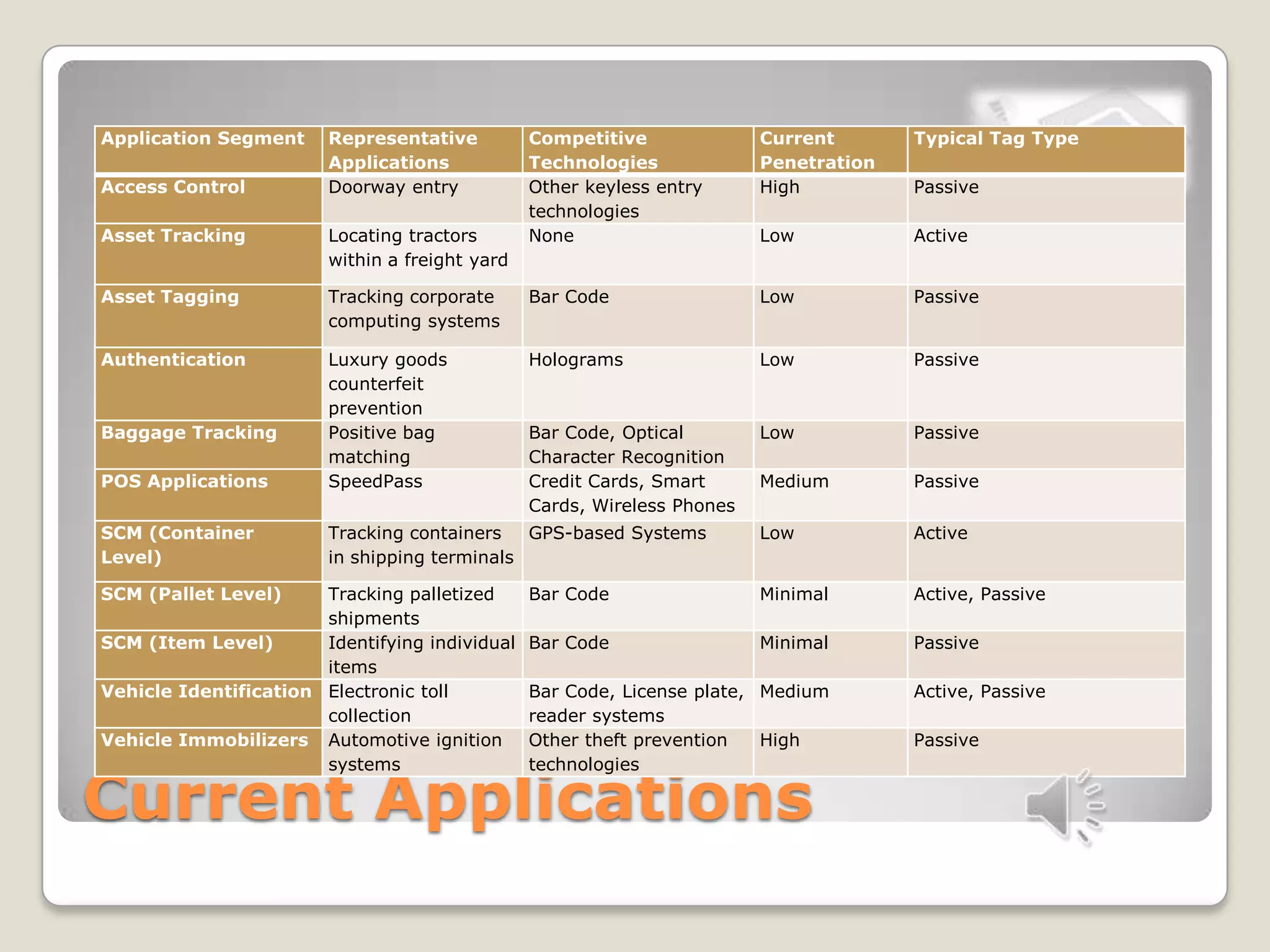
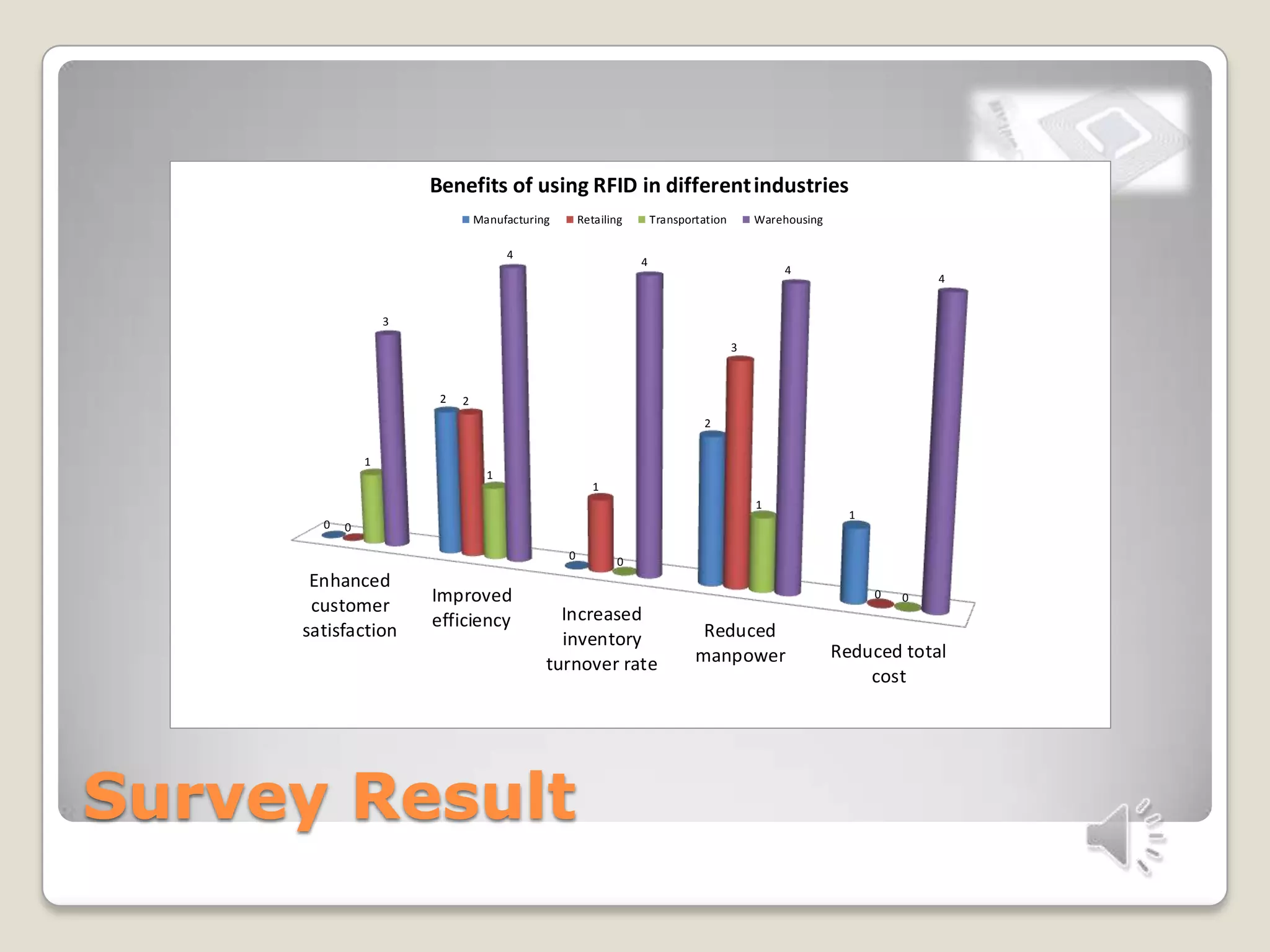
This document discusses RFID technology and its applications. It defines RFID and its components, including tags, readers, and antennas. It describes the different types of tags and provides examples of current RFID applications in various industries like retail, transportation, and supply chain management. The document also summarizes the results of an online survey on RFID benefits and presents opportunities for further development and use in medical and library settings.