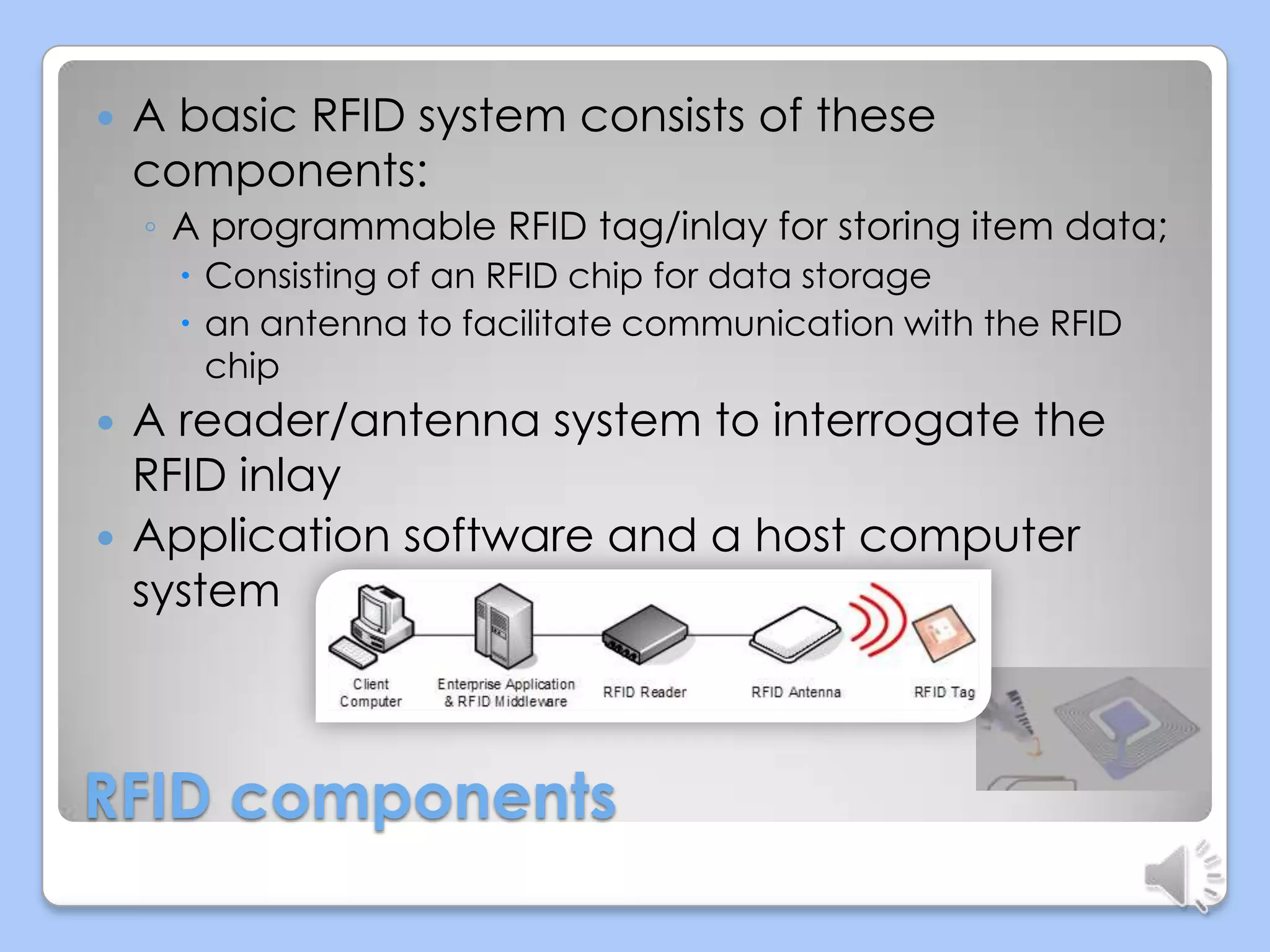
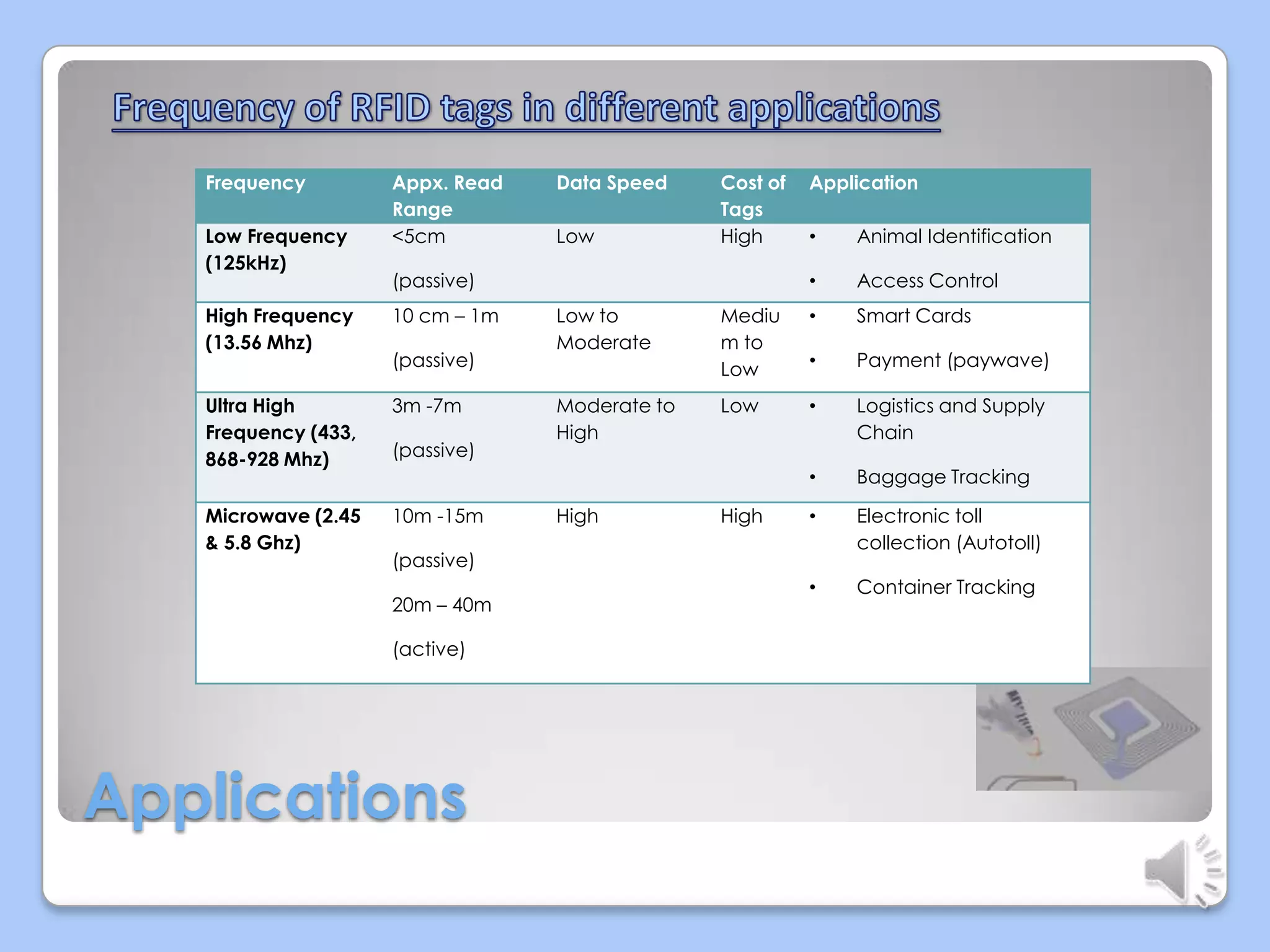
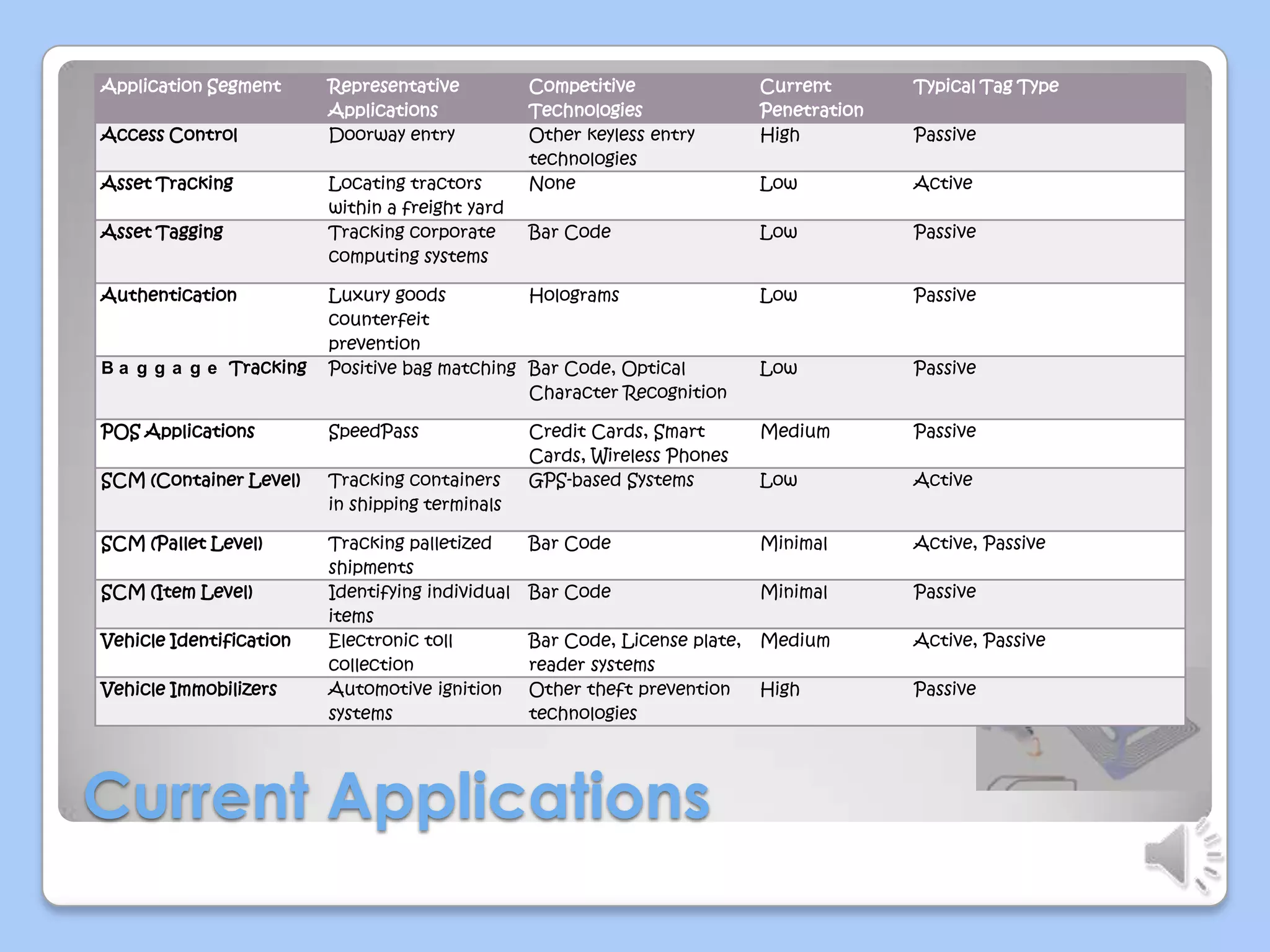
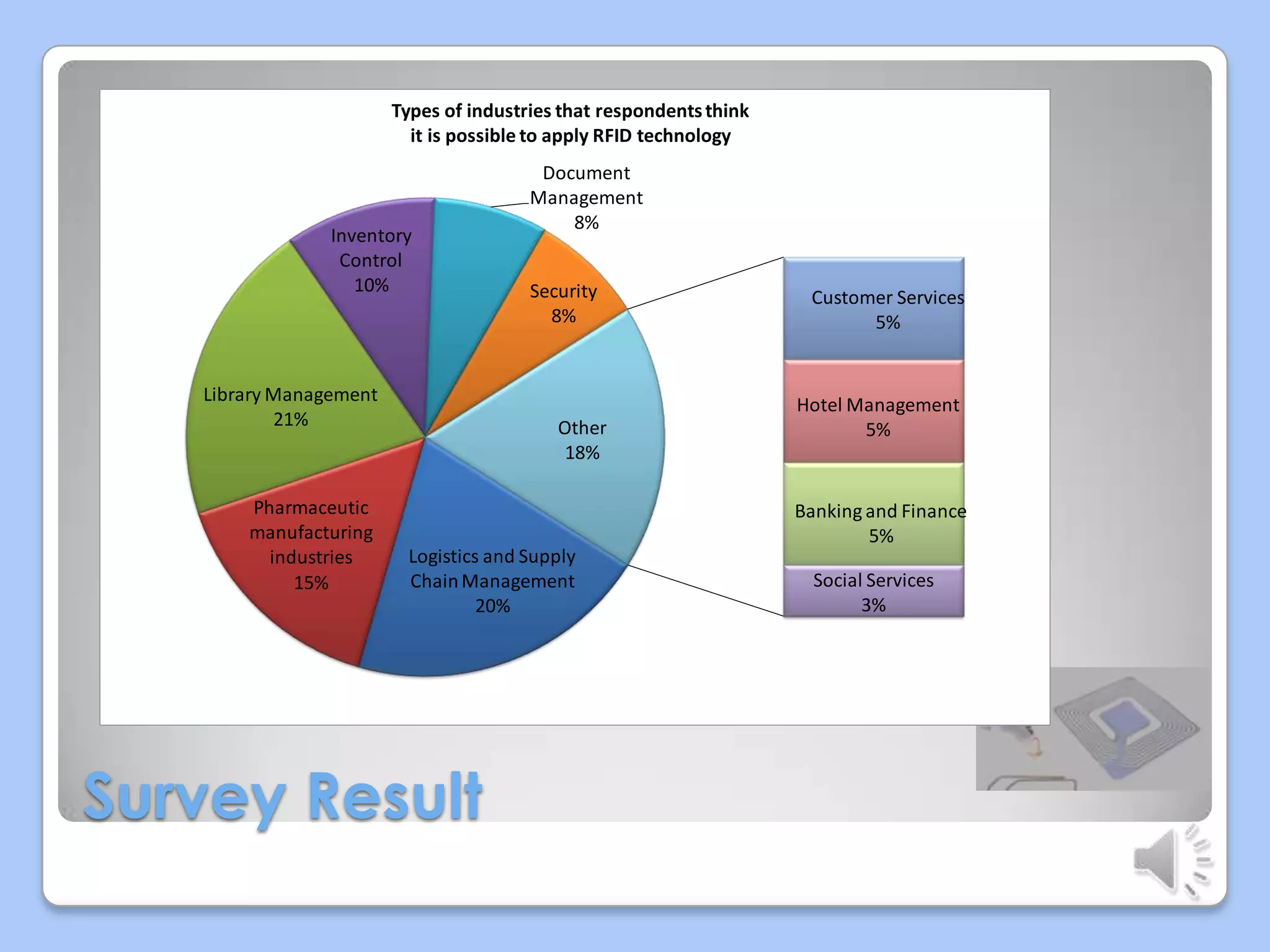
This document discusses radio frequency identification (RFID) technology. It describes the basic components of an RFID system including RFID tags, readers, and application software. It outlines the three main types of RFID tags and discusses their typical read ranges and applications. The document also provides examples of current RFID applications in various industries and presents results of a survey on possible areas for future RFID use. It concludes that RFID provides benefits over barcodes but also faces challenges related to costs and standardization.