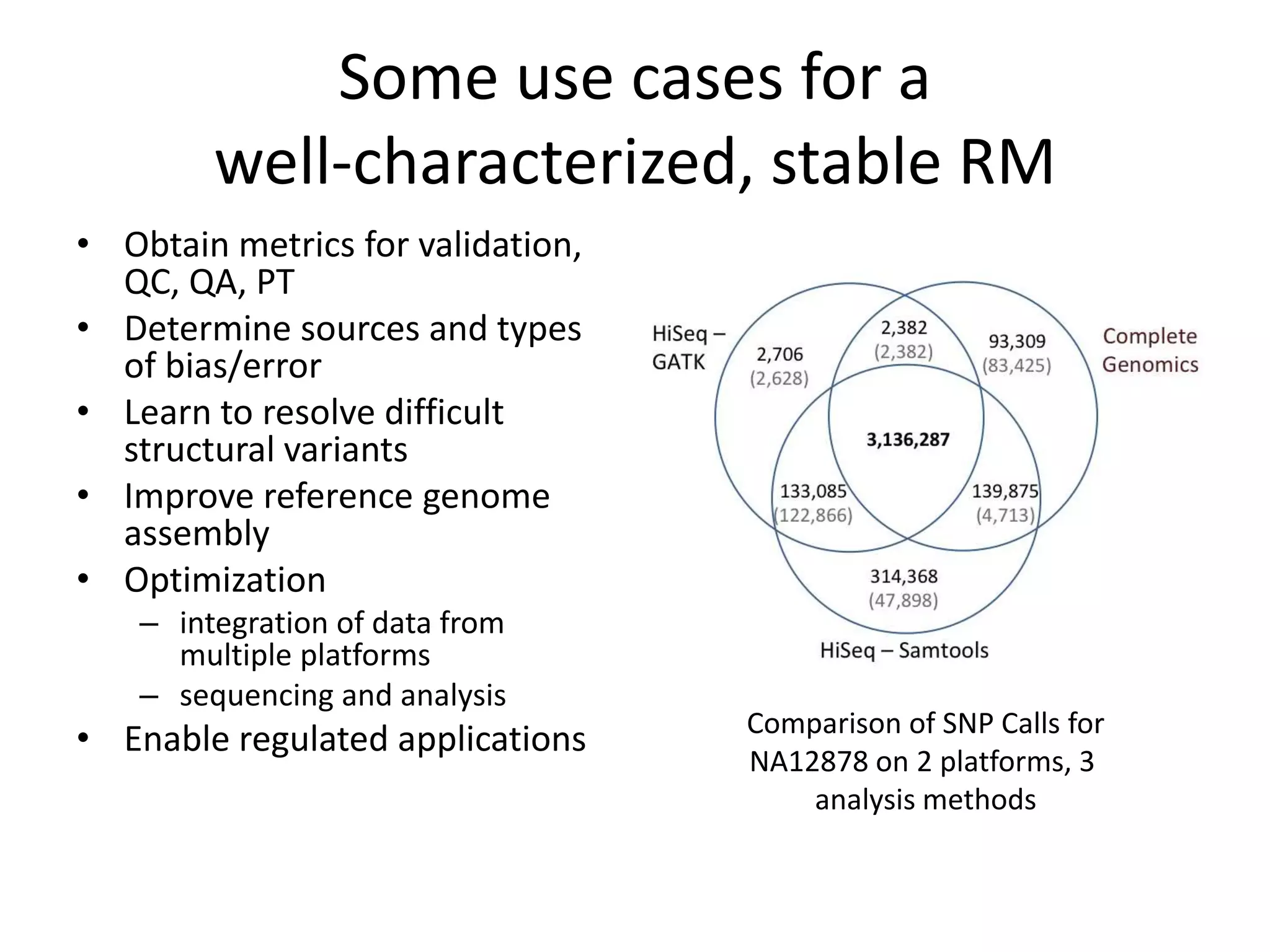
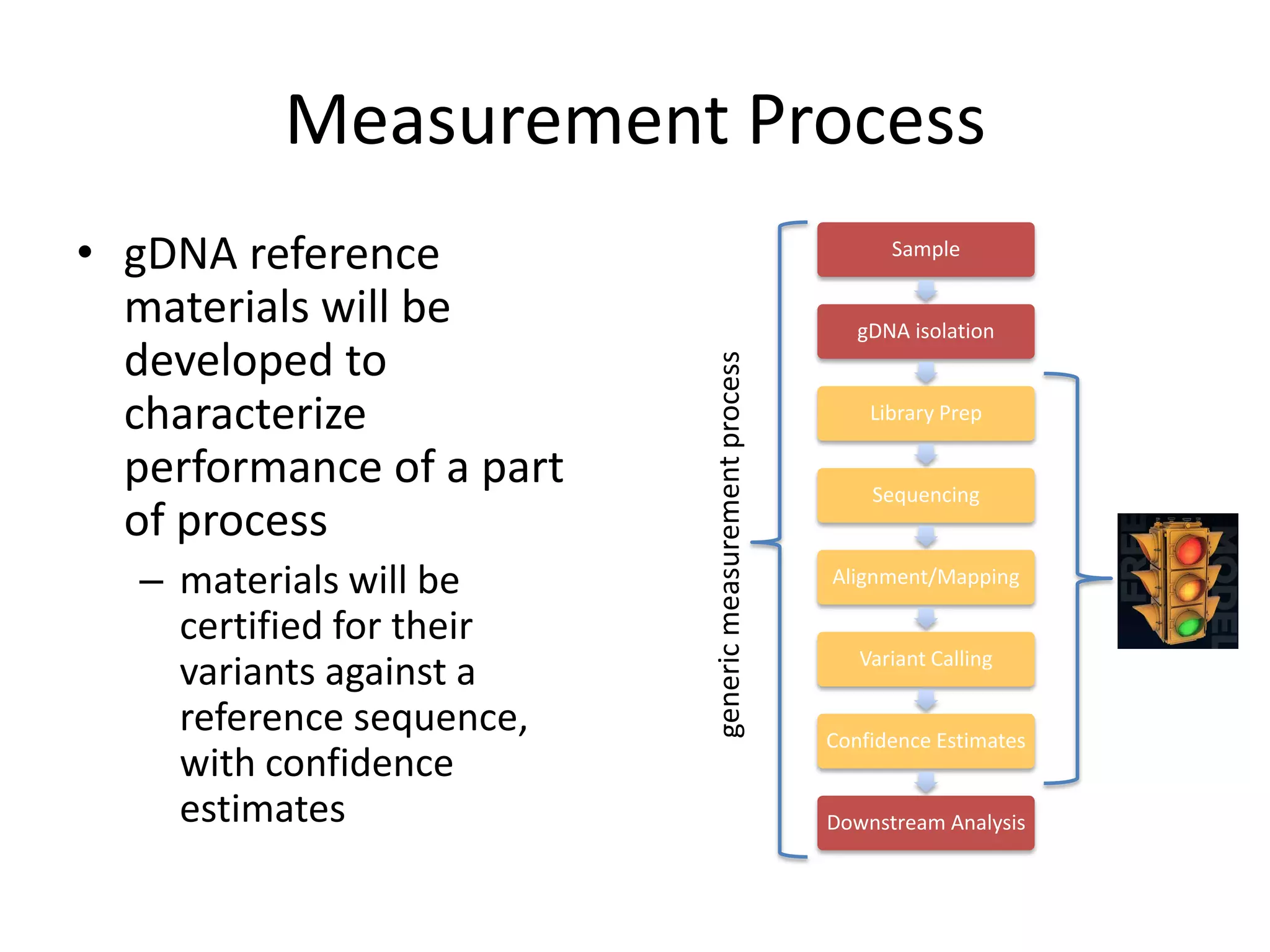
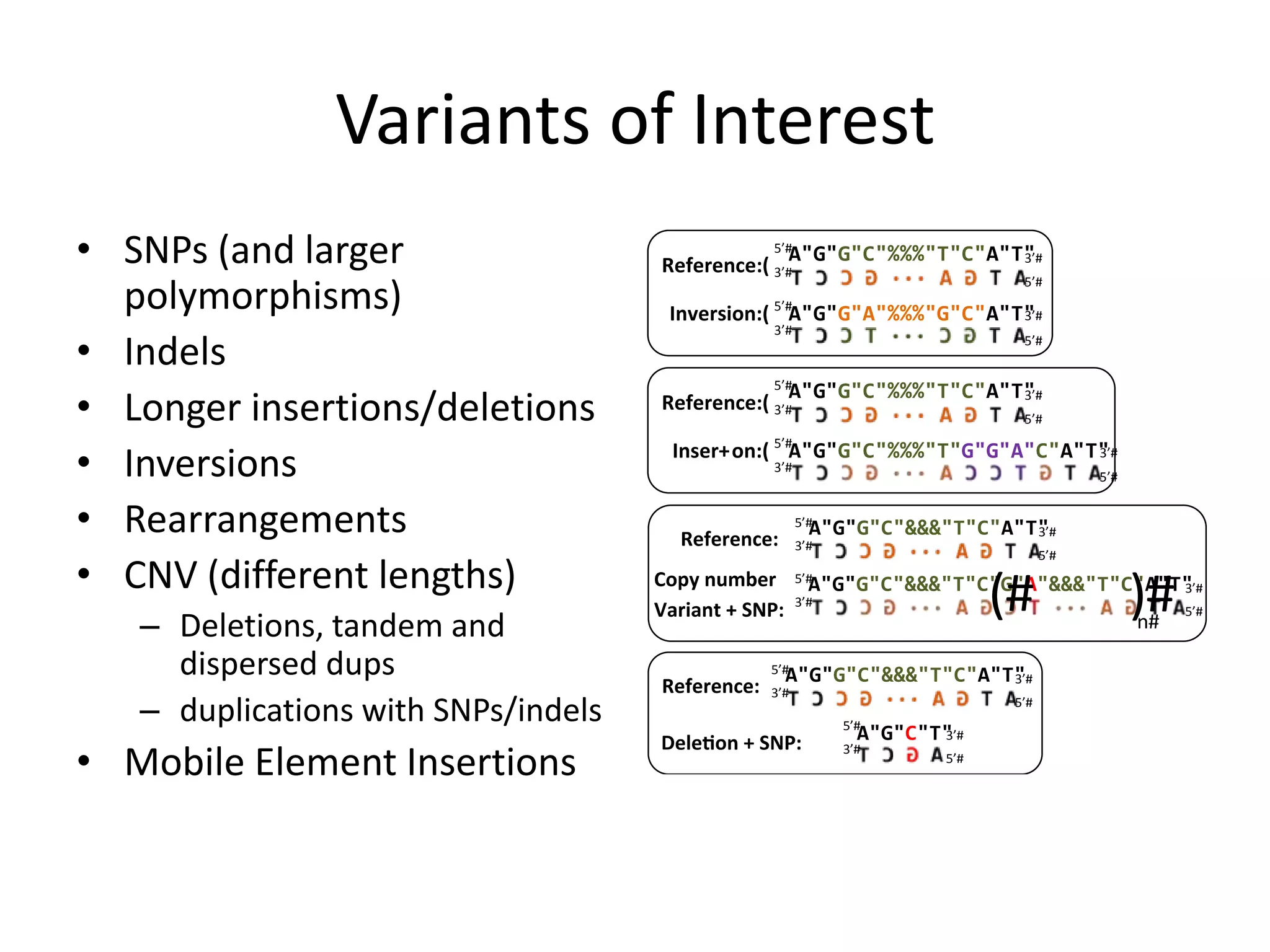
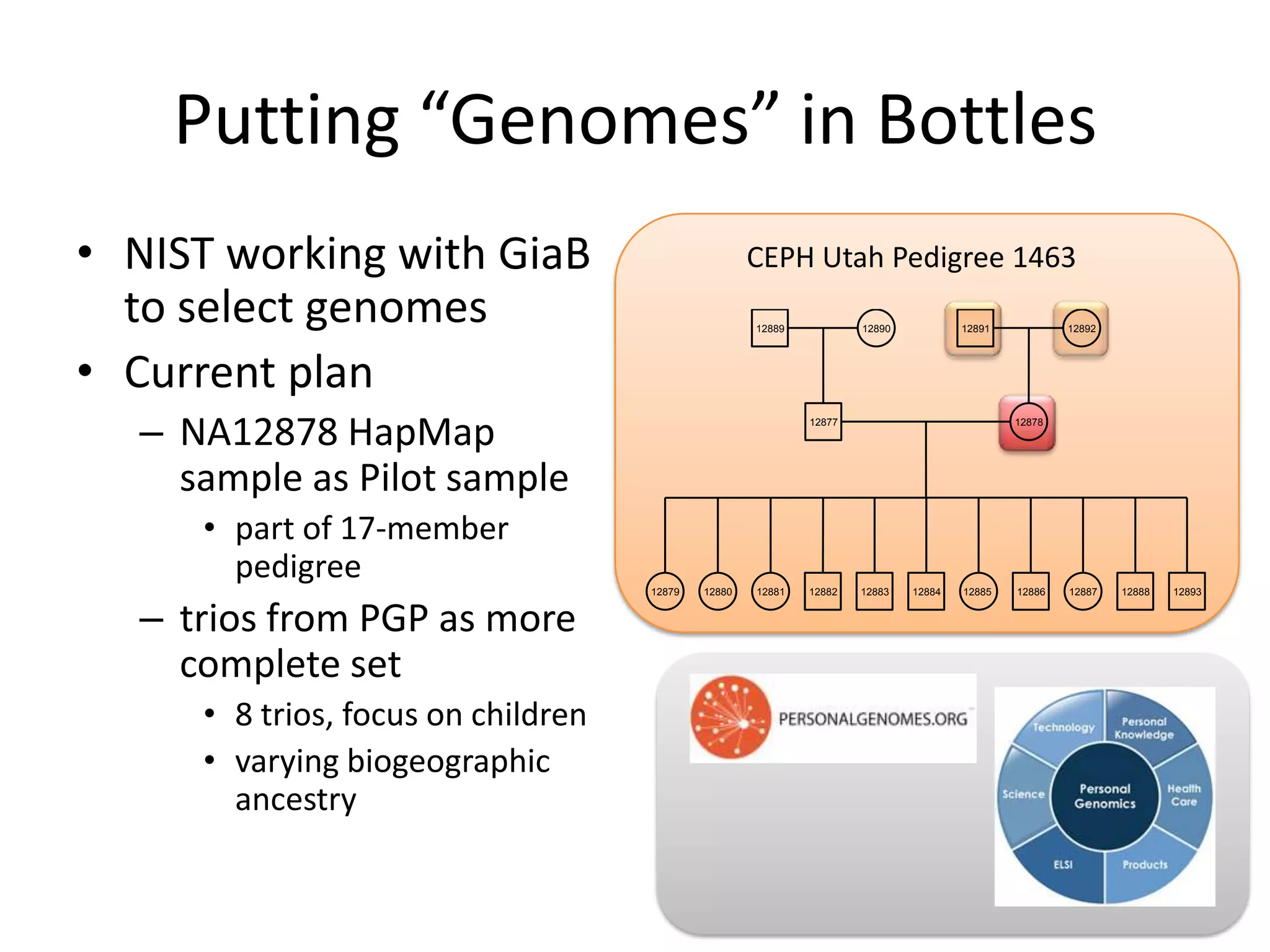
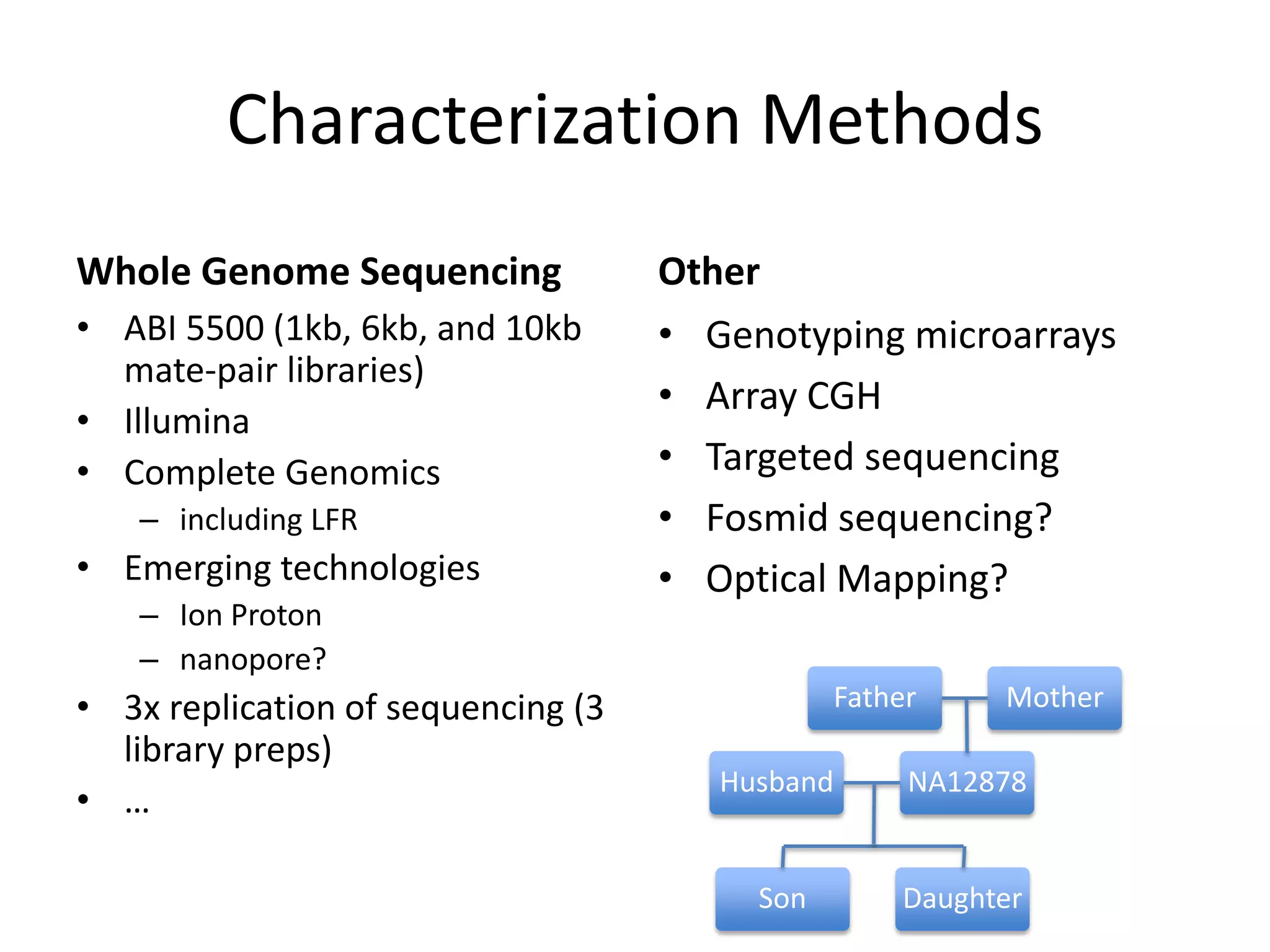
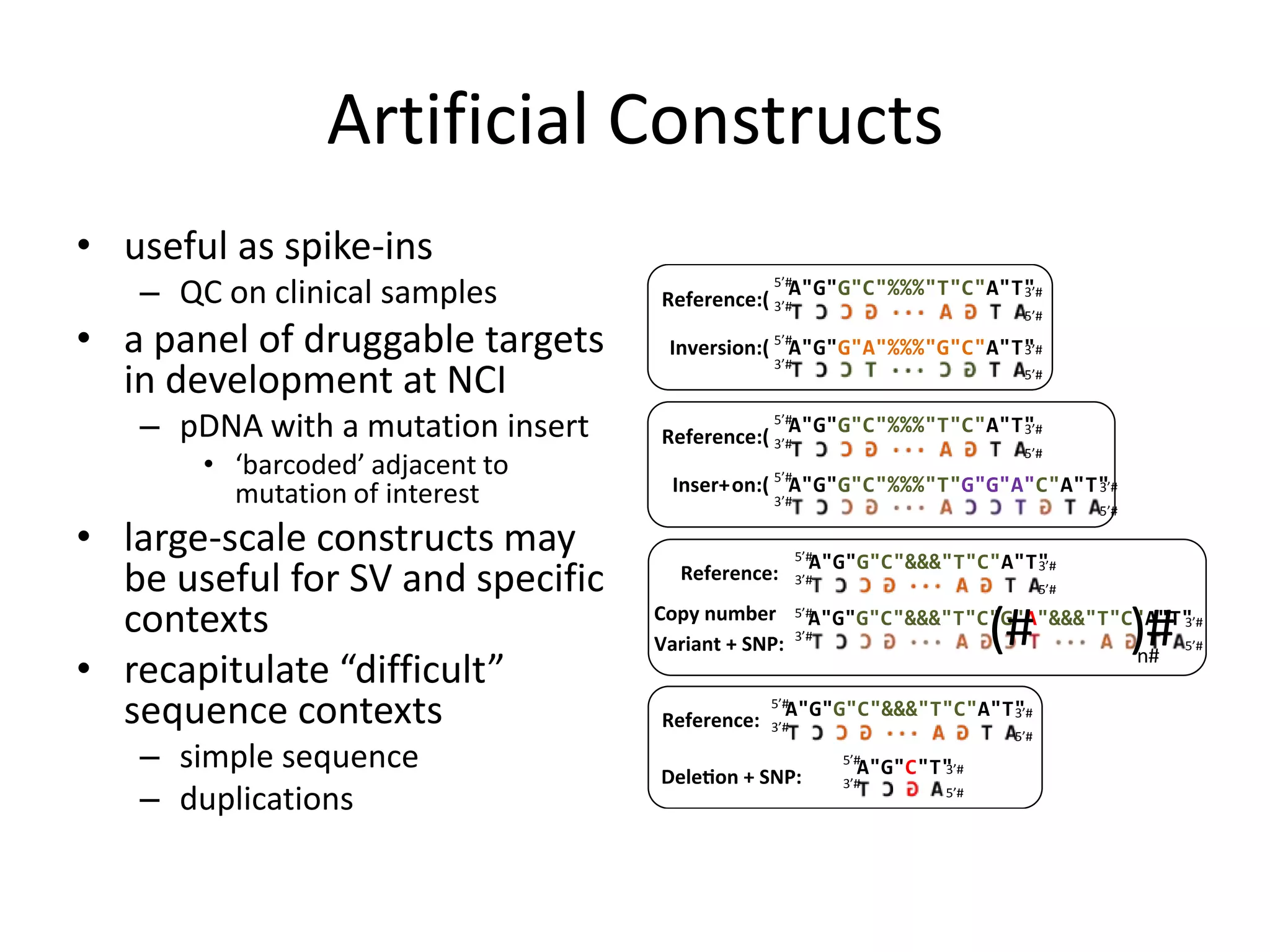
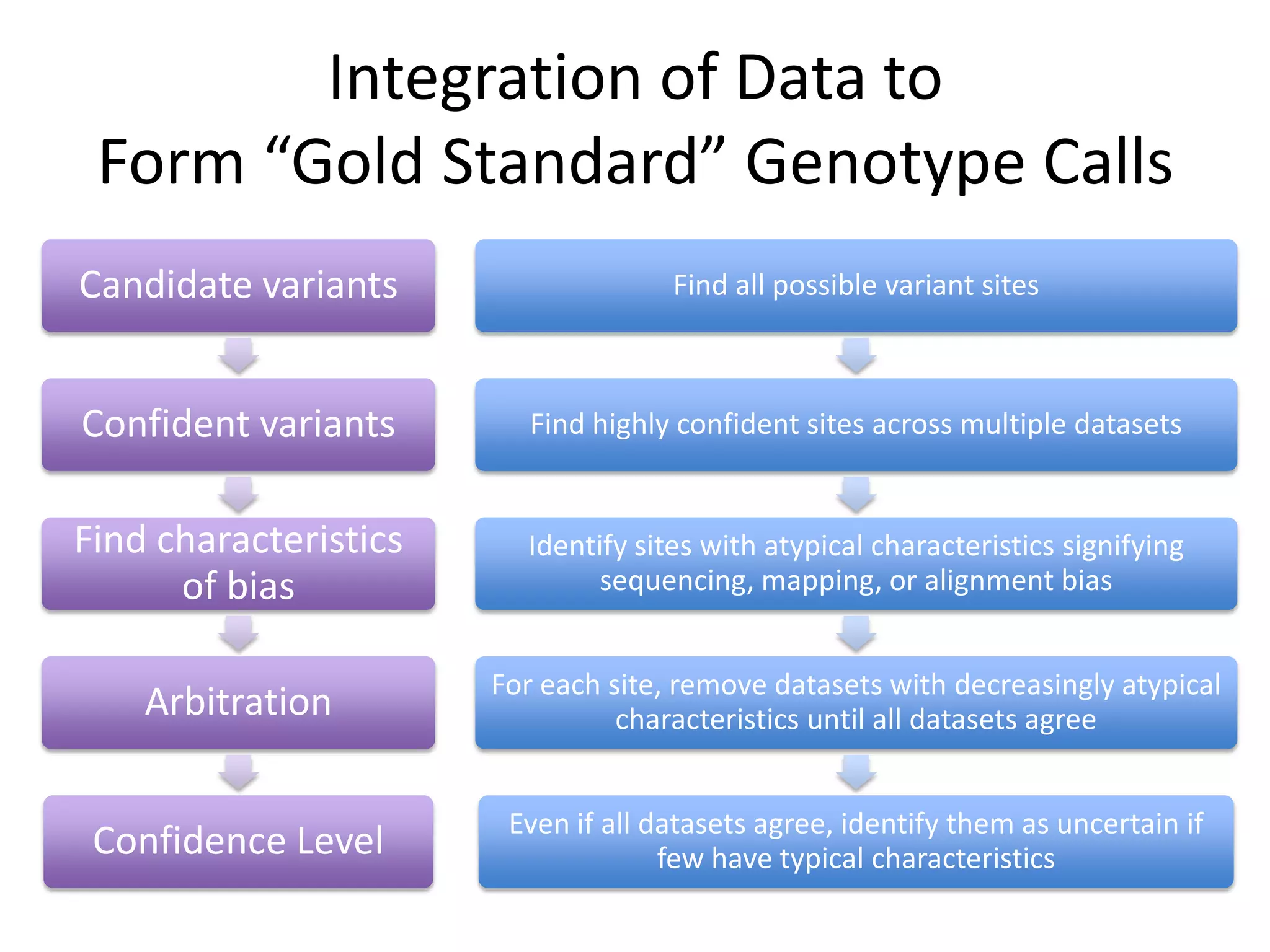
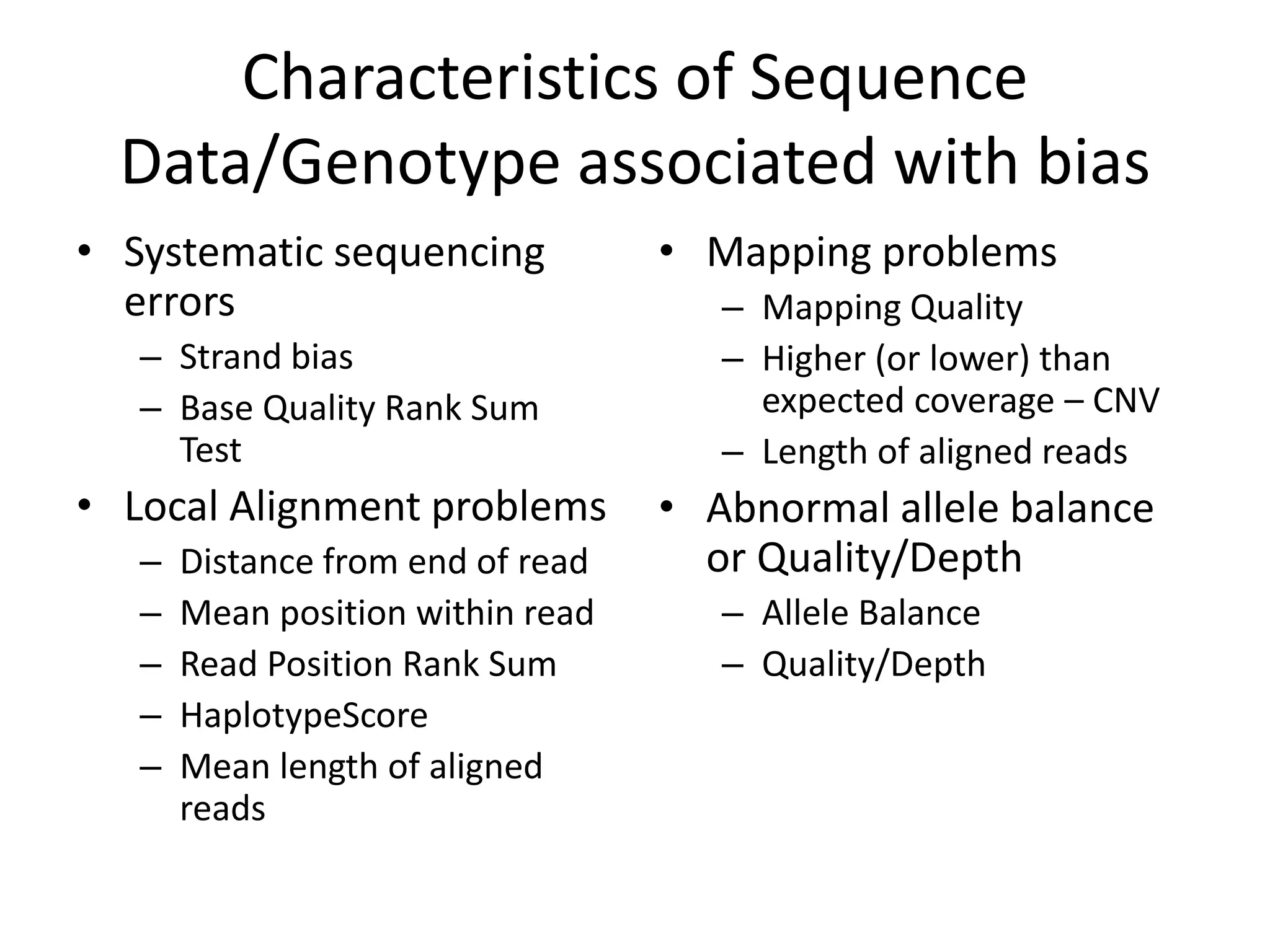
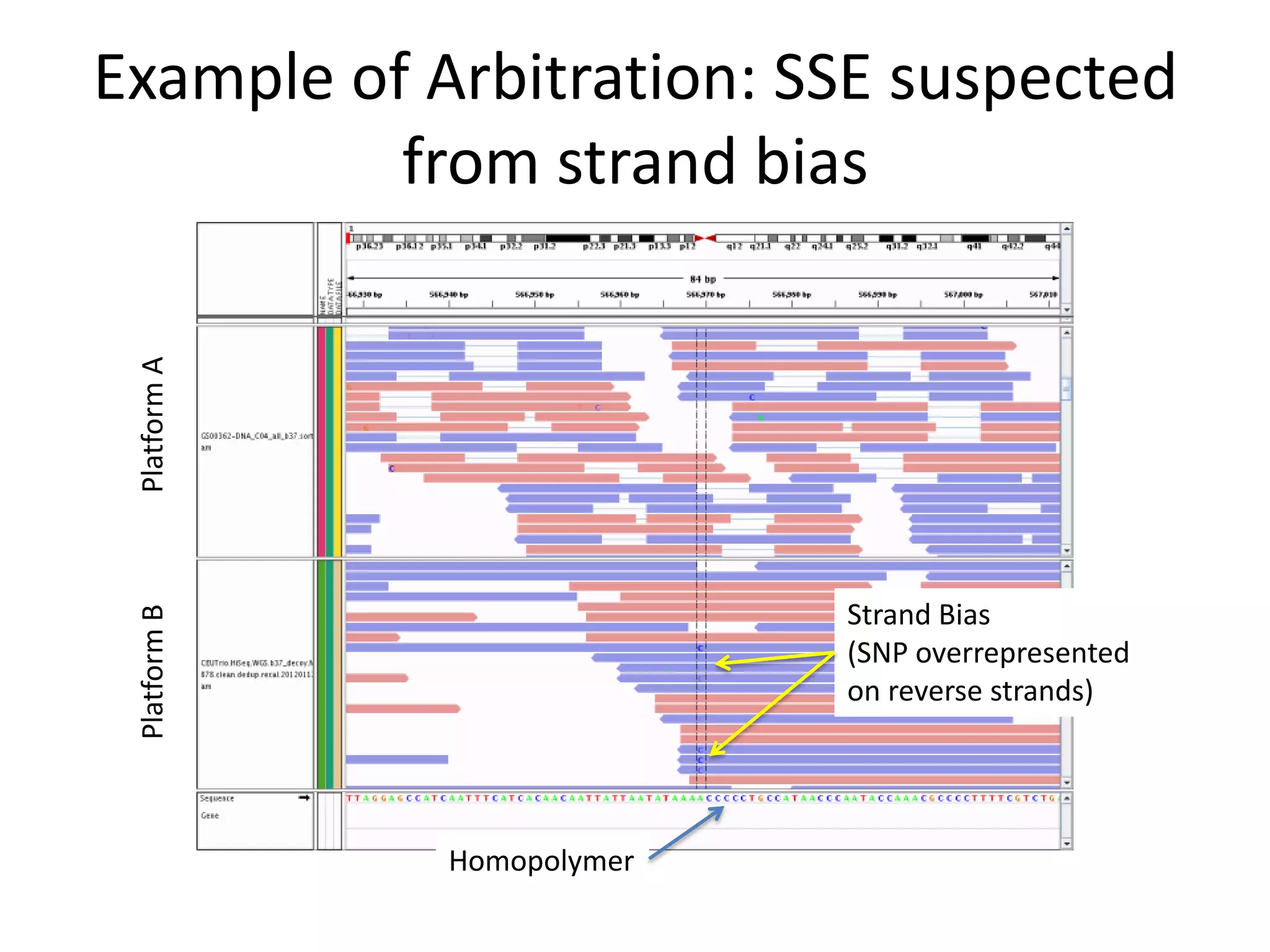
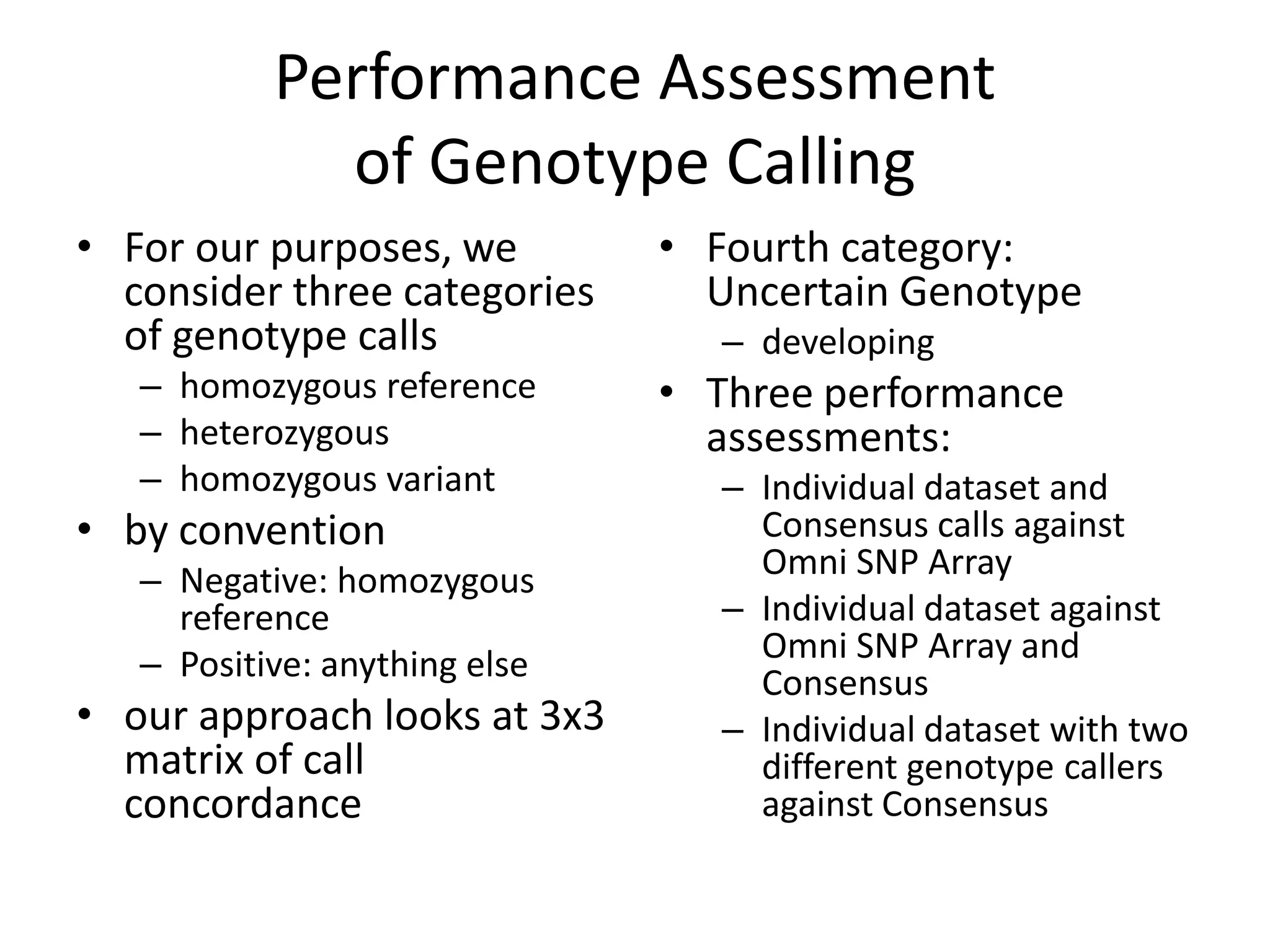
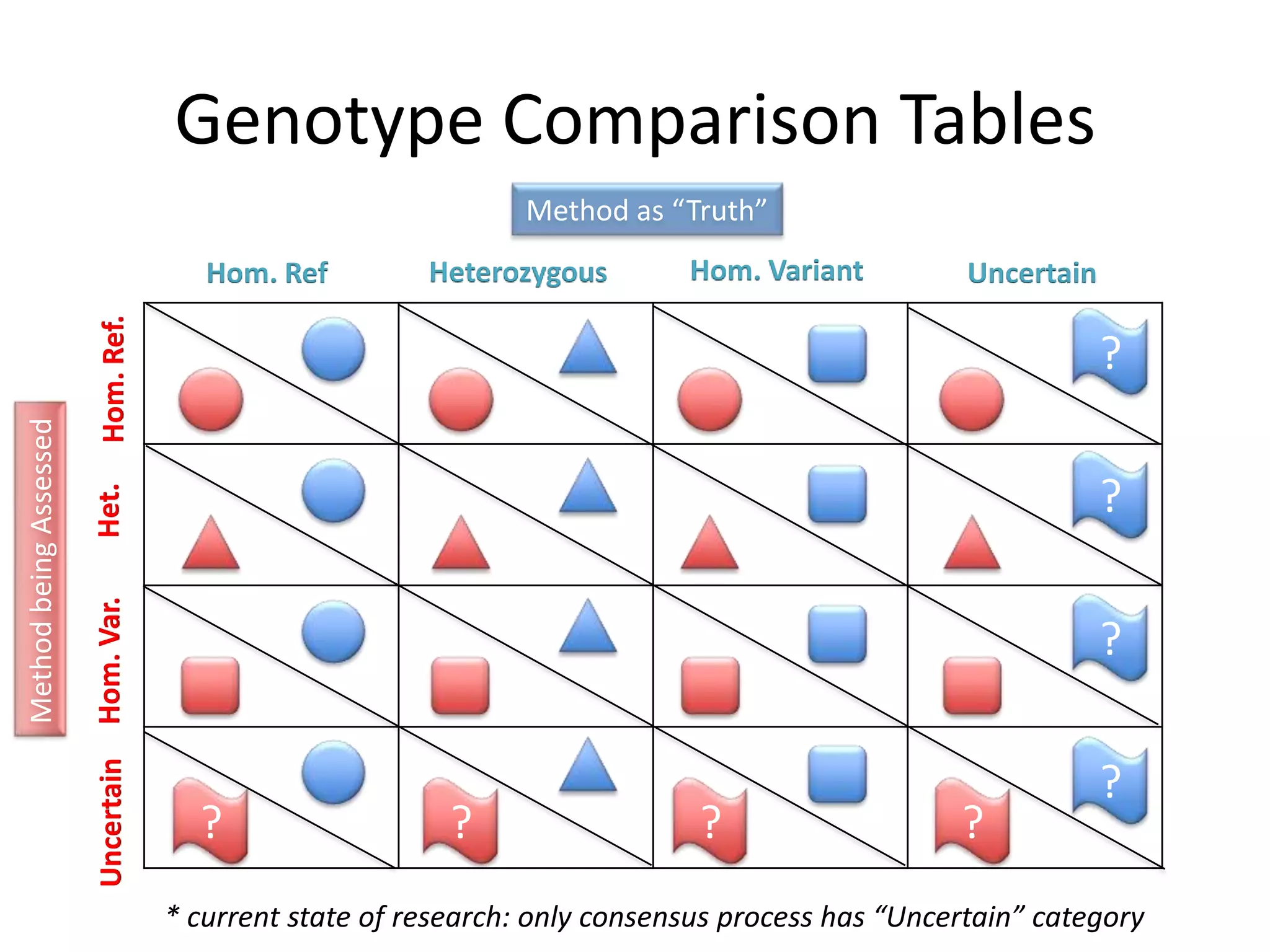
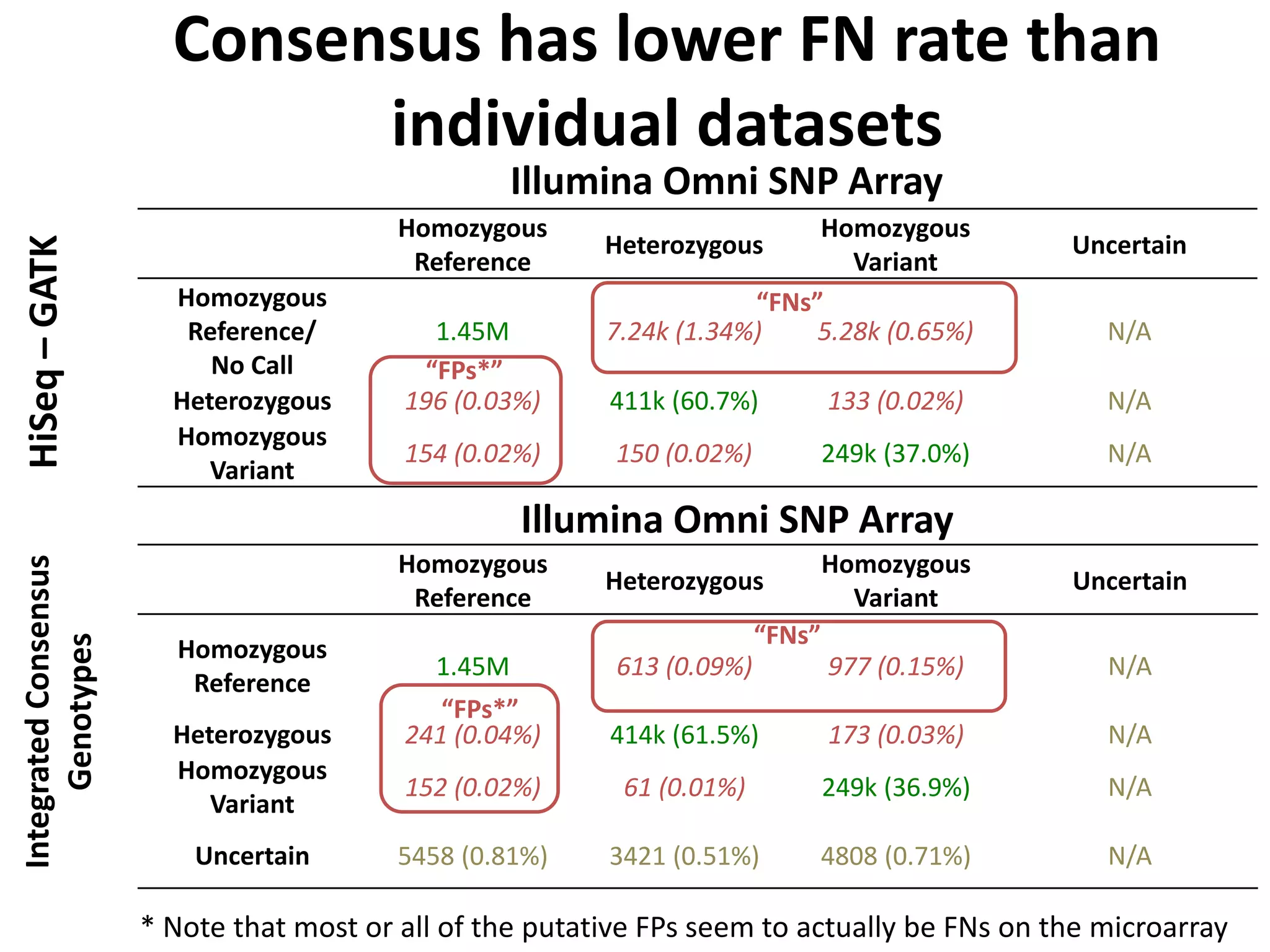
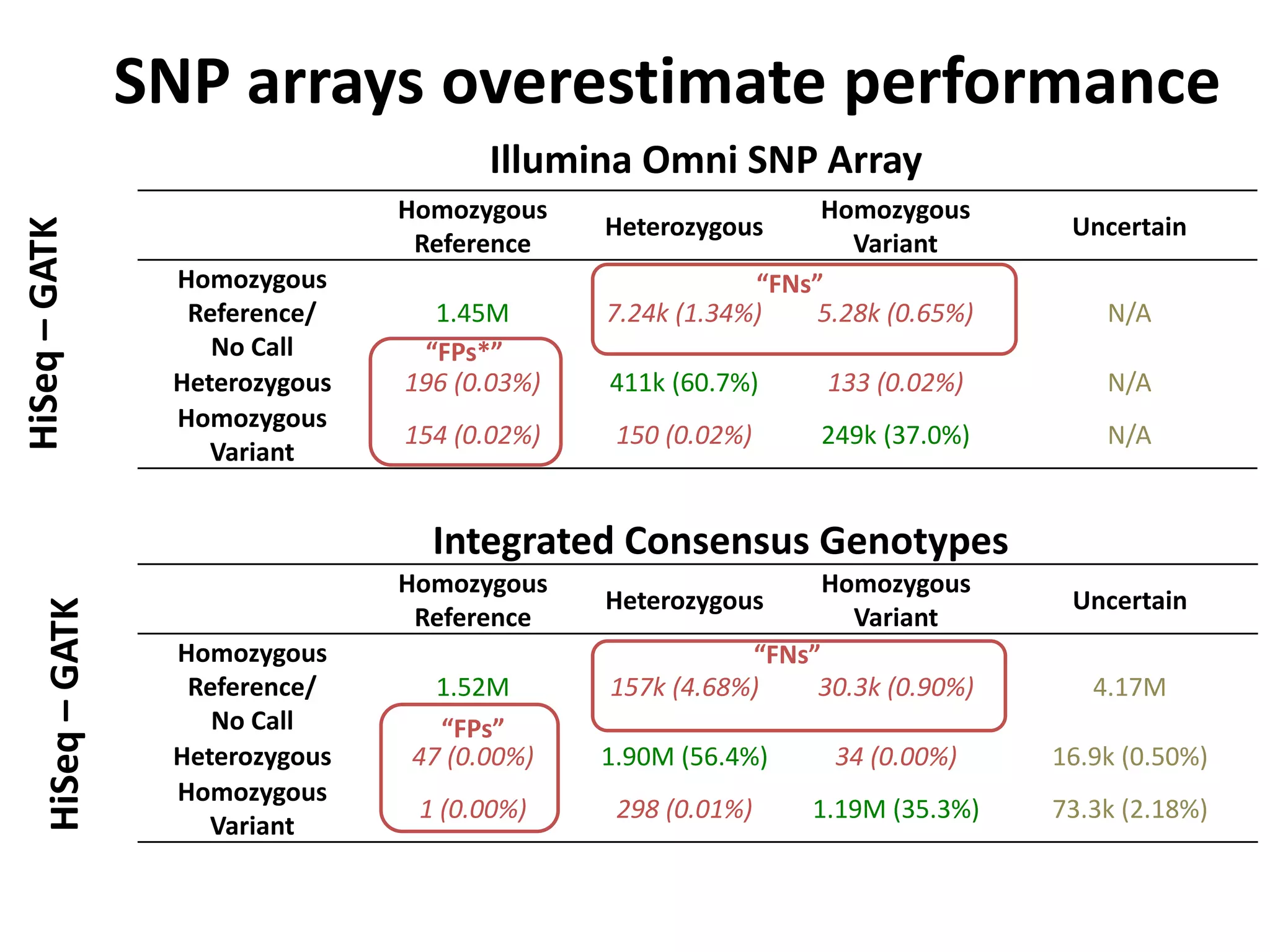
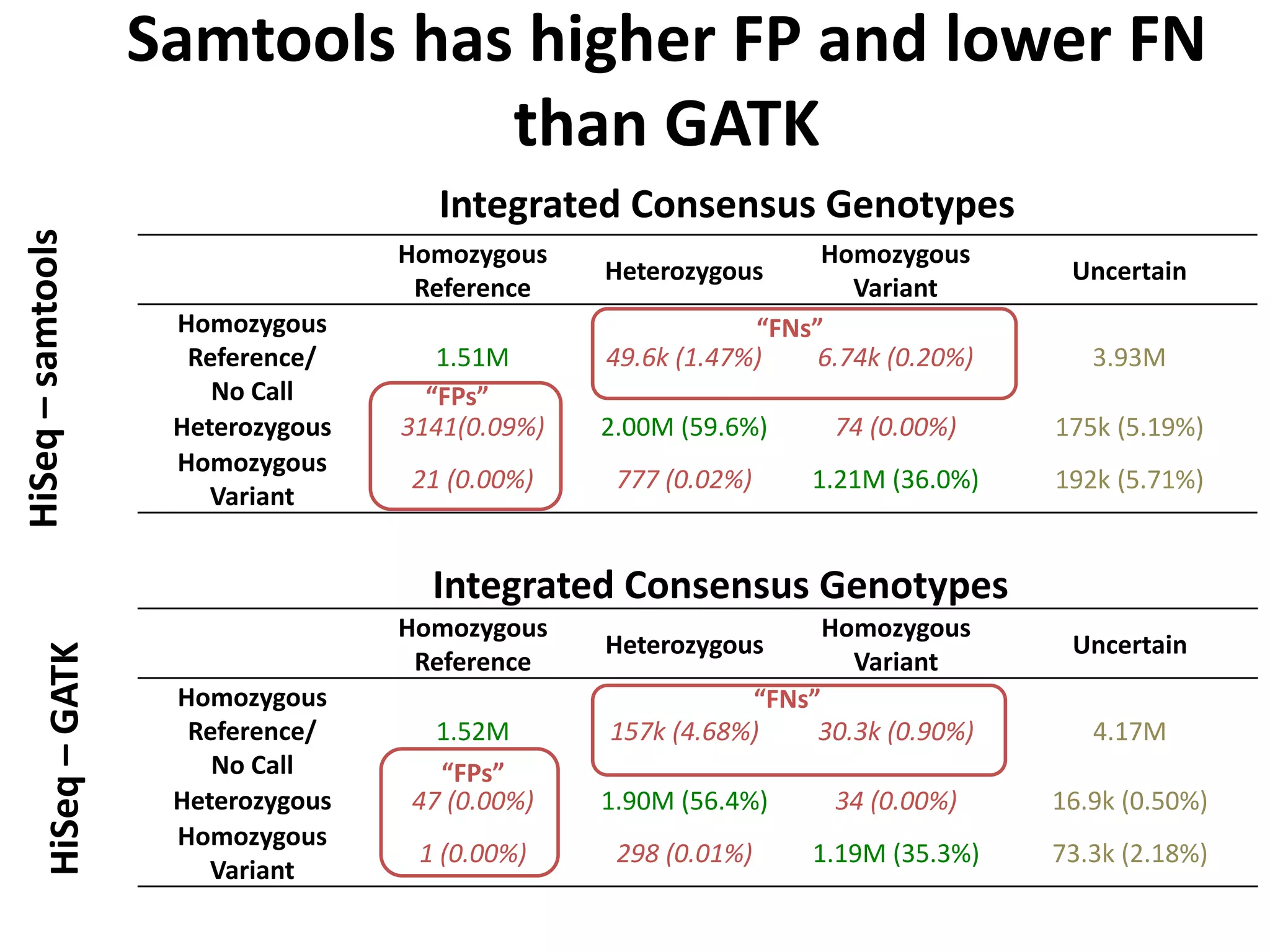
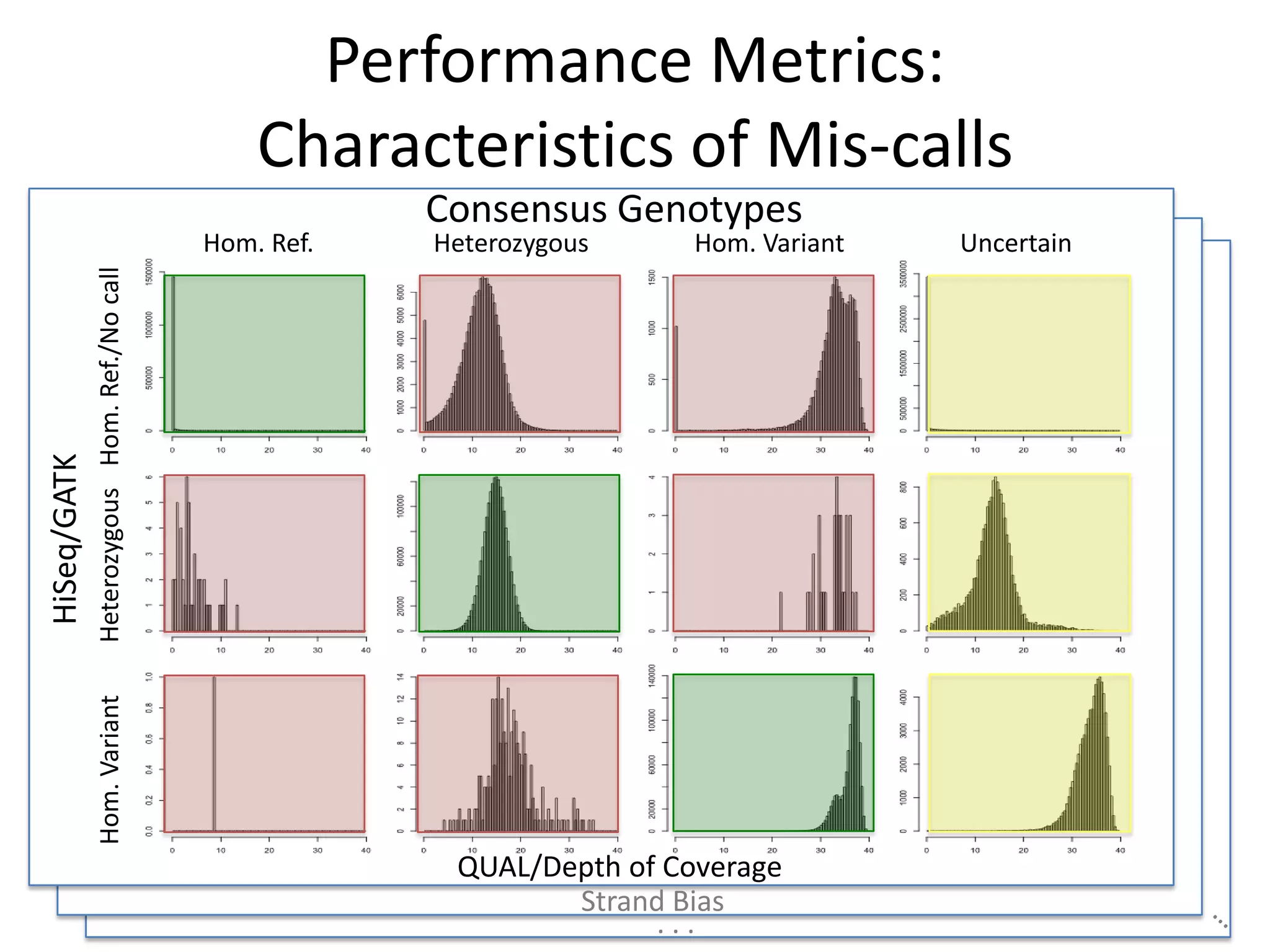
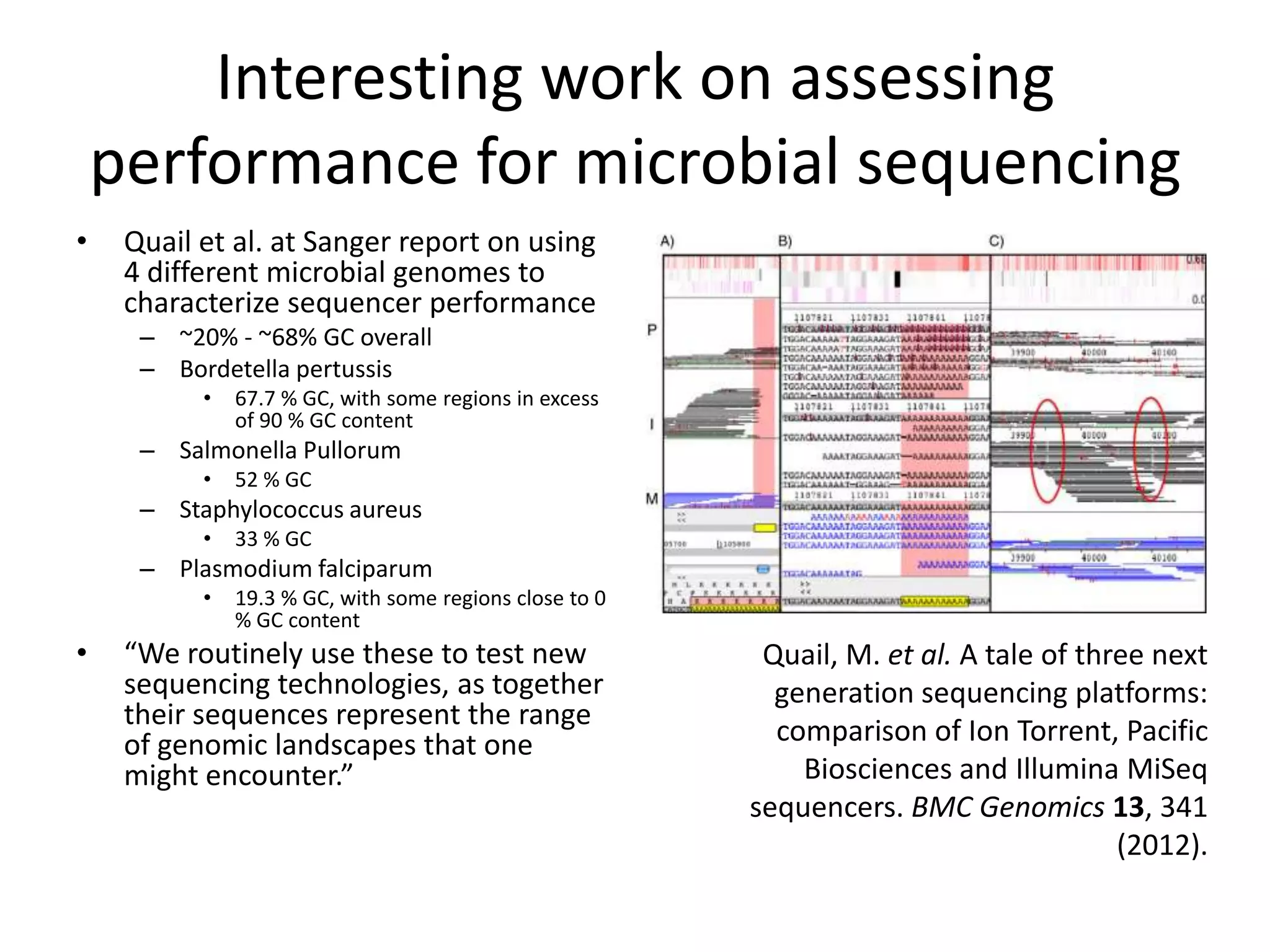
This document discusses NIST's program for developing human genome reference materials. It describes some use cases for well-characterized reference materials, such as validation, quality control, and improving genome assembly. The document outlines NIST's process for characterizing the performance of genome sequencing and variant calling using reference samples like NA12878. It discusses challenges with data integration and assessing sequencing performance.