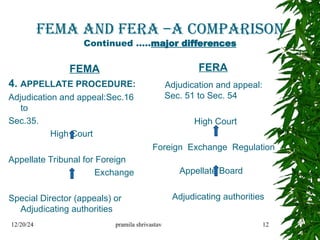
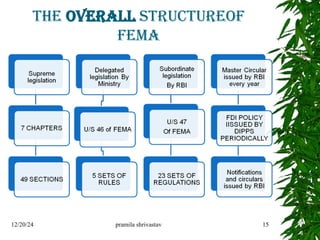
The document discusses cross-border transactions, detailing their types such as financing, trading, and shared services, and the regulations governing exchange control. It outlines the evolution of related laws in India, specifically the Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA) and the Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA), highlighting their objectives and distinctions from previous legislation. Additionally, it emphasizes the implications of these laws on foreign contributions and the enforcement actions taken against violations.



























![THE BLACK MONEY ACT - EXEMPT
THE BLACK MONEY (UNDISCLOSED FOREIGN INCOME
AND ASSETS) AND IMPOSITION OF TAX ACT, 2015
NO. 22 OF 2015 [26th May, 2015.]
An Act to make provisions to deal with the problem of the Black money
that is undisclosed foreign income and assets, the procedure for dealing
with such income and assets and to provide for imposition of tax on any
undisclosed foreign income and asset held outside India and for matters
connected therewith or incidental thereto.
THE RULES FRAMED UNDER THE NEW LAW PROVIDE FOR
EXEMPTION FROM PROSECUTION UNDER FEMA TO THOSE
DISCLOSING THEIR ASSETS.
RBI on 30TH
SEPTEMBER said no action under FEMA will be taken against
declarations under one-time black money compliance window, which ends on
Wednesday.
In a communication to banks, the Reserve Bank said: "No proceedings shall lie
under the Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999 (FEMA) against the
declarant with respect to an asset held abroad for which taxes and penalties
under the provisions of Black Money Act have been paid." RBI has already
notified the Foreign Exchange Management Regulations, 2015, in this regard.
12/20/24 pramila shrivastav 30](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/13-241220093357-35c7b0fc/85/13-NJA-PRESENTATION-ppt-cross-border-transaction-30-320.jpg)

