Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX




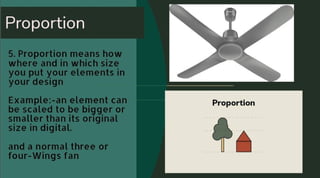







The principles of design are a set of fundamental concepts that serve as guidelines for creating aesthetically pleasing and effective visual compositions in various fields, including graphic design, art, architecture, and more. These principles help designers organize and arrange elements to achieve balance, harmony, and visual interest. There are several widely recognized principles of design: Balance: Balance refers to the distribution of visual weight in a design. There are two main types of balance: Symmetrical Balance: Elements are evenly distributed on either side of a central axis, creating a mirror-like effect. Asymmetrical Balance: Visual weight is distributed unevenly but still achieves balance through careful arrangement of elements. Unity/Harmony: Unity or harmony is the cohesive relationship between the various elements in a design. It ensures that all components work together to create a unified and visually pleasing whole. Emphasis/Focal Point: Emphasis involves creating a focal point in a design to draw the viewer's attention. It can be achieved through contrast, color, size, or placement of elements. Contrast: Contrast involves the juxtaposition of different elements to create visual interest. It can be achieved through variations in color, size, shape, texture, or other visual attributes. Repetition/Pattern: Repetition involves using similar elements throughout a design to create consistency and a sense of unity. Patterns, whether simple or complex, can add visual interest and structure. Proportion/Scale: Proportion and scale involve the relative size and scale of elements within a design. Ensuring that elements are appropriately sized in relation to each other contributes to a balanced and visually pleasing composition. Movement/Rhythm: Movement and rhythm guide the viewer's eye through a design. This can be achieved through the arrangement of elements, the use of lines, or patterns that create a sense of flow and continuity. Hierarchy: Hierarchy establishes the order of importance within a design. It helps the viewer navigate and understand the content by emphasizing certain elements over others. Economy: Economy in design involves the efficient use of elements without unnecessary complexity. Striving for simplicity and clarity can enhance the overall impact of a design. White Space/Negative Space: White space, also known as negative space, is the area around and between design elements. It is crucial for providing visual breathing room and emphasizing key elements. These principles are interrelated, and successful design often involves a thoughtful combination of them. Designers use these principles as a foundation to create visually compelling and communicative works across various mediums and disciplines.











