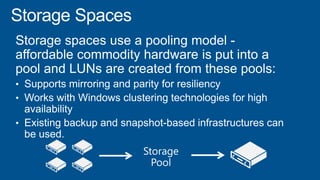
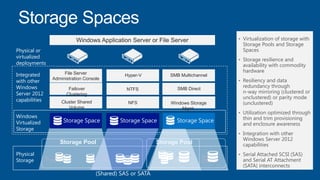
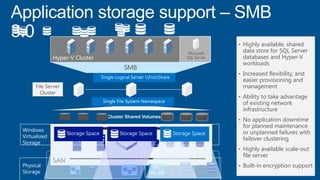
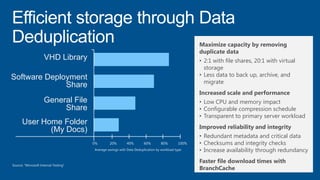
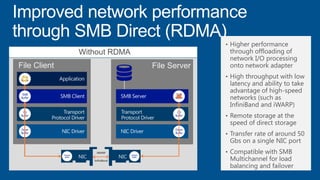
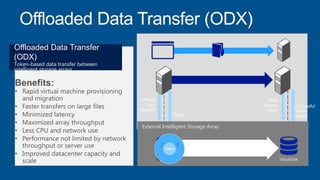
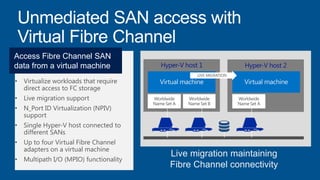
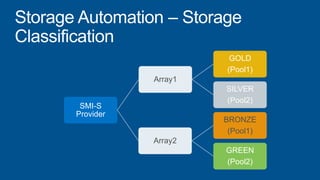
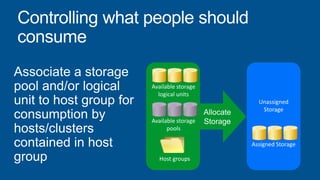
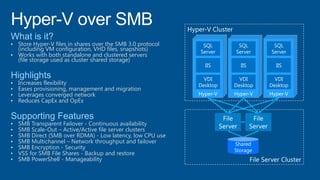
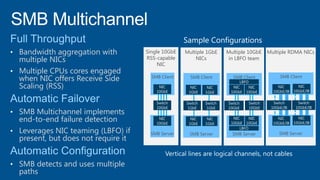
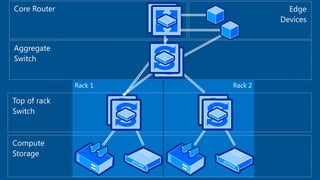
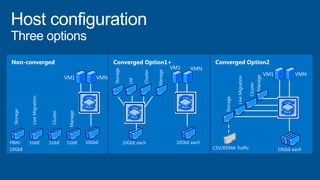
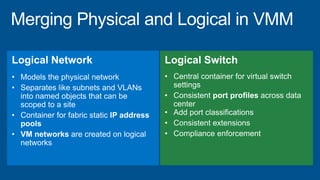
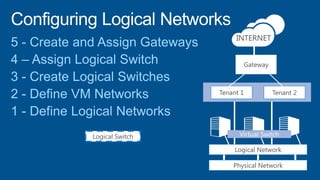
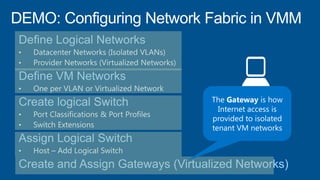
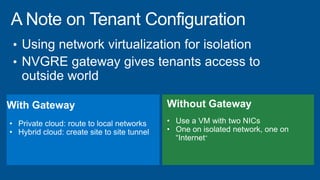
Windows Server 2012 introduces new storage technologies like Storage Spaces and SMB 3.0 that can replace traditional SANs. These technologies provide high performance storage with easier administration and lower costs when used together. They enable virtualized storage through storage pools and spaces, storage resilience through hardware redundancy, and optimization of storage utilization.