Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX


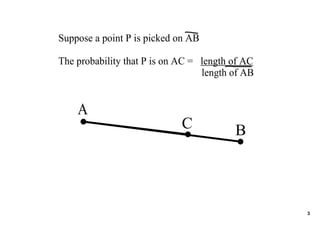
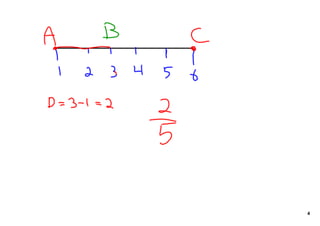
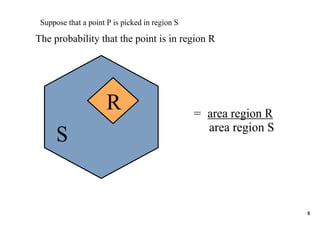

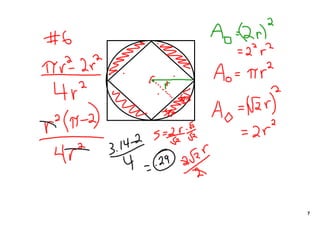

The document introduces geometric probability and how to calculate the probability of a random point falling in a specific region. It explains that the probability is equal to the length of the region divided by the total length for a line, and the probability is equal to the area of the region divided by the total area for a two-dimensional region. It then indicates it will provide practice problems for students to work through.







