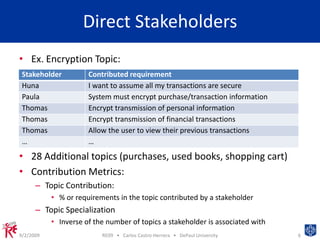
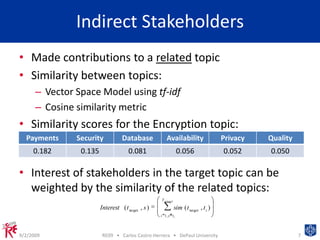
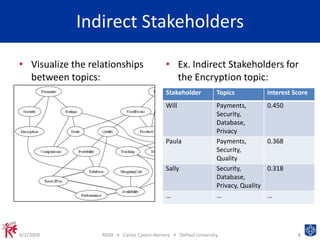
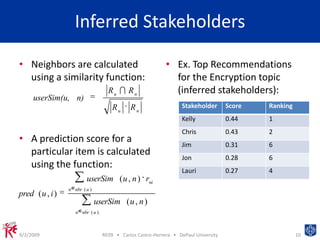
This document presents a machine learning approach to identify expert stakeholders for requirements elicitation. It analyzes contributions from students to identify direct stakeholders who contributed to specific topics, indirect stakeholders who contributed to related topics, and inferred stakeholders with similar contribution patterns. The approach clusters topics and calculates metrics to identify relevant stakeholders. It provides a proof of concept for using data mining to analyze stakeholders' contributions and identify potential experts for requirements elicitation.