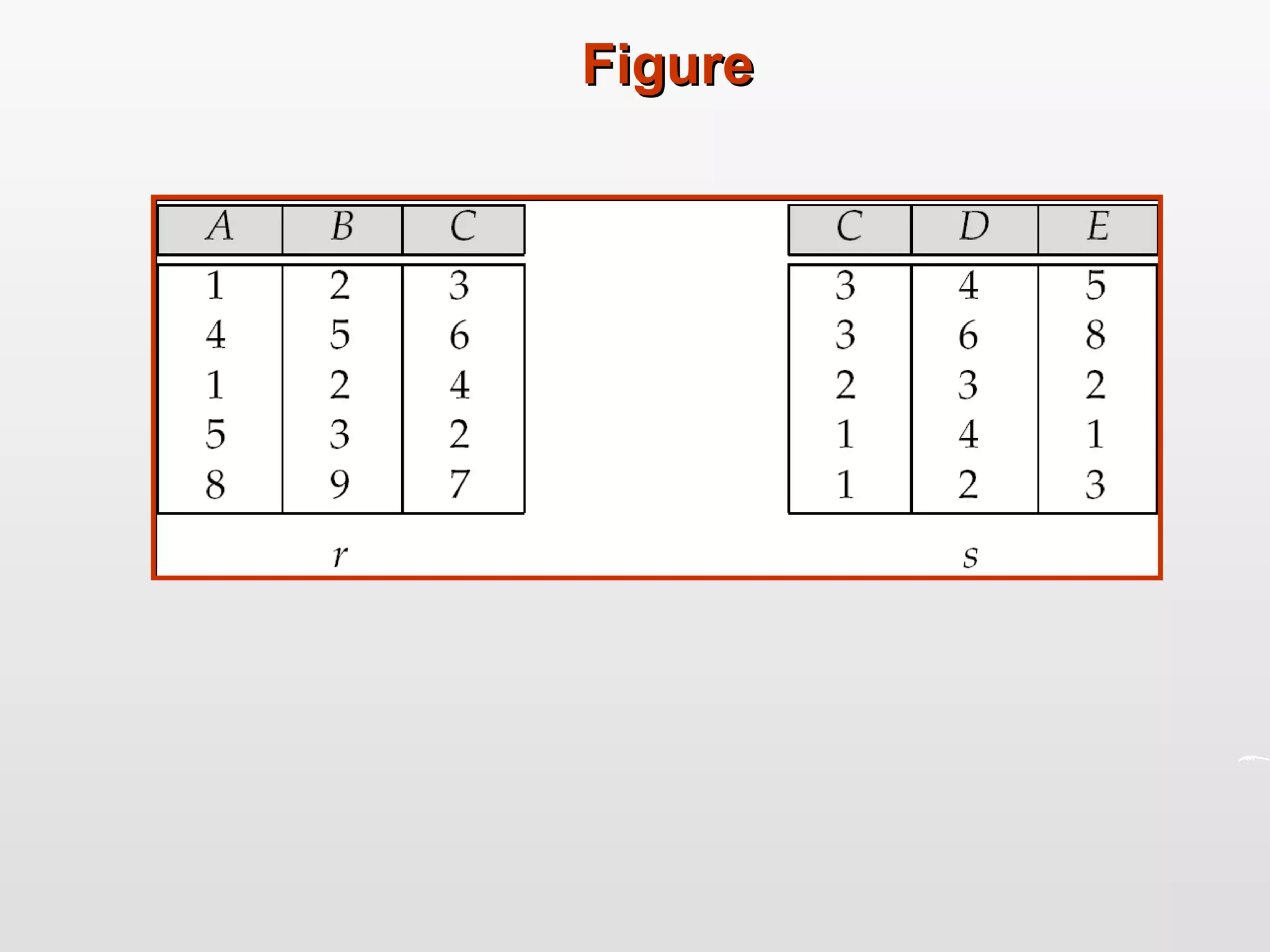
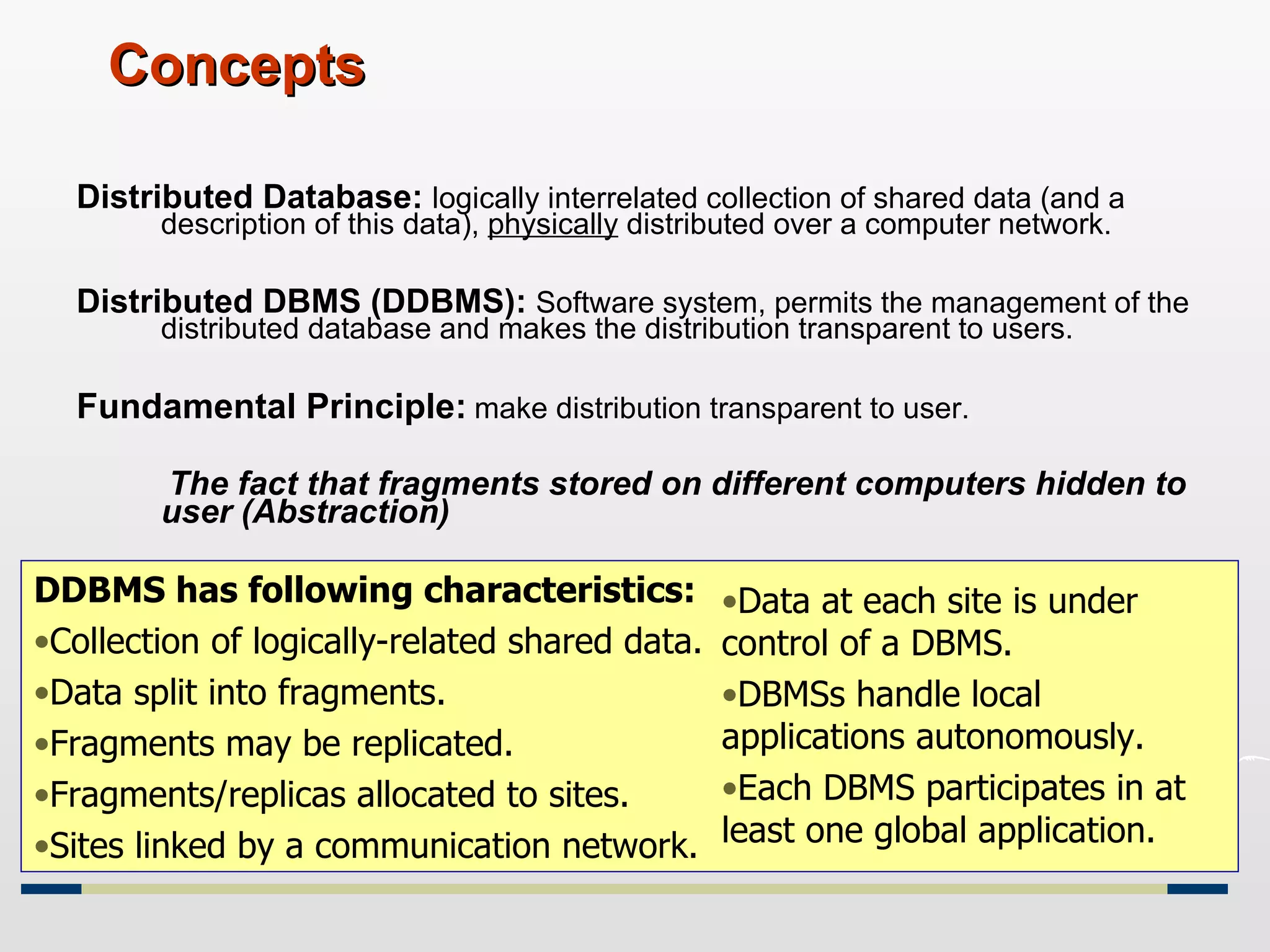
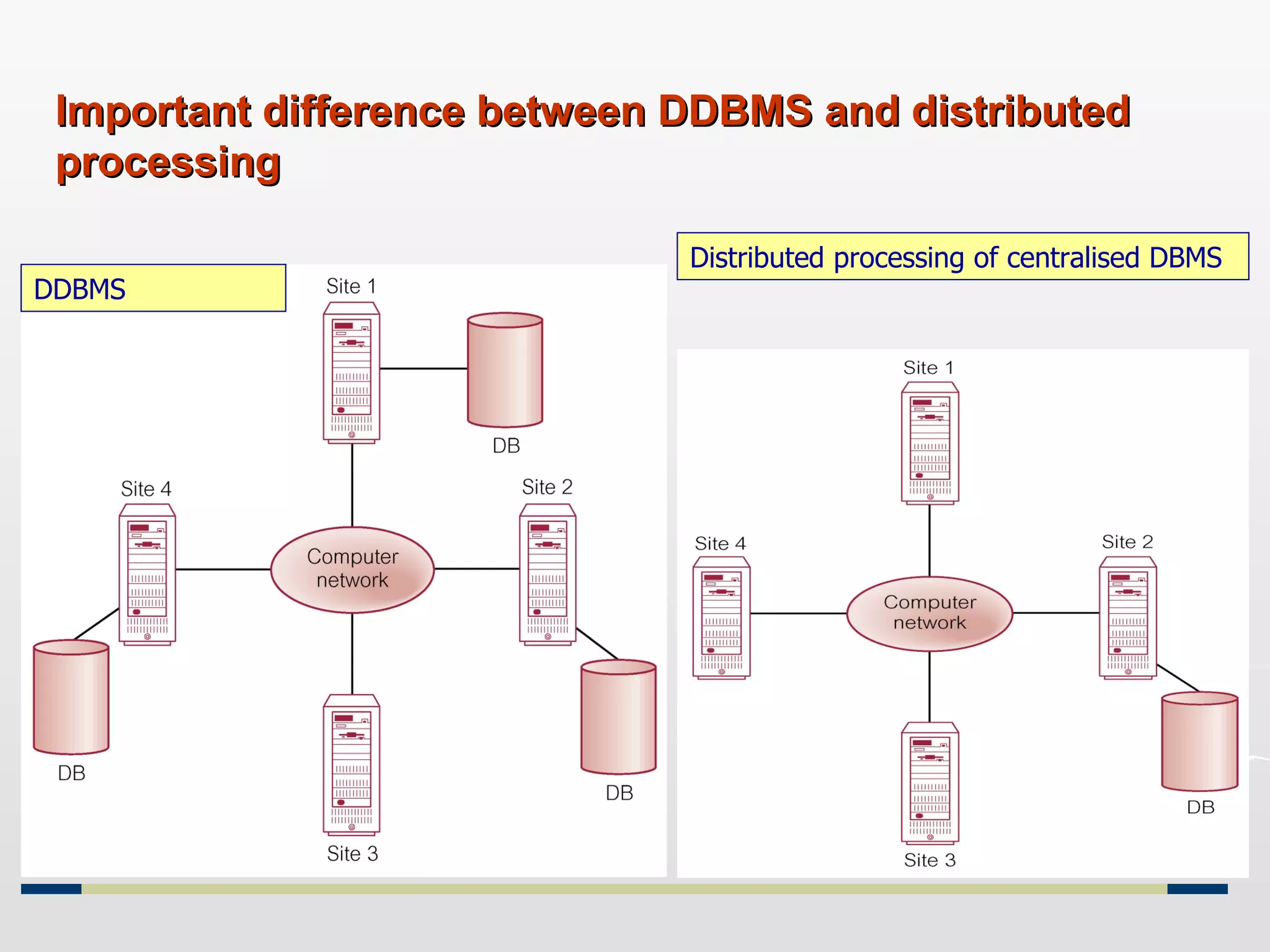
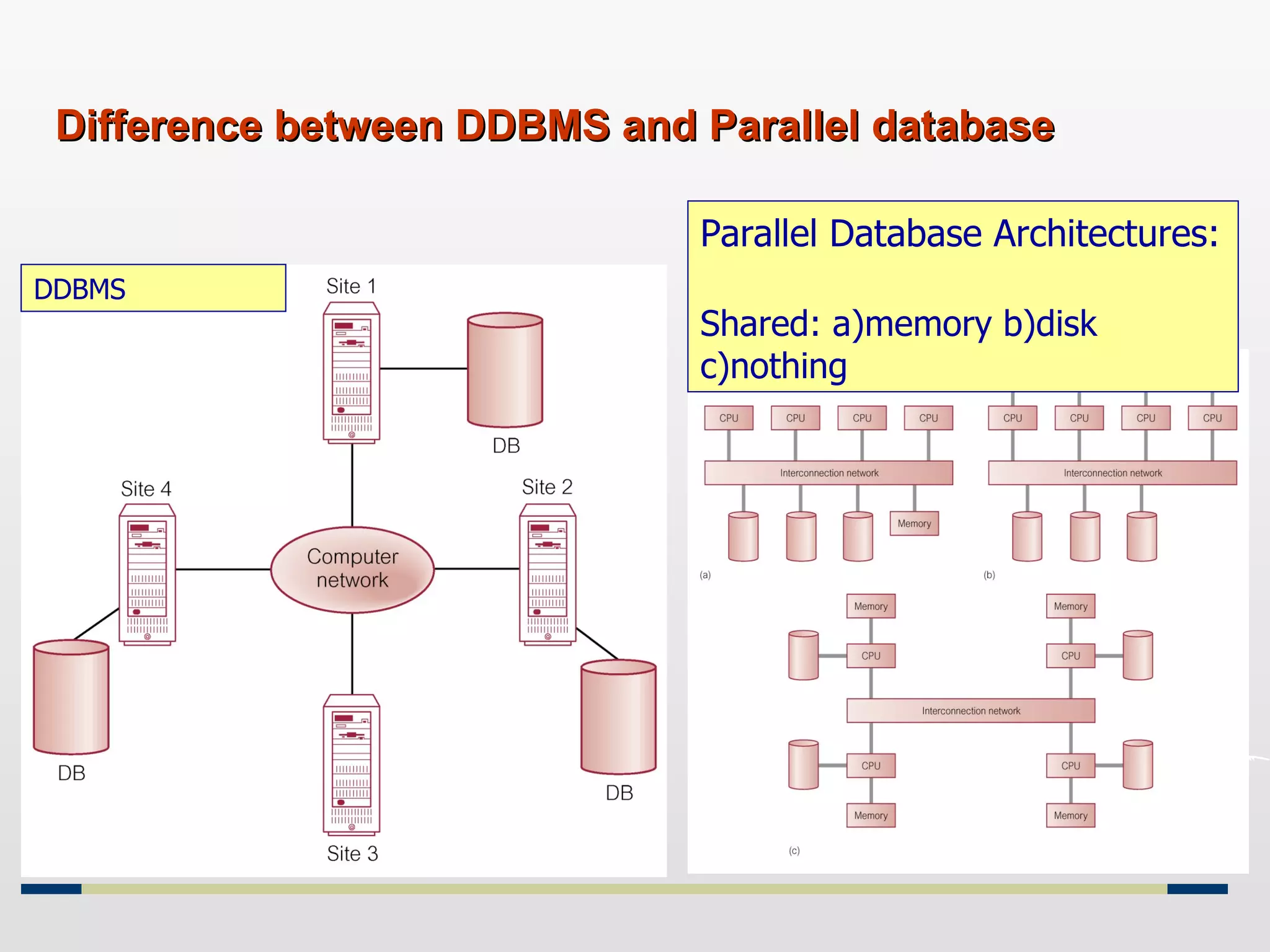
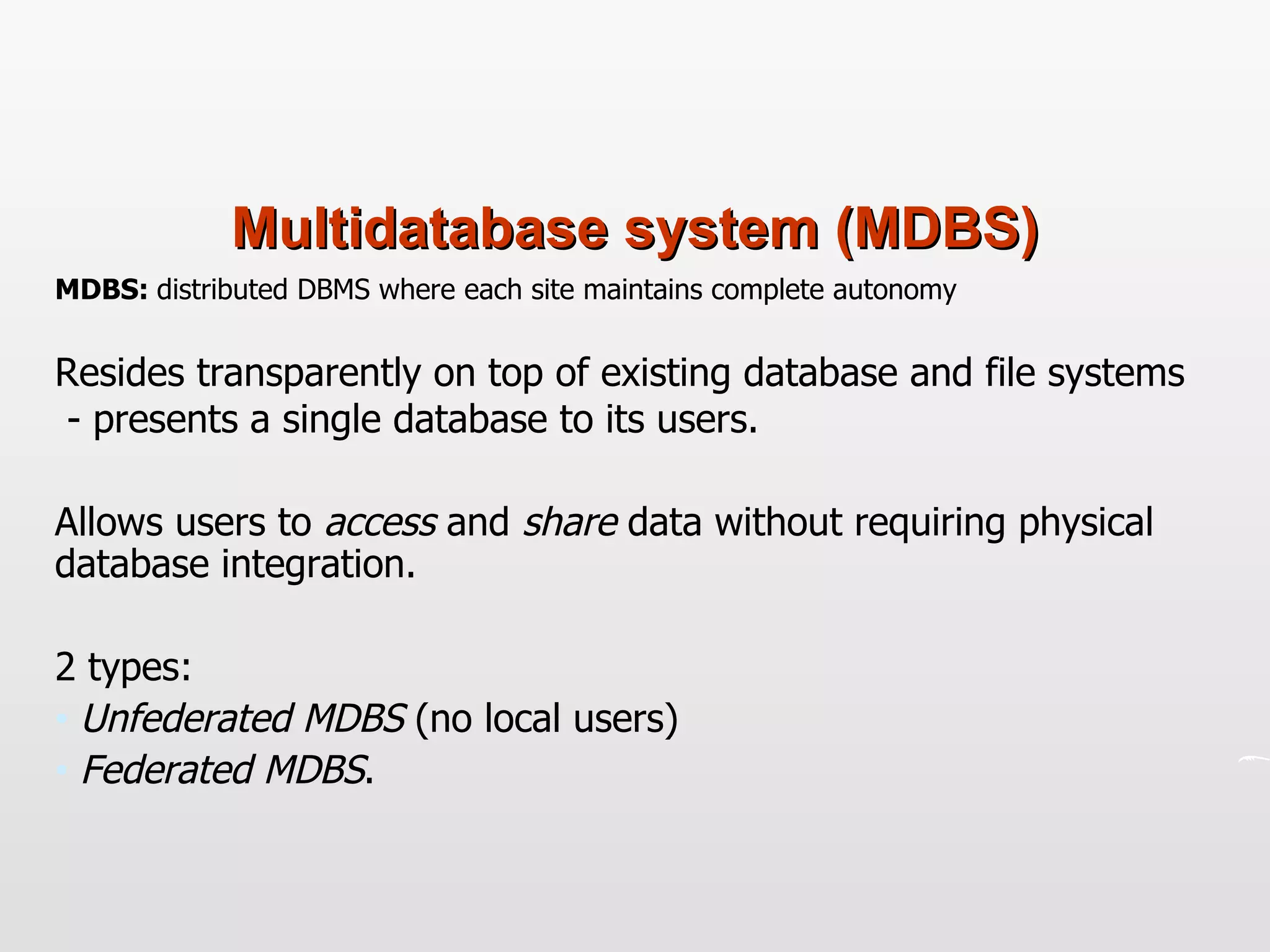
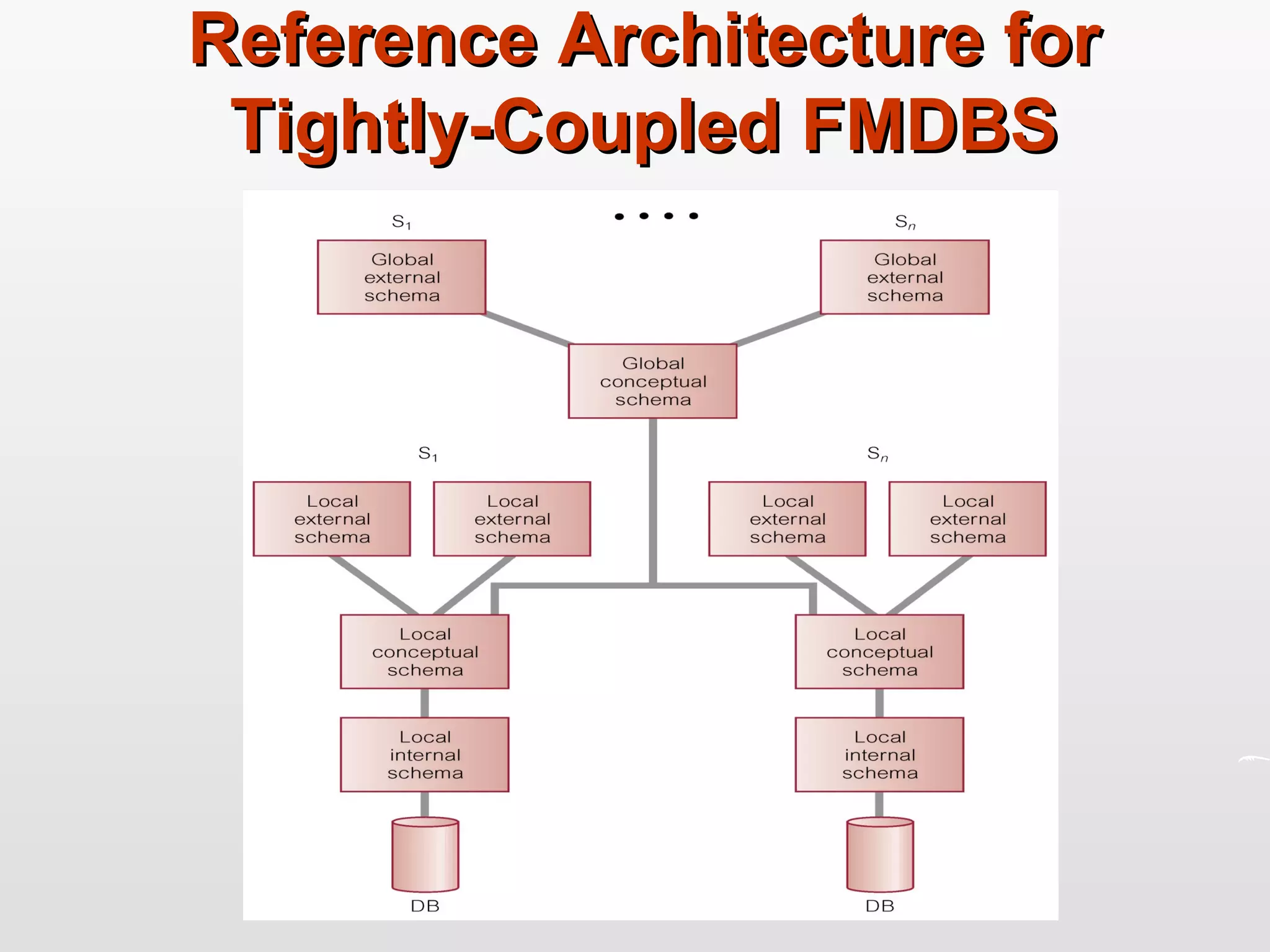
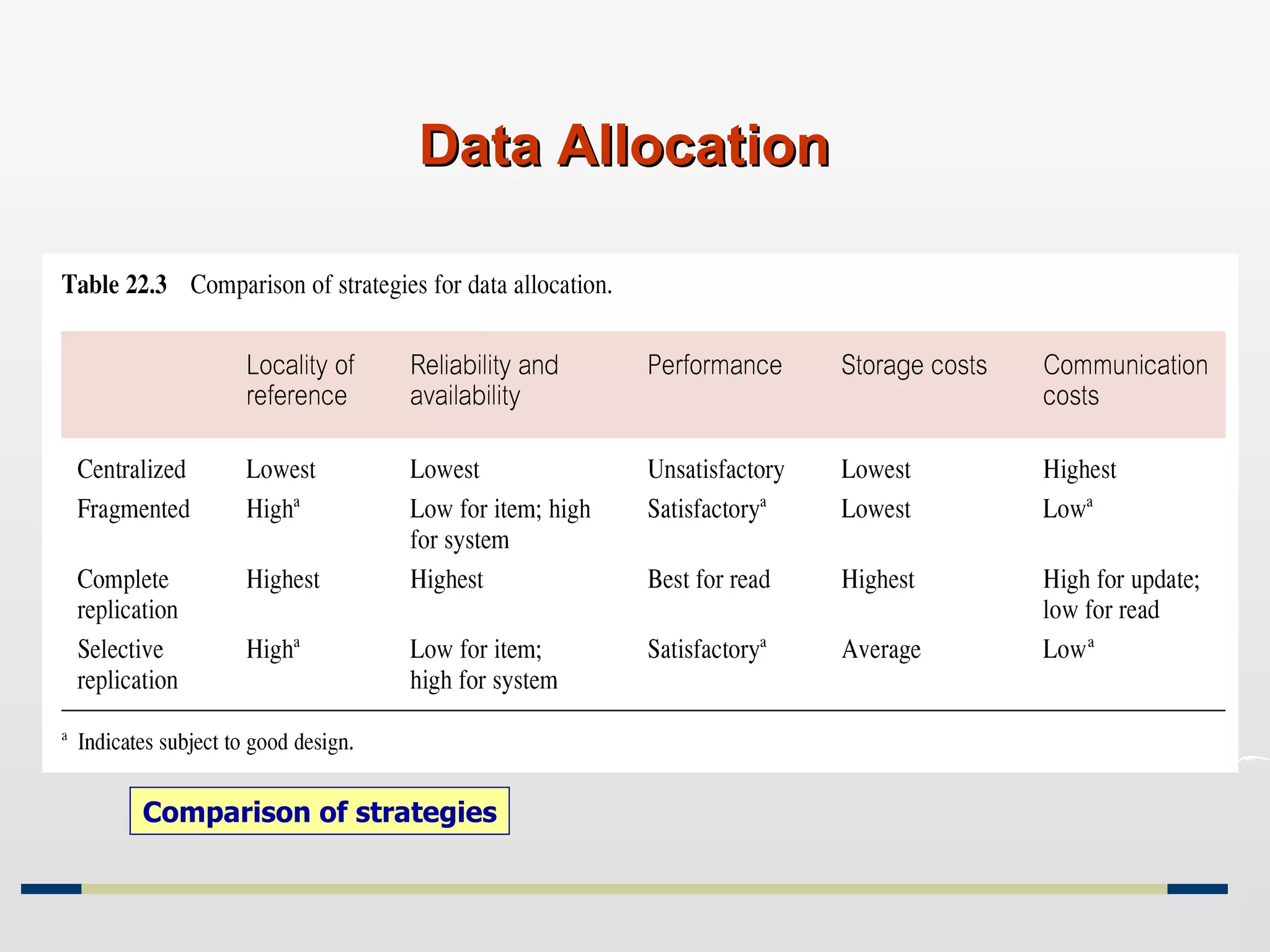
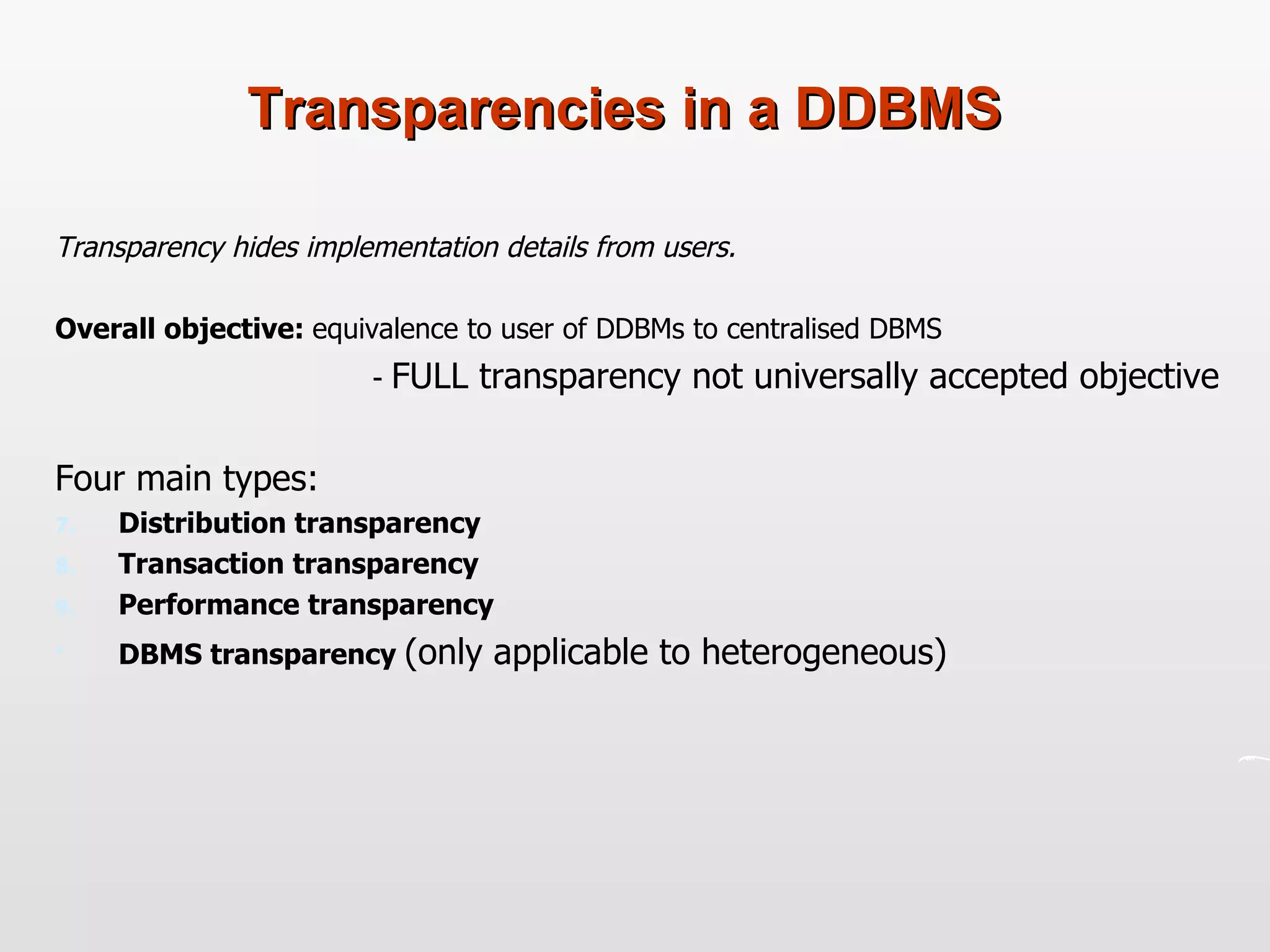
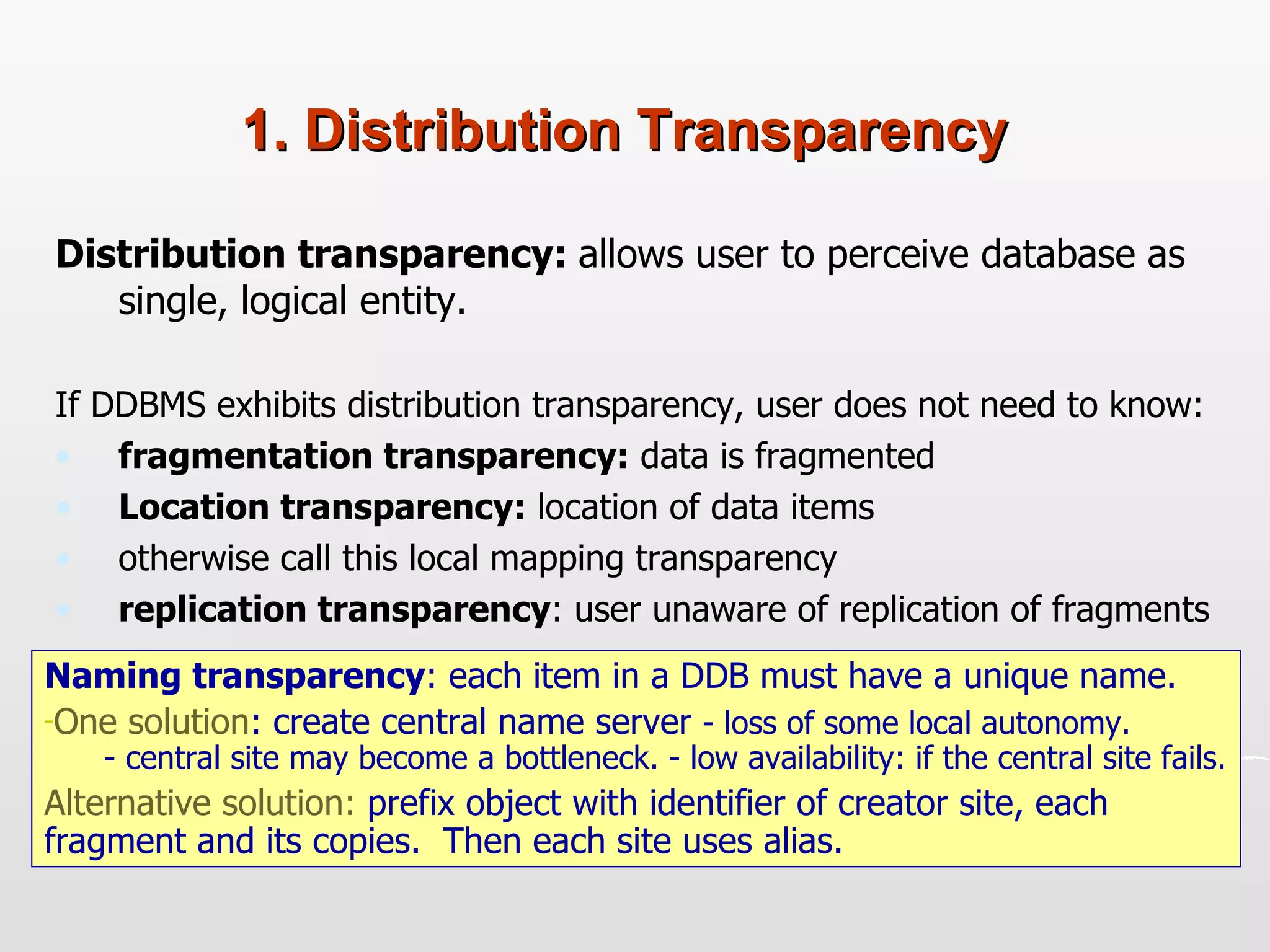
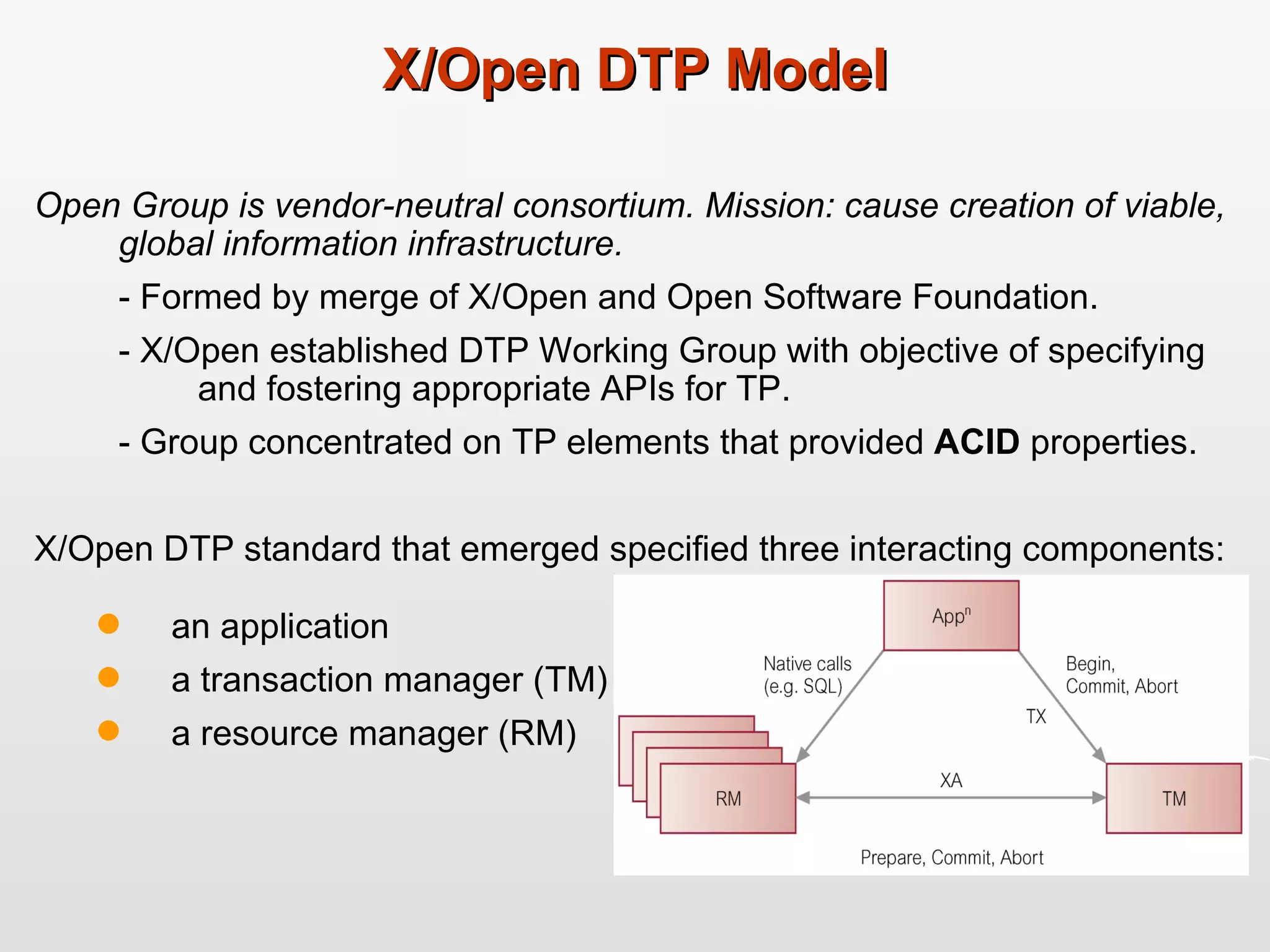
Distributed databases allow data to be stored across multiple computers or sites connected through a network. The data is logically interrelated but physically distributed. A distributed database management system (DDBMS) makes the distribution transparent to users and allows sites to operate autonomously while participating in global applications. Key aspects of DDBMS include distributed transactions, concurrency control, data fragmentation and replication, distributed query processing, and ensuring transparency of the distribution.





















































![C Code using LDAP API #include <stdio.h> #include <ldap.h> main( ) { LDAP *ld; LDAPMessage *res, *entry; char *dn, *attr, *attrList [ ] = {“telephoneNumber”, NULL}; BerElement *ptr; int vals, i; // Open a connection to server ld = ldap_open(“aura.research.bell-labs.com”, LDAP_PORT); ldap_simple_bind(ld, “avi”, “avi-passwd”); … actual query (next slide) … ldap_unbind(ld); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1ddbmsjan2011u-110522154141-phpapp01/75/1-ddbms-jan-2011_u-106-2048.jpg)
![C Code using LDAP API (Cont.) ldap_search_s(ld, “o=Lucent, c=USA”, LDAP_SCOPE_SUBTREE, “cn=Korth”, attrList, /* attrsonly*/ 0, &res); /*attrsonly = 1 => return only schema not actual results*/ printf(“found%d entries”, ldap_count_entries(ld, res)); for (entry=ldap_first_entry(ld, res); entry != NULL; entry=ldap_next_entry(id, entry)) { dn = ldap_get_dn(ld, entry); printf(“dn: %s”, dn); /* dn: DN of matching entry */ ldap_memfree(dn); for(attr = ldap_first_attribute(ld, entry, &ptr); attr != NULL; attr = ldap_next_attribute(ld, entry, ptr)) { // for each attribute printf(“%s:”, attr); // print name of attribute vals = ldap_get_values(ld, entry, attr); for (i = 0; vals[i] != NULL; i ++) printf(“%s”, vals[i]); // since attrs can be multivalued ldap_value_free(vals); } } ldap_msgfree(res);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1ddbmsjan2011u-110522154141-phpapp01/75/1-ddbms-jan-2011_u-107-2048.jpg)