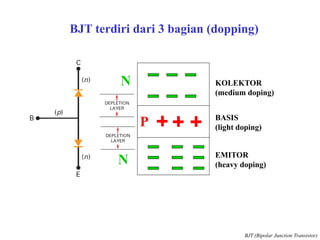
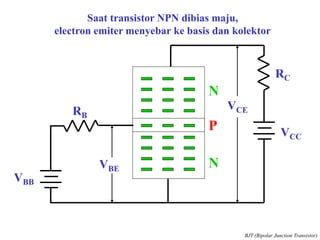
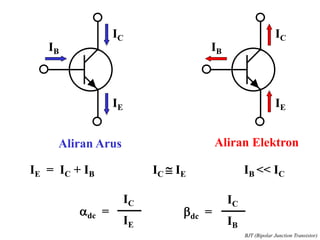
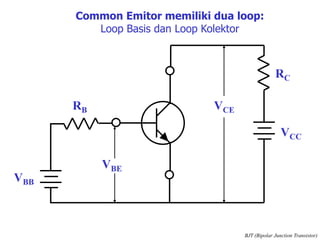
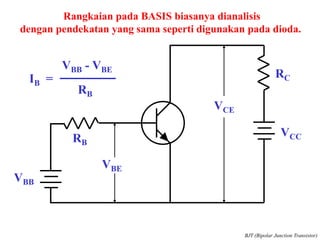
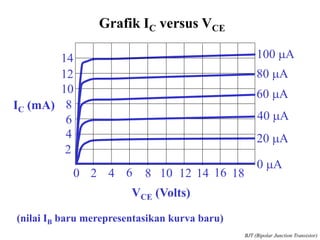
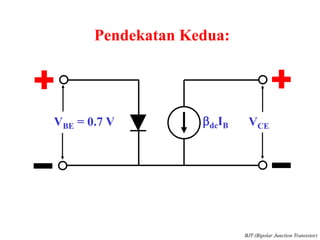
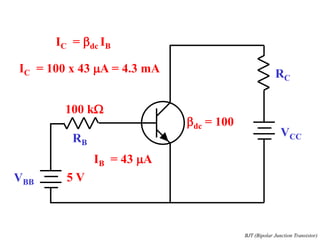
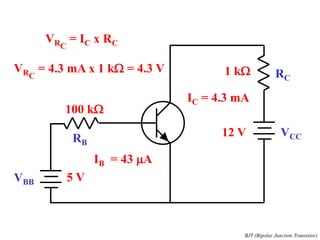
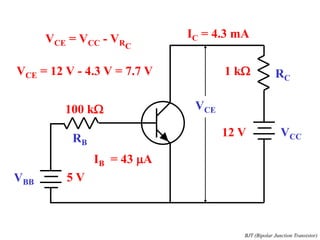
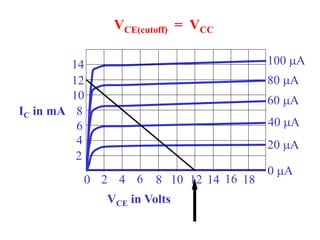
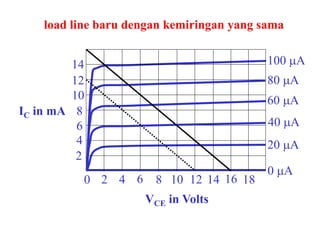
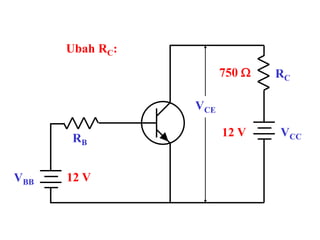
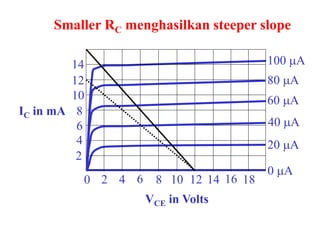
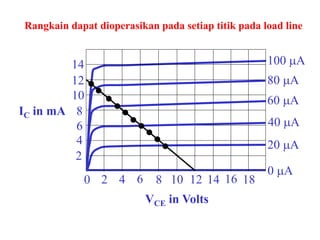
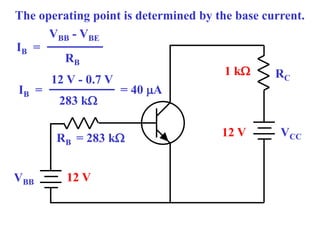
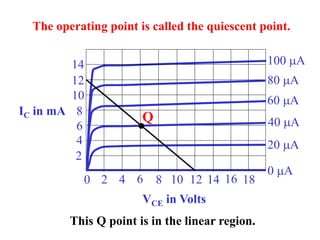
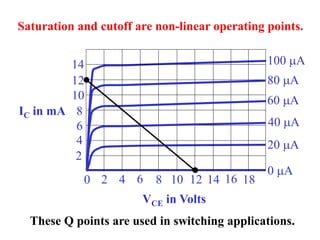
This document discusses the basics of bipolar junction transistors (BJT), including their structure, current flow, common configurations, characteristics curves, approaches to analysis, and operating regions. It specifically examines the common emitter configuration, showing how to determine the operating point (or quiescent point) from the load line graph by considering the base bias voltage and resistance. The importance of transistor current gain in setting the operating point is also highlighted.