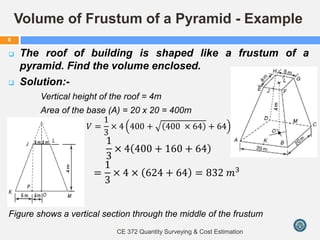
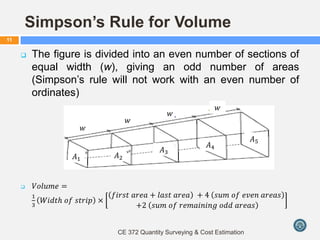
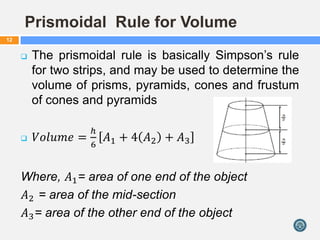
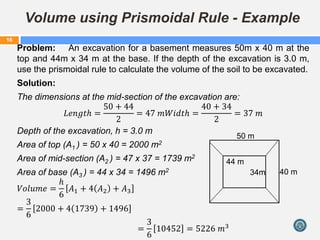
This document discusses calculating volumes of different shapes that are commonly encountered in quantity surveying and cost estimation. It begins by defining volume and identifying regular solids such as cubes, rectangular prisms, cylinders, pyramids, cones, and frustums. Formulas to calculate the volumes of these shapes are provided. The document then discusses calculating volumes of irregular shapes using trapezoidal, Simpson's, and prismoidal rules. Examples of applying these rules to practical problems are worked out. The key concepts covered are formulas for regular solids, techniques for irregular shapes, and applying these to quantity surveying problems involving excavation and construction volumes.